|
Myrichthys Colubrinus
''Myrichthys colubrinus'', the banded snake eel, ringed snake eel or harlequin snake eel, is a snake eel from the Indo-Pacific. It occasionally makes its way into the aquarium trade. It grows to a size of in length. The ringed snake eel resembles the venomous sea snake, ''Laticauda colubrina The yellow-lipped sea krait (''Laticauda colubrina''), also known as the banded sea krait or colubrine sea krait, is a species of venomous sea snake found in tropical Indo-Pacific oceanic waters. The snake has distinctive black stripes and a yel ...'' which is a form of Batesian mimicry. It also adjusts its behaviour to swim freely during the day, whereas other snake eels tend to stay hidden and roam at night. In 2021, it was first recorded in Hawaii. References External links * Photos oMyrichthys colubrinusin iNaturalist colubrinus Fish described in 1781 Taxa named by Pieter Boddaert {{Anguilliformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieter Boddaert
Pieter Boddaert (1730 – 6 May 1795) was a Dutch physician and natural history, naturalist. Early life, family and education Boddaert was the son of a Middelburg jurist and poet by the same name (1694–1760). The younger Pieter obtained his M.D. at the University of Utrecht in 1764. Career He became a lecturer on natural history at his alma mater, University of Utrecht. Fourteen letters survive of his correspondence with Carl Linnaeus between 1768 and 1775. He was a friend of Albert Schlosser, whose Cabinet of curiosities, cabinet of "curiosities" of natural history he described. In 1783 he published 50 copies of an identification key of Edmé-Louis Daubenton's ''Planches enluminées'', the colored plates of illustrations for the comte de Buffon's monumental ''Histoire Naturelle'' (published 1749–1789), assigning binomial scientific names to the plates. As many of these were the first Linnaean taxonomy, Linnaean scientific names to be proposed, they remain in use. In 2017 the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake Eel
Ophichthidae is a family of fish in the order Anguilliformes, commonly known as the snake eels. The term "Ophichthidae" comes from Greek ''ophis'' ("serpent") and ''ichthys'' ("fish"). Snake eels are also burrowing eels. They are named for their physical appearance, as they have long, cylindrical, snake-like bodies. This family is found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate waters. They inhabit a wide range of habitats, from coastal shallows and even rivers, to depths below . Most species are bottom dwellers, hiding in mud or sand to capture their prey of crustaceans and small fish, but some are pelagic. These species range in total length from to or more. Many species lack fins altogether, improving their ability to burrow into the substrate like worms. They are often spotted or striped in colour, mimicking the appearance of venomous sea snakes to deter predators. Often, they are washed ashore by large storms. Genera Currently, 62 recognized genera are placed in this famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia. It does not include the temperate and polar regions of the Indian and Pacific oceans, nor the Tropical Eastern Pacific, along the Pacific coast of the Americas, which is also a distinct marine realm. The term is especially useful in marine biology, ichthyology, and similar fields, since many marine habitats are continuously connected from Madagascar to Japan and Oceania, and a number of species occur over that range, but are not found in the Atlantic Ocean. The region has an exceptionally high species richness, with the world's highest species richness being found in at its heart in the Coral Triangle, and a remarkable gradient of decreasing species richness radiating outward in al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
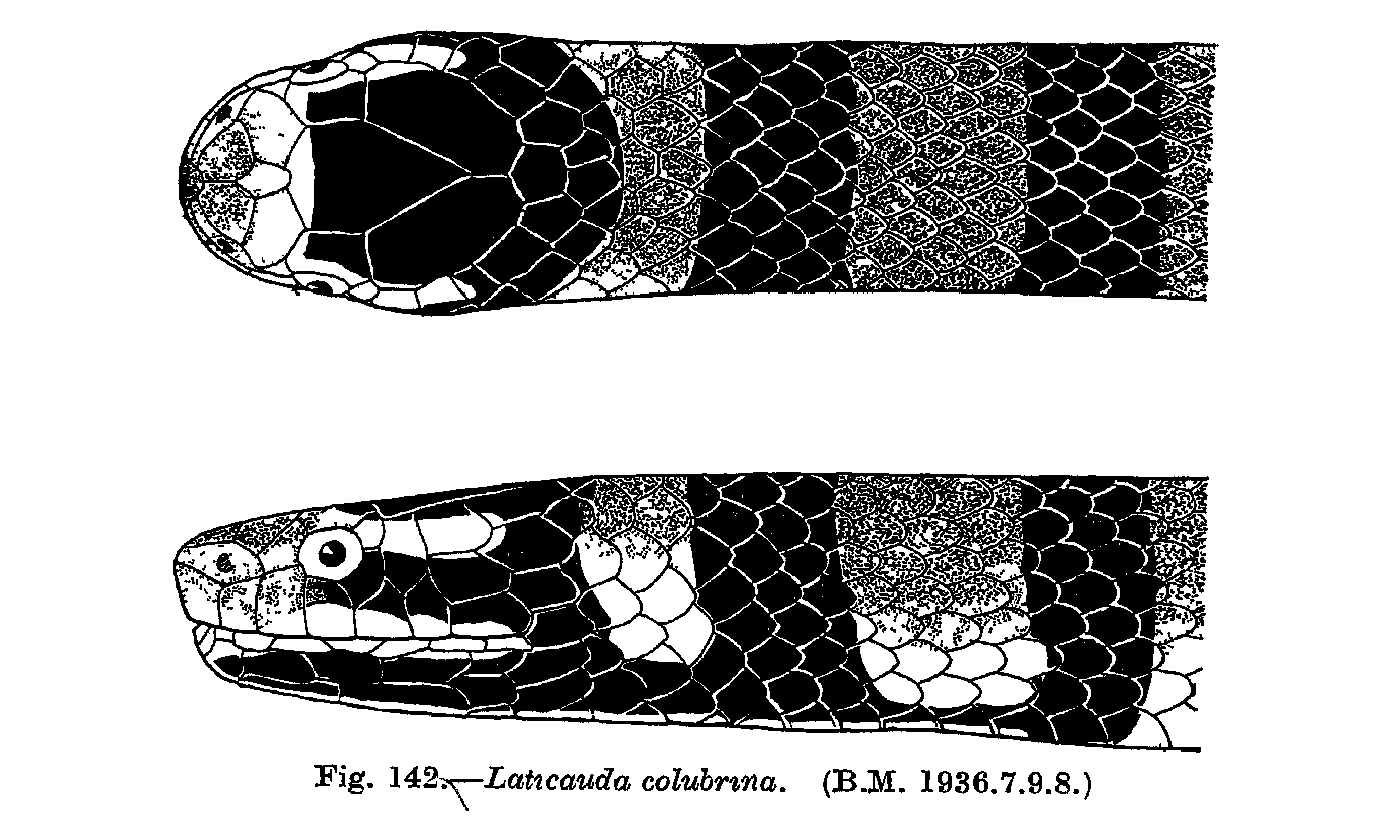
Laticauda Colubrina
The yellow-lipped sea krait (''Laticauda colubrina''), also known as the banded sea krait or colubrine sea krait, is a species of venomous sea snake found in tropical Indo-Pacific oceanic waters. The snake has distinctive black stripes and a yellow snout, with a paddle-like tail for use in swimming. It spends much of its time under water to hunt, but returns to land to digest, rest, and reproduce. It has very potent neurotoxic venom, which it uses to prey on eels and small fish. Because of its affinity to land, the yellow-lipped sea krait often encounters humans, but the snake is not aggressive and only attacks when feeling threatened. Description The head of a yellow-lipped sea krait is black, with lateral nostrils and an undivided rostral scale. The upper lip and snout are characteristically colored yellow, and the yellow color extends backward on each side of the head above the eye to the temporal scales. The body of the snake is subcylindrical, and is taller than it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batesian Mimicry
Batesian mimicry is a form of mimicry where a harmless species has evolved to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species directed at a predator of them both. It is named after the English naturalist Henry Walter Bates, after his work on butterflies in the rainforests of Brazil. Batesian mimicry is the most commonly known and widely studied of mimicry complexes, such that the word mimicry is often treated as synonymous with Batesian mimicry. There are many other forms however, some very similar in principle, others far separated. It is often contrasted with Müllerian mimicry, a form of mutually beneficial convergence between two or more harmful species. However, because the mimic may have a degree of protection itself, the distinction is not absolute. It can also be contrasted with functionally different forms of mimicry. Perhaps the sharpest contrast here is with aggressive mimicry where a predator or parasite mimics a harmless species, avoiding detection and improving its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrichthys
''Myrichthys'' is a genus of snake eels currently containing 11 recognized species found in tropical and warm temperate oceans worldwide. Species * '' Myrichthys aspetocheiros'' McCosker & Rosenblatt, 1993 (longfin spotted snake eel) * ''Myrichthys breviceps'' ( J. Richardson, 1848) (Sharptail eel) * '' Myrichthys colubrinus'' (Boddaert, 1781) (harlequin snake eel) * '' Myrichthys maculosus'' ( Cuvier, 1816) (tiger snake eel) * '' Myrichthys magnificus'' ( C. C. Abbott, 1860) (magnificent snake eel) * '' Myrichthys ocellatus'' ( Lesueur, 1825) (gold-spotted eel) * '' Myrichthys paleracio'' McCosker & G. R. Allen, 2012McCosker, J.E. & Allen, G.R. (2012): ''Description of a new Snake Eel (Pisces: Ophichthidae: Myrichthys) from the Philippines.'' aqua, International Journal of Ichthyology, 18 (1): 35-40. * '' Myrichthys pantostigmius'' D. S. Jordan & E. A. McGregor, 1898 (clarion snake eel) * '' Myrichthys pardalis'' (Valenciennes Valenciennes (, also , , ; nl, label=also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1781
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a vertebrate, true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed placodermi, external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |