|
Mönchgut Nature Reserve
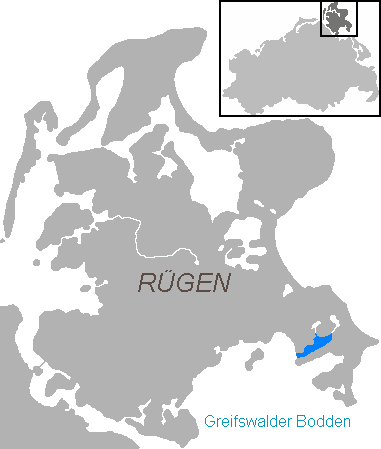
Mönchgut (''Monk's Estates'' in German) is a peninsula of 29.44 square kilometers with 6600 inhabitants in the southeast of Rügen island in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It lies just between the Greifswalder Bodden and the rest of the Baltic Sea. Mönchgut contains the districts of Göhren and Thiessow; the peninsula is part of the Mönchgut-Granitz administration area. It is also a part of the Biosphere Reserve of Südost-Rügen. The name translates as ''the monks' estates''. In 1252, Jaromar II, Prince of Rügen sold the area to the Cistercian monks of Eldena Abbey, which was founded by one of his predecessors, Jaromar I, Prince of Rügen in 1199 and by that time also belonged to the Danish Principality of Rügen. To separate the monks' possessions from the rest of the island, a ditch was dug between Baabe and Sellin, known as ''Mönchsgraben'' ("monks' ditch"). Today, a large wooden gate built upon the bridge over the ''Mönchsgraben'' marks the entrance to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mönchgut Rügen
Mönchgut (''Monk's Estates'' in German) is a peninsula of 29.44 square kilometers with 6600 inhabitants in the southeast of Rügen island in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It lies just between the Greifswalder Bodden and the rest of the Baltic Sea. Mönchgut contains the districts of Göhren and Thiessow; the peninsula is part of the Mönchgut-Granitz administration area. It is also a part of the Biosphere Reserve of Südost-Rügen. The name translates as ''the monks' estates''. In 1252, Jaromar II, Prince of Rügen sold the area to the Cistercian monks of Eldena Abbey, which was founded by one of his predecessors, Jaromar I, Prince of Rügen in 1199 and by that time also belonged to the Danish Principality of Rügen. To separate the monks' possessions from the rest of the island, a ditch was dug between Baabe and Sellin, known as ''Mönchsgraben'' ("monks' ditch"). Today, a large wooden gate built upon the bridge over the ''Mönchsgraben'' marks the entrance to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaromar I, Prince Of Rügen
Jaromar I was a Prince of Rügen between 1170 and 1218. Background Jaromar was a Ranish nobleman, who was a native of the island of Rügen. Jaromar rose to be ruler of the Principality of Rügen as result of the Danish conquest of Rügen in 1168. His predecessor was Tetzlav, who in 1168 had submitted to the Danish. Danish conquest The Danish organized a war to Christianize the formerly pagan islanders and to destroy the pagan strongholds and cult places. This action also served to have their piracy and raids to Danish lands ended. The Danish navy, led by among other militaries, Archbishop Absalon, conquered and destroyed the fortress of Cape Arkona. The temple fortress of Arkona (''Jaromarsburg'') had been the religious centre of the Slavic Rani. The island of Rügen was incorporated into the Danish Archdiocese of Roskilde. The Danish set up Rügen as their vassal. Jaromar, who was not committed to hitherto pagan rulers of the island, accepted Christianity and promised loyal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsulas Of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all continents. The size of a peninsula can range from tiny to very large. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula. Peninsulas form due to a variety of causes. Etymology Peninsula derives , which is translated as 'peninsula'. itself was derived , or together, 'almost an island'. The word entered English in the 16th century. Definitions A peninsula is usually defined as a piece of land surrounded on most, but not all sides, but is sometimes instead defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. A peninsula may be bordered by more than one body of water, and the body of water does not have to be an ocean or a sea. A piece of land on a very tight river bend or one between two rivers is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrow-gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and . Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structure gauges, and lighter rails, they can be less costly to build, equip, and operate than standard- or broad-gauge railways (particularly in mountainous or difficult terrain). Lower-cost narrow-gauge railways are often used in mountainous terrain, where engineering savings can be substantial. Lower-cost narrow-gauge railways are often built to serve industries as well as sparsely populated communities where the traffic potential would not justify the cost of a standard- or broad-gauge line. Narrow-gauge railways have specialised use in mines and other environments where a small structure gauge necessitates a small loading gauge. In some countries, narrow gauge is the standard; Japan, Indonesia, Taiwan, New Zealand, South Africa, and the Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the French Revolutionary Wars consisting of the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). The Napoleonic Wars are often described as five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1803–1806), the Fourth (1806–1807), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–1814), and the Seventh (1815) plus the Peninsular War (1807–1814) and the French invasion of Russia (1812). Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a republic in chaos; he subsequently created a state with stable financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustavia, Rügen
Gustavia was a 19th-century unfinished Swedish town on the island of Rügen, the construction of which began and had to be aborted during the Napoleonic Wars. Background The Swedish Empire was involved in several wars, with Swedish Pomerania frequently turning into a battlefield. Not having a port on the isle of Rügen proved disadvantageous in situations when access to nearby Stralsund was blocked by enemy forces on the mainland.Krüger, pp.2,3 In situations like that, Swedish landing forces often suffered casualties when they were deployed at Rügen's unsecured beaches.Krüger, p.3 Thus, in 1806 plans for a port city on Rügen's southeastern shore were drafted.Krüger, p.2 Furthermore, Sweden hoped to be able to easily block any naval access to Stralsund, Greifswald and Wolgast with a fortified port city on the Mönchgut peninsula. This port was to be named after the contemporary Swedish monarch, Gustav IV Adolf, who planned Gustavia not only as a naval base, but also as a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav IV Adolf Of Sweden
Gustav IV Adolf or Gustav IV Adolph (1 November 1778 – 7 February 1837) was King of Sweden from 1792 until he was deposed in a coup in 1809. He was also the last Swedish monarch to be the ruler of Finland. The occupation of Finland in 1808–09 by Russian forces was the immediate cause of Gustav's violent overthrow by officers of his own army. Following his abdication on 29 March 1809, an Instrument of Government was hastily written, which severely circumscribed the powers of the monarchy. The "Instrument" was adopted in 1809 on 6 June, the National Day of Sweden now as well as in his time. It remained in force until replaced in 1974. The crown, now with strictly limited powers, passed to Gustav's uncle Charles XIII, who had no legitimate children; this want of heirs set into motion the quest for a successor, who was found the following year in the person of Jean-Baptiste Jules Bernadotte, the first monarch of the present royal family. ch 37 pp 203-19 Early life Gustav Adolf w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greifswalder Oie
Greifswalder Oie (literally "Greifswald's isle") is a small island in the Baltic Sea, located east of Rügen on the German coast. The island covers an area of about 54 hectares. The isle forms part of the municipality of Kröslin. Geography The Greifswalder Oie is about 1,550 metres long, a maximum of 570 metres wide and, at the cliffs on its eastern side, a maximum of 19 metres high. It is about 12 kilometres off the shore of Usedom and belongs administratively to the municipality of Kröslin on the mainland. On the island, with its striking steep coast, is a 49 metre high lighthouse with one of the strongest beacons in the Baltic. The whole island is a nature reserve. It was formed during the last ice age, the Weichselian glaciation, by several glacial depositions from Scandinavia. On the Oie a total of three different deposition phases are evident, so that rocks originating in different parts of Scandinavia may be found on the island. History Around 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Having (bay)
The Having is an inlet in the northeast of the Rügischer Bodden, the northern half of the Bay of Greifswald, which cuts deeply into the peninsula of Mönchgut, the southeastern tip of the German island of Rügen. The inlet is about 5.7 kilometres long, 1.1 kilometres wide and has an area of 7.5 km². It opens towards the southwest onto the Rügische Bodden. The Having is up to eight metres deep. In the south the Having is bounded by the narrow, elongated peninsula of Reddevitzer Höft, in the north by the Granitz. In the north there are two narrow waterways to the lakes of Selliner See and Neuensiener See. The heights around the bay climb to over 30 metres. There are no settlements on the shores of the Having itself. The inlet is part of the Mönchgut Nature Reserve in the Southeast Rügen Biosphere Reserve The Southeast Rügen Biosphere Reserve (german: Biosphärenreservat Südost-Rügen) is a biosphere reserve in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sellin
Sellin is a municipality on the Island of Rügen, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. History First mentions of Sellin date to 1295. From 1880 on, the town gained importance as a Baltic Sea spa town. After the '' Wende'' in 1989, the building stock in the village was extensively renovated. In 1992, Sellin Pier was rebuilt and was officially opened on 2 April 1998. Culture and sights ''Wilhelmstraße'', with its houses from the resort architecture period (turn of the 19th and 20th century), runs up to the steep coast, up to 30 metres high - where there is a steep flight of steps or a lift to Sellin Pier or the promenade on the South Beach (''Südstrand''). Sellin has the longest pier on Rügen: 394 metres. Since 1991 the historic centre has been thoroughly renovated as part of a programme of urban development. Other sights are the ''Galerie Hartwich'' in the old fire station (''Feuerwehrhaus''), the Amber Museum with its associated workshop and the ''Gnadenkirche''. The S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |