|
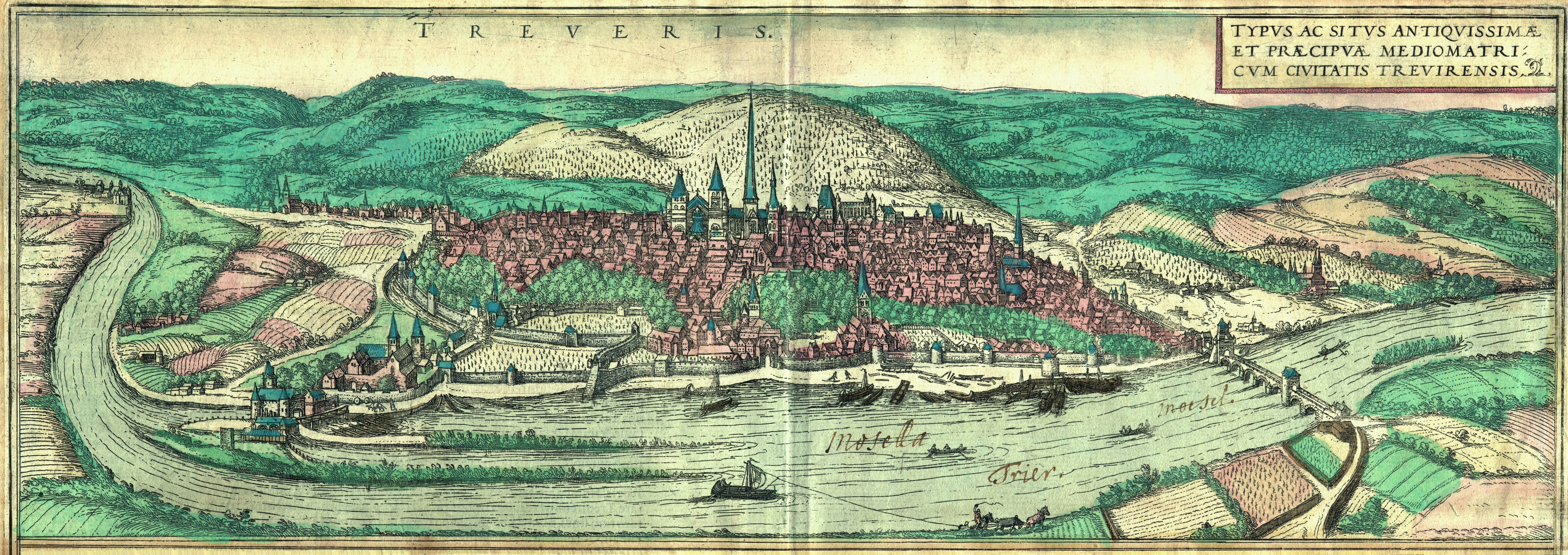
Mülheim An Der Mosel
Mülheim is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – in the Bernkastel-Wittlich district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Geography Location The municipality lies surrounded by vineyards, meadows and forests in the natural and cultivated landscape of the Moselle valley not far from the university city of Trier. Mülheim is found on the river’s right bank, where the valley begins to broaden out into country marked by even slopes on the banks and by former riverbeds. The village lies at the foot of a small, narrow mountain, a former river island surrounded by an old riverbed of the Moselle that has now been cut off from the mainstream. This is planted all round with grapevines and is purportedly the only mountain in Europe wholly given over to winegrowing. Mülheim belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Bernkastel-Kues, whose seat is in the like-named town. Nearby municipalities Neighbouring municip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Germany
MunicipalitiesCountry Compendium. A companion to the English Style Guide European Commission, May 2021, pages 58–59. (german: Gemeinden, singular ) are the lowest level of official territorial division in . This can be the second, third, fourth or fifth level of territorial division, depending on the status of the municipality and the '' Land'' (federal state) it is part of. The city-states Berlin and Hamburg are second-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteomedia AG
Meteomedia is a company founded by Jörg Kachelmann, which operates a large network of Weather stations in Switzerland, Austria and Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou .... The company's services include weather forecasts, severe weather warnings and meteorological consultancy. In 2013, MeteoGroup acquired Meteomedia.{{Cite web , url=http://www.meteogroup.com/gb/about-us/press-corner/press/article/meteogroup-reaches-agreement-to-acquire-leading-european-weather-business.html , title=Press release by MeteoGroup about acquisition of Meteomedia , access-date=2014-04-03 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140118190737/http://www.meteogroup.com/gb/about-us/press-corner/press/article/meteogroup-reaches-agreement-to-acquire-leading-european-weather-business.html ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Trier
Trier in Rhineland-Palatinate, whose history dates to the Roman Empire, is often claimed to be the oldest city in Germany. Traditionally it was known in English by its French name of Treves. Prehistory The first traces of human settlement in the area of the city show evidence of linear pottery settlements dating from the early Neolithic period. Since the last pre-Christian centuries, members of the Celtic tribe of the Treveri settled in the area of today's Trier. Roman Empire The Romans under Julius Caesar first subdued the Treveri in 58 to 50 BC. No later than 16 BC, at the foot of the hill later christened the Petrisberg, upon which a military camp had been set up in 30 BC and abandoned again a few months later, the Romans founded the city of ("City of Augustus in the land of the Treveri"), which has a claim to being the oldest city in Germany. The honour of being named after the Emperor was only locally shared by Augsburg and Augst in northern Switzerland. Follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and early medieval Germanic languages and are thus equated at least approximately with Germanic-speaking peoples, although different academic disciplines have their own definitions of what makes someone or something "Germanic". The Romans named the area belonging to North-Central Europe in which Germanic peoples lived ''Germania'', stretching East to West between the Vistula and Rhine rivers and north to south from Southern Scandinavia to the upper Danube. In discussions of the Roman period, the Germanic peoples are sometimes referred to as ''Germani'' or ancient Germans, although many scholars consider the second term problematic since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. The very concept of "Germanic peoples" has become the subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century bc, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . " e Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe."; in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treveri
The Trēverī (Gaulish: *''Trēueroi'') were a Celtic tribe of the Belgae group who inhabited the lower valley of the Moselle from around 150 BCE, if not earlier, until their displacement by the Franks. Their domain lay within the southern fringes of the ''Silva Arduenna'' (Ardennes Forest), a part of the vast Silva Carbonaria, in what are now Luxembourg, southeastern Belgium and western Germany; its centre was the city of Trier (''Augusta Treverorum''), to which the Treveri give their name. Celtic in language, according to Tacitus they claimed Germanic descent.Tacitus writes, "The Treveri and Nervii are even eager in their claims of a German origin, thinking that the glory of this descent distinguishes them from the uniform level of Gallic effeminacy." ''Germania'' XXVIII. They possibly contained both Gallic and Germanic influences. Although early adopters of Roman material culture, the Treveri had a chequered relationship with Roman power. Their leader Indutiomarus led the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schloss Veldenz
Schloss Veldenz in the Hunsrück upland, on a steep vale draining into the Mosel is a castle ruin about southeast of the village of Veldenz in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Location The site is in the district of Bernkastel-Wittlich in Rhineland-Palatinate (''Rheinland-Pfalz''). It is on a hill spur, roughly above sea level and above the level of the Mosel. It is on northern hills of the Hunsrück in a side valley of the Mosel through which the ''Veldenzer Bach'' flows. The town of Bernkastel-Kues is northeast, the county town of Wittlich is about northwest, and the nearest city is Trier, southwest (all distances in a straight line). History The first written reference to the castle was in the year 1156 (possibly a few years earlier). Frederick I (Barbarossa) confirmed the holding by Bishop '' Albert I of Verdun'' of the castle together with the surrounding land. Since the 12th century, the Counts of Veldenz have been the feudal lords of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schloss Veldenz BW 1
''Schloss'' (; pl. ''Schlösser''), formerly written ''Schloß'', is the German term for a building similar to a château, palace, or manor house. Related terms appear in several Germanic languages. In the Scandinavian languages, the cognate word ''slot''/''slott'' is normally used for what in English could be either a palace or a castle (instead of words in rarer use such as ''palats''/''palæ'', ''kastell'', or ''borg''). In Dutch, the word ''slot'' is considered to be more archaic. Nowadays, one commonly uses ''paleis'' or ''kasteel''. But in English, the term does not appear, for instance, in the United Kingdom, this type of structure would be known as a stately home or country house. Most ''Schlösser'' were built after the Middle Ages as residences for the nobility, not as true fortresses, although originally, they often were fortified. The usual German term for a true castle is ''burg'', that for a fortress is ''festung'', and — the slightly more archaic term — ''v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
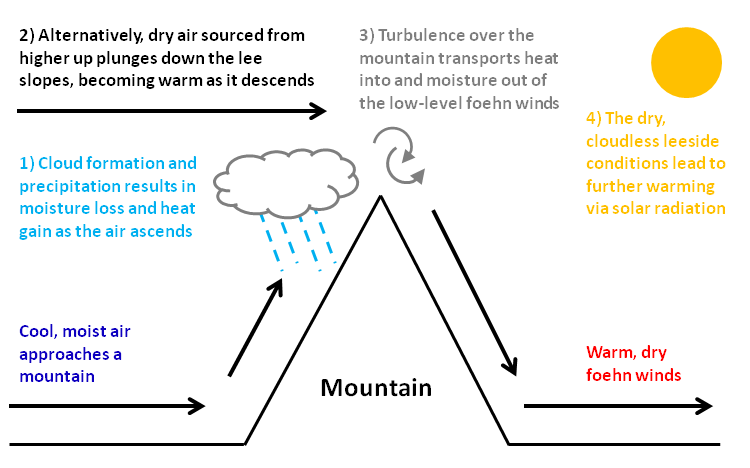
Foehn Wind
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the lee (downwind side) of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as 14 °C (25 °F) in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (german: Föhn, ) arose in the Alpine region. Originating from Latin ''(ventus) favonius'', a mild west wind of which Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by rm, favuogn or just ''fuogn'', the term was adopted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
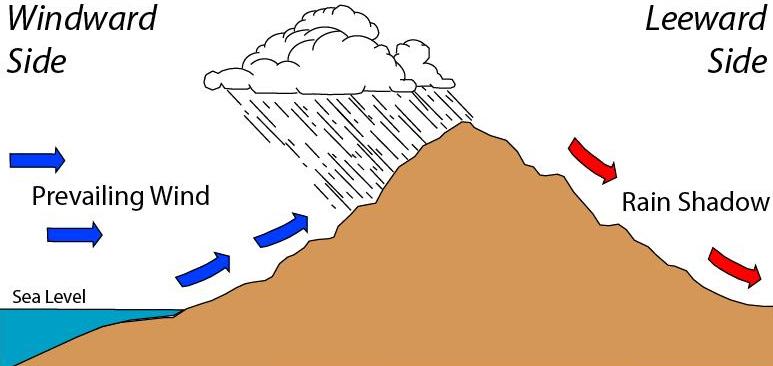
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is driven upslope towards the peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of dry climate region behind the mountain crests. This climate typically takes the form of shrub–steppe, xeric shrublands or even d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |