Batesian mimicry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
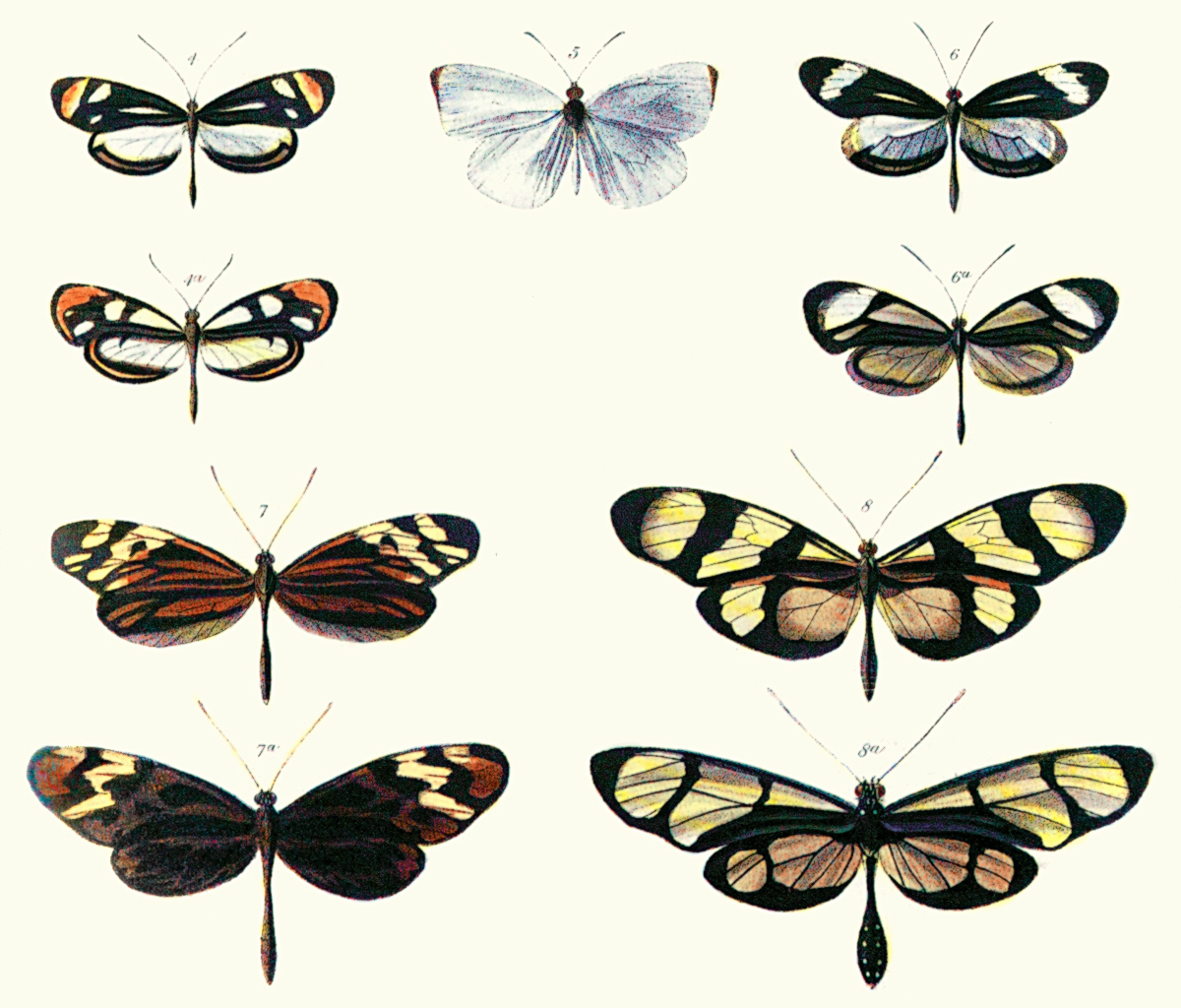 Batesian mimicry is a form of
Batesian mimicry is a form of
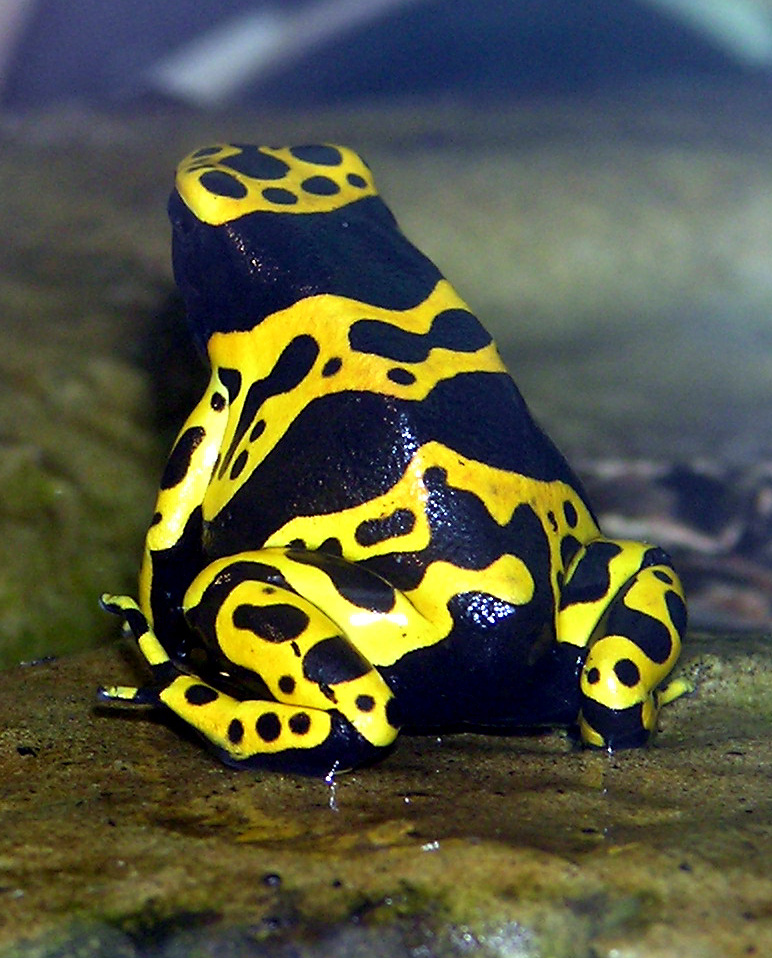
 Most living things have predators and therefore are in a constant
Most living things have predators and therefore are in a constant
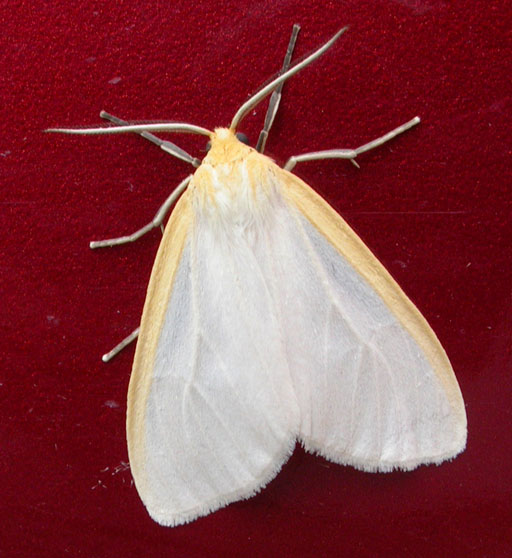 Predators may identify their prey by sound as well as sight; mimics have accordingly evolved to deceive the
Predators may identify their prey by sound as well as sight; mimics have accordingly evolved to deceive the
Review of Contributions to an insect fauna of the Amazon valley by Charles Darwin
The Complete Works of Charles Darwin Online.
Biographical sketch of Bates, with picture
{{DEFAULTSORT:Batesian Mimicry Mimicry Antipredator adaptations Chemical ecology
 Batesian mimicry is a form of
Batesian mimicry is a form of mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry ...
where a harmless species has evolved to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species directed at a predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
of them both. It is named after the English naturalist Henry Walter Bates
Henry Walter Bates (8 February 1825, in Leicester – 16 February 1892, in London) was an English naturalist and explorer who gave the first scientific account of mimicry in animals. He was most famous for his expedition to the rainforests ...
, after his work on butterflies
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises t ...
in the rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfo ...
s of Brazil.
Batesian mimicry is the most commonly known and widely studied of mimicry complexes, such that the word mimicry is often treated as synonymous with Batesian mimicry. There are many other forms however, some very similar in principle, others far separated. It is often contrasted with Müllerian mimicry
Müllerian mimicry is a natural phenomenon in which two or more well-defended species, often foul-tasting and sharing common predators, have come to mimicry, mimic each other's honest signal, honest aposematism, warning signals, to their mutuali ...
, a form of mutually beneficial convergence between two or more harmful species. However, because the mimic may have a degree of protection itself, the distinction is not absolute. It can also be contrasted with functionally different forms of mimicry. Perhaps the sharpest contrast here is with aggressive mimicry where a predator or parasite mimics a harmless species, avoiding detection and improving its foraging
Foraging is searching for wild food resources. It affects an animal's fitness because it plays an important role in an animal's ability to survive and reproduce. Foraging theory is a branch of behavioral ecology that studies the foraging behavi ...
success.
The imitating species is called the ''mimic'', while the imitated species (protected by its toxicity, foul taste or other defenses) is known as the ''model''. The predatory species mediating indirect interactions between the mimic and the model is variously known as the '' ignalreceiver'', ''dupe'' or ''operator''. By parasitizing the honest warning signal of the model, the Batesian mimic gains an advantage, without having to go to the expense of arming itself. The model, on the other hand, is disadvantaged, along with the dupe. If impostors appear in high numbers, positive experiences with the mimic may result in the model being treated as harmless. At higher frequency there is also a stronger selective advantage for the predator to distinguish mimic from model. For this reason, mimics are usually less numerous than models, an instance of frequency dependent selection. Some mimetic populations have evolved multiple forms (polymorphism
Polymorphism, polymorphic, polymorph, polymorphous, or polymorphy may refer to:
Computing
* Polymorphism (computer science), the ability in programming to present the same programming interface for differing underlying forms
* Ad hoc polymorphis ...
), enabling them to mimic several different models and thereby to gain greater protection. Batesian mimicry is not always perfect. A variety of explanations have been proposed for this, including limitations in predators' cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thoug ...
.
While visual signals have attracted most study, Batesian mimicry can employ deception of any of the sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system rec ...
s; some moths mimic the ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
warning signals sent by unpalatable moths to bat predators, constituting auditory Batesian mimicry, while some weakly electric fish
An electric fish is any fish that can generate electric fields. Most electric fish are also electroreceptive, meaning that they can sense electric fields. The only exception is the stargazer family. Electric fish, although a small minority, inc ...
appear to mimic the electrolocation signals of strongly electric fish, probably constituting electrical mimicry.
Historical background

Henry Walter Bates
Henry Walter Bates (8 February 1825, in Leicester – 16 February 1892, in London) was an English naturalist and explorer who gave the first scientific account of mimicry in animals. He was most famous for his expedition to the rainforests ...
(1825–1892) was an English explorer
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
- naturalist who surveyed the Amazon rainforest with Alfred Russel Wallace in 1848. While Wallace returned in 1852, Bates remained for over a decade. His field research included collecting almost a hundred species of butterflies
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises t ...
from the families Ithomiinae
Ithomiini is a butterfly tribe in the nymphalid subfamily Danainae. It is sometimes referred to as the tribe of clearwing butterflies or glasswing butterflies. Some authors consider the group to be a subfamily (Ithomiinae). These butterflies ar ...
and Heliconiinae, as well as thousands of other insects specimens. In sorting these butterflies into similar groups based on appearance, inconsistencies began to arise. Some appeared superficially similar to others, even so much so that Bates could not tell some species apart based only on wing appearance. However, closer examination of less obvious morphological characters seemed to show that they were not even closely related. Shortly after his return to England he read a paper on his theory of mimicry at a meeting of the Linnean Society of London
The Linnean Society of London is a learned society dedicated to the study and dissemination of information concerning natural history, evolution, and taxonomy. It possesses several important biological specimen, manuscript and literature colle ...
on 21 November 1861, which was then published in 1862 as 'Contributions to an Insect Fauna of the Amazon Valley' in the society's '' Transactions''.; Reprint: He elaborated on his experiences further in '' The Naturalist on the River Amazons''.
Bates put forward the hypothesis that the close resemblance between unrelated species was an antipredator adaptation
Anti-predator adaptations are mechanisms developed through evolution that assist prey organisms in their constant struggle against predators. Throughout the animal kingdom, adaptations have evolved for every stage of this struggle, namely by av ...
. He noted that some species showed very striking coloration, and flew in a leisurely manner, almost as if taunting predators to eat them. He reasoned that these butterflies were unpalatable to birds and other insectivore
A robber fly eating a hoverfly
An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant that eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects.
The first vertebrate insectivores wer ...
s, and were thus avoided by them. He extended this logic to forms that closely resembled such protected species, mimicking their warning coloration but not their toxicity.
This naturalistic explanation fitted well with the recent account of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
by Wallace and Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
, as outlined in his famous 1859 book ''The Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
''. Because this Darwinian
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that ...
explanation required no supernatural forces, it met with considerable criticism from anti-evolutionists, both in academic circles and in the broader social realm.
Aposematism
 Most living things have predators and therefore are in a constant
Most living things have predators and therefore are in a constant evolutionary arms race
In evolutionary biology, an evolutionary arms race is an ongoing struggle between competing sets of co-evolving genes, phenotypic and behavioral traits that develop escalating adaptations and counter-adaptations against each other, resembling ...
to develop antipredator adaptation
Anti-predator adaptations are mechanisms developed through evolution that assist prey organisms in their constant struggle against predators. Throughout the animal kingdom, adaptations have evolved for every stage of this struggle, namely by av ...
s, while the predator adapts to become more efficient at defeating the prey's adaptations. Some organisms have evolved to make detection less likely, for example by nocturnality
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sen ...
and camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
. Others have developed chemical defences such as the deadly toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849 ...
s of certain snakes and wasps, or the noxious scent of the skunk
Skunks are mammals in the family Mephitidae. They are known for their ability to spray a liquid with a strong, unpleasant scent from their anal glands. Different species of skunk vary in appearance from black-and-white to brown, cream or gi ...
. Such prey often send clear and honest warning signals to their attackers with conspicuous aposematic (warning) patterns. The brightness of such warning signs is correlated with the level of toxicity of the organism.
In Batesian mimicry, the mimic effectively copies the coloration of an aposematic animal, known as the model, to deceive predators into behaving as if it were distasteful. The success of this dishonest display depends on the level of toxicity of the model and the abundance of the model in the geographical area. The more toxic the model is, the more likely it is that the predator will avoid the mimic. The abundance of the model species is also important for the success of the mimic because of frequency dependent selection. When the model is abundant, mimics with imperfect model patterns or slightly different coloration from the model are still avoided by predators. This is because the predator has a strong incentive to avoid potentially lethal organisms, given the likelihood of encountering one. However, in areas where the model is scarce or locally extinct, mimics are driven to accurate aposematic coloration. This is because predators attack imperfect mimics more readily where there is little chance that they are the model species. Frequency dependent selection may also have driven Batesian mimics to become polymorphic in rare cases where a single genetic switch controls appearance, as in the swallowtail butterflies (the Papilionidae) such as the pipevine swallowtail.
Classification and comparisons
Batesian mimicry is a case of protective ordefensive mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry f ...
, where the mimic does best by avoiding confrontations with the signal receiver. It is a ''disjunct'' system, which means that all three parties are from different species. An example would be the robber fly
The Asilidae are the robber fly family, also called assassin flies. They are powerfully built, bristly flies with a short, stout proboscis enclosing the sharp, sucking hypopharynx. The name "robber flies" reflects their notoriously aggressive pre ...
''Mallophora bomboides
''Mallophora bomboides'', also known as the Florida bee killer, is a predaceous species of robber fly of the family Asilidae that feeds primarily on bumblebees. ''M. bomboides'' is a noteworthy instance of Batesian mimicry given its close resembla ...
'', which is a Batesian mimic of its bumblebee
A bumblebee (or bumble bee, bumble-bee, or humble-bee) is any of over 250 species in the genus ''Bombus'', part of Apidae, one of the bee families. This genus is the only extant group in the tribe Bombini, though a few extinct related gene ...
model and prey, ''B. americanorum'' (now more commonly known as '' Bombus pensylvanicus''), which is noxious to predators due to its sting.
Batesian mimicry stands in contrast to other forms such as aggressive mimicry, where the mimic profits from interactions with the signal receiver. One such case of this is in fireflies, where females of one species mimic the mating signals of another species, deceiving males to come close enough for them to eat. Mimicry sometimes does not involve a predator at all though. Such is the case in ''dispersal mimicry'', where the mimic once again benefits from the encounter. For instance, some fungi have their spores dispersed by insects by smelling like carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures ...
. In protective mimicry, the meeting between mimic and dupe is not such a fortuitous occasion for the mimic, and the signals it mimics tend to lower the probability of such an encounter.
A case somewhat similar to Batesian mimicry is that of mimetic weeds, which imitate agricultural crops. In weed or Vavilovian mimicry
In plant biology, Vavilovian mimicry (also crop mimicry or weed mimicry) is a form of mimicry in plants where a weed evolves to share one or more characteristics with a domesticated plant through generations of artificial selection. It is name ...
, the weed survives by having seeds which winnowing machinery identifies as belonging to the crop. Vavilovian mimicry is not Batesian, because man and crop are not enemies. By contrast, a leaf-mimicking plant, the chameleon vine, employs Batesian mimicry by adapting its leaf shape and colour to match that of its host to deter herbivores from eating its edible leaves.
Another analogous case within a single species has been termed ''Browerian mimicry'' (after Lincoln P. Brower
Lincoln Pierson Brower (September 10, 1931 – July 17, 2018) was an American entomologist and ecologist, known for his work on monarch butterflies through six decades, including on their automimicry, chemical ecology and conservation. G. Pasteu ...
and Jane Van Zandt BrowerBrower, L. P. (1970) Plant poisons in a terrestrial food chain and implications for mimicry theory. In K. L. Chambers (ed) ''Biochemical Coevolution'' Corvallis, OR: Oregon State Univ. pp. 69-82.). This is a case of automimicry; the model is the same species as its mimic. Equivalent to Batesian mimicry within a single species, it occurs when there is a ''palatability spectrum'' within a population of harmful prey. For example, monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
(''Danaus plexippus'') caterpillars feed on milkweed species of varying toxicity. Some feed on more toxic plants and store these toxins within themselves. The more palatable caterpillars thus profit from the more toxic members of the same species.
Another important form of protective mimicry is Müllerian mimicry
Müllerian mimicry is a natural phenomenon in which two or more well-defended species, often foul-tasting and sharing common predators, have come to mimicry, mimic each other's honest signal, honest aposematism, warning signals, to their mutuali ...
, discovered by and named after the naturalist Fritz Müller
Johann Friedrich Theodor Müller (31 March 1822 – 21 May 1897), better known as Fritz Müller, and also as Müller-Desterro, was a German biologist who emigrated to southern Brazil, where he lived in and near the German community of Blumenau, ...
. In Müllerian mimicry both model and mimic are aposematic, so mimicry may be mutual, does not necessarily constitute a bluff or deception and as in the wasps and bees may involve many species in a mimicry ring.
Imperfect Batesian mimicry
In imperfect Batesian mimicry, the mimics do not exactly resemble their models. An example of this is the fly ''Spilomyia longicornis
''Spilomyia longicornis'' is a species of syrphid fly, also known as a flower fly or hoverfly, in the family Syrphidae. Although the appearance of ''S. longicornis'' is remarkably similar to a vespid wasp, it is a fly and cannot sting.Penney, H. ...
'', which mimics vespid wasps. However, it is not a perfect mimic. Wasps have long black antennae and this fly does not. Instead, they wave their front legs above their heads to look like the antennae on the wasps. Many reasons have been suggested for imperfect mimicry.
Imperfect mimics may simply be evolving towards perfection.
They may gain advantage from resembling multiple models at once.
Humans may evaluate mimics differently from actual predators.
Mimics may confuse predators by resembling both model and nonmimic at the same time (satiric mimicry).
Kin selection may enforce poor mimicry.
The selective advantage of better mimicry may not outweigh the advantages of other strategies like thermoregulation or camouflage.
Only certain traits may be required to deceive predators; for example, tests on the sympatry
In biology, two related species or populations are considered sympatric when they exist in the same geographic area and thus frequently encounter one another. An initially interbreeding population that splits into two or more distinct species s ...
/ allopatry border (where the two are in the same area, and where they are not) of the mimic '' Lampropeltis elapsoides'' and the model ''Micrurus fulvius
''Micrurus fulvius'', commonly known as the eastern coral snake, Behler John L.; King, F. Wayne (1979). ''The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Reptiles and Amphibians''. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. 743 pp., 657 color plates. LCCCN 7 ...
'' showed that color proportions in these snakes were important in deceiving predators but that the order of the colored rings was not.
Acoustic mimicry
 Predators may identify their prey by sound as well as sight; mimics have accordingly evolved to deceive the
Predators may identify their prey by sound as well as sight; mimics have accordingly evolved to deceive the hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is audit ...
of their predators. Bats are nocturnal predators that rely on echolocation to detect their prey. Some potential prey are unpalatable to bats, and produce an ultrasonic aposematic signal, the auditory equivalent of warning coloration. In response to echolocating red bats and big brown bats, tiger moth
The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer aircraft. ...
s such as '' Cycnia tenera'' produce warning sounds. Bats learn to avoid the harmful moths, but similarly avoid other species such as some pyralid moths that produce such warning sounds as well. Acoustic mimicry complexes, both Batesian and Müllerian, may be widespread in the auditory world.
Electrical mimicry
The electric eel, ''Electrophorus'', is capable of delivering a powerful electric shock that can stun or kill its prey. Bluntnose knifefishes, '' Brachyhypopomus'', create an electric discharge pattern similar to the low voltage electrolocation discharge of the electric eel. This is thought to be Batesian mimicry of the powerfully-protected electric eel.See also
*Phylogenetics of mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry ...
* ''Papilio dardanus
''Papilio dardanus'', the African swallowtail, mocker swallowtail or flying handkerchief, is a species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae (the swallowtails). The species is broadly distributed throughout Sub-Saharan Africa. The British e ...
'' (females mimic multiple model species)
* Locomotor mimicry Locomotor mimicry is a subtype of Batesian mimicry in which animals avoid predation by mimicking the movements of another species phylogenetically separated. This can be in the form of mimicking a less desirable species or by mimicking the predator ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*Cott, H.B.
Hugh Bamford Cott (6 July 1900 – 18 April 1987) was a British zoologist, an authority on both natural and military camouflage, and a scientific illustrator and photographer. Many of his field studies took place in Africa, where he was especia ...
(1940) ''Adaptive Coloration in Animals''. Methuen and Co, Ltd., London Provides many examples of Batesian Mimicry
* For a historical perspective.
* Wickler, W. (1968) ''Mimicry in Plants and Animals'' (Translated from the German) McGraw-Hill, New York. Especially the first two chapters.
* Edmunds, M. 1974. ''Defence in Animals: A Survey of Anti-Predator Defences''. Harlow, Essex & NY: Longman 357 p. Chapter 4 discusses this phenomenon.
* A detailed discussion of the different forms of mimicry.
* Ruxton, G. D.; Speed, M. P.; Sherratt, T. N. (2004). ''Avoiding Attack. The Evolutionary Ecology of Crypsis, Warning Signals and Mimicry''. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Chapter 10 and 11 provide an up-to-date synopsis.
External links
Review of Contributions to an insect fauna of the Amazon valley by Charles Darwin
The Complete Works of Charles Darwin Online.
Biographical sketch of Bates, with picture
{{DEFAULTSORT:Batesian Mimicry Mimicry Antipredator adaptations Chemical ecology