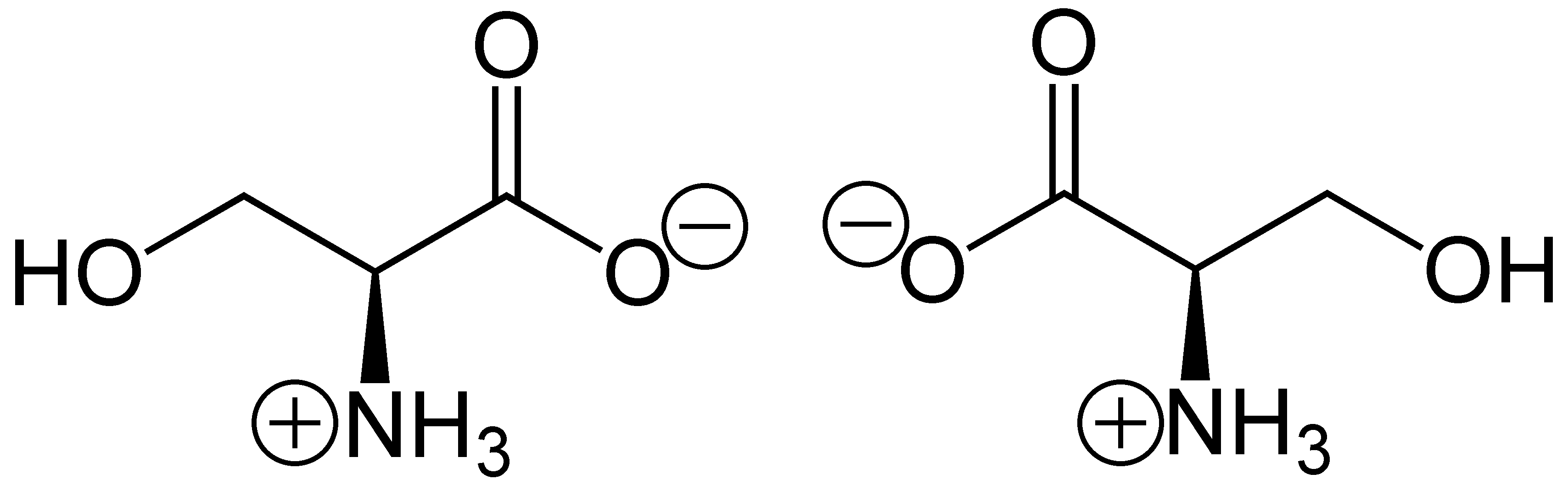|
Myosin Light-chain Phosphatase
Myosin light-chain phosphatase, also called myosin phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.53; systematic name yosin-light-chainphosphate phosphohydrolase), is an enzyme (specifically a serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatase) that dephosphorylates the regulatory light chain of myosin II: : yosin light-chainphosphate + H2O = yosin light-chain+ phosphate This dephosphorylation reaction occurs in smooth muscle tissue and initiates the relaxation process of the muscle cells. Thus, myosin phosphatase undoes the muscle contraction process initiated by myosin light-chain kinase. The enzyme is composed of three subunits: the catalytic region (protein phosphatase 1, or PP1), the myosin binding subunit (MYPT1), and a third subunit (M20) of unknown function. The catalytic region uses two manganese ions as catalysts to dephosphorylate the light-chains on myosin, which causes a conformational change in the myosin and relaxes the muscle. The enzyme is highly conserved and is found in all organis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossbridge
The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction based on muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement. According to the sliding filament theory, the myosin ( thick filaments) of muscle fibers slide past the actin ( thin filaments) during muscle contraction, while the two groups of filaments remain at relatively constant length. The theory was independently introduced in 1954 by two research teams, one consisting of Andrew Huxley and Rolf Niedergerke from the University of Cambridge, and the other consisting of Hugh Huxley and Jean Hanson from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It was originally conceived by Hugh Huxley in 1953. Andrew Huxley and Niedergerke introduced it as a "very attractive" hypothesis. Before the 1950s there were several competing theories on muscle contraction, including electrical attraction, protein folding, and protein modification. The novel theory directly introduced a new concept called cross-bridge t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telokin
Telokin (also known as kinase-related protein or KRP) is an abundant protein found in smooth-muscle. It is identical to the C-terminus of myosin light-chain kinase. Telokin may play a role in the stabilization of unphosphorylated smooth-muscle myosin filaments. Because of its origin as the C-terminal end of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase, it is called "telokin" (from a combination of the Greek telos, "end" and kinase). Nomenclature and classification Telokin's systematic name is ATP: yosin light chainO-phosphotransferase and its recommended name is myosin-light-chain kinase. (). The gene ''MYLK'', a muscle member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, encodes myosin light chain kinase which is a calcium/ calmodulin dependent enzyme. Four transcript variants that produce four isoforms of the calcium/calmodulin dependent enzyme have been identified as well as two transcripts that produce two isoforms of telokin. The two transcripts that produce the two telokin i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ROCK1
ROCK1 is a protein serine/threonine kinase also known as rho-associated, coiled-coil-containing protein kinase 1. Other common names are ROKβ and P160ROCK. ROCK1 is a major downstream effecter of the small GTPase RhoA and is a regulator of the actomyosin cytoskeleton which promotes contractile force generation. ROCK1 plays a role in cancer and in particular cell motility, metastasis, and angiogenesis. Gene and expression ROCK1 is also the name of the gene that encodes the protein ROCK1, a serine/threonine kinase. ROCK1 is activated when bound to the GTP-bound form of RhoA. The human ROCK1 gene is located on human chromosome 18 with specific location of 18q11.1. The location of the base pair starts at 18,529,703 and ends at 18,691,812 bp and translates into 1354 amino acids. ROCK1 has a ubiquitous tissue distribution, but subcellularly it is thought to colocalize with the centrosomes. This is consistent with its function as a key modulator of cell motility, tumor cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RhoA
Transforming protein RhoA, also known as Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), is a small GTPase protein in the Rho family of GTPases that in humans is encoded by the ''RHOA'' gene. While the effects of RhoA activity are not all well known, it is primarily associated with cytoskeleton regulation, mostly actin stress fibers formation and actomyosin contractility. It acts upon several effectors. Among them, ROCK1 (Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1) and DIAPH1 (Diaphanous Homologue 1, a.k.a. hDia1, homologue to mDia1 in mouse, diaphanous in ''Drosophila'') are the best described. RhoA, and the other Rho GTPases, are part of a larger family of related proteins known as the Ras superfamily, a family of proteins involved in the regulation and timing of cell division. RhoA is one of the oldest Rho GTPases, with homologues present in the genomes since 1.5 billion years. As a consequence, RhoA is somehow involved in many cellular processes which emerged throughout evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
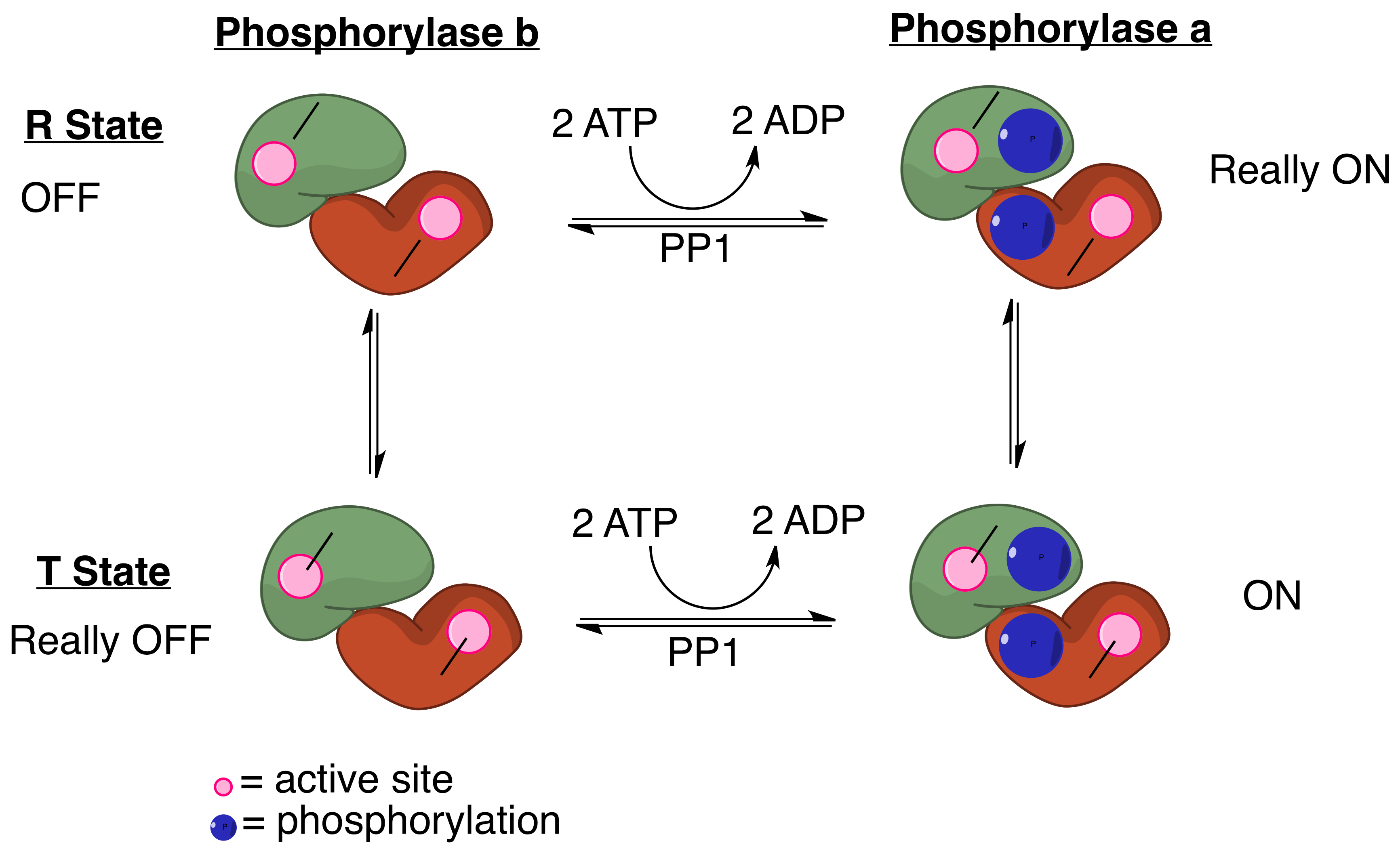
PP1 Mechanism For Myosin Phosphatase
Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) belongs to a certain class of phosphatases known as protein serine/threonine phosphatases. This type of phosphatase includes metal-dependent protein phosphatases (PPMs) and aspartate-based phosphatases. PP1 has been found to be important in the control of glycogen metabolism, muscle contraction, cell progression, neuronal activities, splicing of RNA, mitosis, cell division, apoptosis, protein synthesis, and regulation of membrane receptors and channels. Structure Each PP1 enzyme contains both a catalytic subunit and at least one regulatory subunit. The catalytic subunit consists of a 30-kD single-domain protein that can form complexes with other regulatory subunits. The catalytic subunit is highly conserved among all eukaryotes, thus suggesting a common catalytic mechanism. The catalytic subunit can form complexes with various regulatory subunits. These regulatory subunits play an important role in substrate specificity as well as compartmenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the " Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L- stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen Synthase
Glycogen synthase (UDP-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase) is a key enzyme in glycogenesis, the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase () that catalyses the reaction of UDP-glucose and (1,4--D-glucosyl)n to yield UDP and (1,4--D-glucosyl)n+1. Structure Much research has been done on glycogen degradation through studying the structure and function of glycogen phosphorylase, the key regulatory enzyme of glycogen degradation. On the other hand, much less is known about the structure of glycogen synthase, the key regulatory enzyme of glycogen synthesis. The crystal structure of glycogen synthase from '' Agrobacterium tumefaciens'', however, has been determined at 2.3 A resolution. In its asymmetric form, glycogen synthase is found as a dimer, whose monomers are composed of two Rossmann-fold domains. This structural property, among others, is shared with related enzymes, such as glycogen phosphorylase and other glycosyltransferases of the GT-B superf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there are two distinct types of cell division: a vegetative division ( mitosis), producing daughter cells genetically identical to the parent cell, and a cell division that produces haploid gametes for sexual reproduction (meiosis), reducing the number of chromosomes from two of each type in the diploid parent cell to one of each type in the daughter cells. In cell biology, mitosis ( /maɪˈtoʊsɪs/) is a part of the cell cycle, in which, replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is preceded by the S stage of interphase (during which the DNA replication occurs) and is oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body. Glycogen functions as one of two forms of energy reserves, glycogen being for short-term and the other form being triglyceride stores in adipose tissue (i.e., body fat) for long-term storage. In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. In the liver, glycogen can make up 5–6% of the organ's fresh weight, and the liver of an adult, weighing 1.5 kg, can store roughly 100–120 grams of glycogen. In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass) and the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 kg stores roughly 400 grams of glycogen. The amount of glycogen stored in the body—particularly within the muscles and liver—mostly depends on physical training, bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |