|
Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cell
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) are a heterogeneous group of immune cells from the myeloid lineage (a family of cells that originate from bone marrow stem cells). MDSCs expand under pathologic conditions such as chronic infection and cancer, as a result of altered haematopoiesis. MDSCs differ from other myeloid cell types in that they have immunosuppressive activities, as opposed to immune-stimulatory properties. Similar to other myeloid cells, MDSCs interact with immune cell types such as T cells, dendritic cells, macrophages and natural killer cells to regulate their functions. Tumors with high levels of infiltration by MDSCs have been associated with poor patient outcome and resistance to therapies. MDSCs can also be detected in the blood. In patients with breast cancer, levels of MDSC in blood are about 10-fold higher than normal. The size of the myeloid suppressor compartment is considered to be an important factor in the success or failure of cancer immunotherapy, hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloid
Myeloid tissue, in the bone marrow sense of the word '' myeloid'' ('' myelo-'' + ''-oid''), is tissue of bone marrow, of bone marrow cell lineage, or resembling bone marrow, and myelogenous tissue (''myelo-'' + '' -genous'') is any tissue of, or arising from, bone marrow; in these senses the terms are usually used synonymously, as for example with chronic myeloid/myelogenous leukemia. In hematopoiesis, myeloid or myelogenous cells are blood cells that arise from a progenitor cell for granulocytes, monocytes, erythrocytes, or platelets (the common myeloid progenitor, that is, CMP or CFU-GEMM), or in a narrower sense also often used, specifically from the lineage of the myeloblast (the myelocytes, monocytes, and their daughter types). Thus, although all blood cells, even lymphocytes, are normally born in the bone marrow in adults, myeloid cells in the narrowest sense of the term can be distinguished from lymphoid cells, that is, lymphocytes, which come from common lymphoid pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
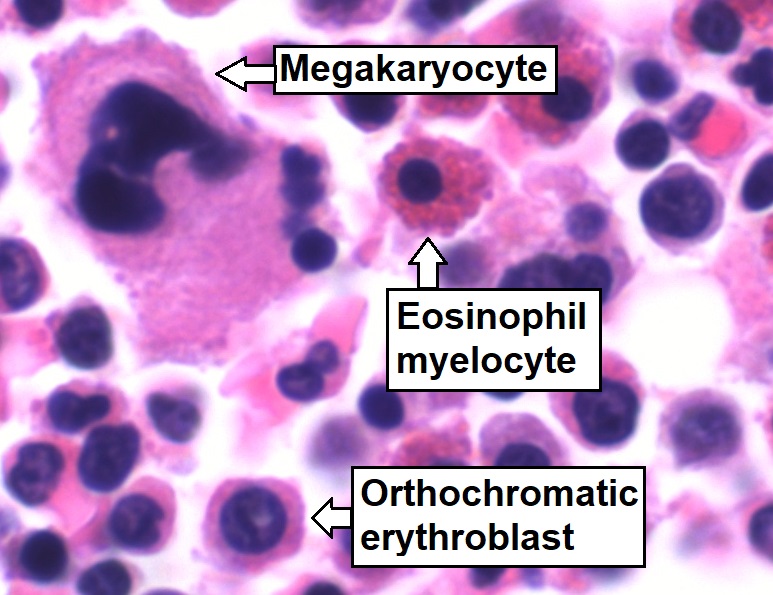
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Stimulating Factors
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) are secreted glycoproteins that bind to receptor proteins on the surfaces of hemopoietic stem cells, thereby activating intracellular signaling pathways that can cause the cells to proliferate and differentiate into a specific kind of blood cell (usually white blood cells. For red blood cell formation, see erythropoietin). They may be synthesized and administered exogenously. However, such molecules can at a latter stage be detected, since they differ slightly from the endogenous ones in, e.g., features of post-translational modification. Etymology The name "colony-stimulating factors" comes from the method by which they were discovered. Hematopoietic stem cells were cultured (see cell culture) on a so-called semisolid matrix, which prevents cells from moving around, so that, if a single cell starts proliferating, all of the cells derived from it will remain clustered around the spot in the matrix where the first cell was originally locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Cell
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exosome (vesicle)
Exosomes are membrane-bound extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are produced in the endosomal compartment of most eukaryotic cells. The multivesicular body (MVB) is an endosome with intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that bud inward into the endosomal lumen. If the MVB fuses with the cell surface (the plasma membrane), these ILVs are released as exosomes. In multicellular organisms, exosomes and other EVs were discovered in biological fluids including blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid. Importantly, exosomes were also identified within the tissue matrix, coined Matrix-Bound Nanovesicles (MBV). They are also released ''in vitro'' by cultured cells into their growth medium A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss ''Physcomitrella patens''. Differen .... Since the size of exosomes is limited by that of the parent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid Oxidation
Fatty is a derogatory term for someone who is Obesity, obese. It may refer also to: People * Mai Fatty, Gambian politician * Roscoe Arbuckle (1887–1933), American actor and comedian * Fatty Briody (1858–1903), American Major League Baseball player * Fatty D (April Fores), American pornographic actress * Bob Fothergill (1897–1938), American Major League Baseball outfielder * William Foulke (footballer) (1874–1916), English cricketer and footballer * Fatty George (1927–1982), Austrian jazz musician * Richard Lamb (1907–1974), Australian racing cyclist * Fatty Lawrence (1903–1976), college gridiron football player * W. T. McLain (1885–1938), college gridiron football player, lawyer, and politician * Charles H. Smith (American football), University of Michigan football player in 1893–1894 * Roland Taylor (1946–2017), retired American Basketball Association and National Basketball Association player * Paul Vautin (born 1959), Australian former rugby league football ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LOX1 (gene)
Linoleate 9S-lipoxygenase (, ''9-lipoxygenase'', ''9S-lipoxygenase'', ''linoleate 9-lipoxygenase'', ''LOX1 (gene)'', ''9S-LOX'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''linoleate:oxygen 9S-oxidoreductase''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : linoleate Linoleic acid (LA) is an organic compound with the formula COOH(CH2)7CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4CH3. Both alkene groups are ''cis''. It is a fatty acid sometimes denoted 18:2 (n-6) or 18:2 ''cis''-9,12. A linoleate is a salt or ester of this acid. L ... + O2 \rightleftharpoons (9S,10E,12Z)-9-hydroperoxy-10,12-octadecadienoate Linoleate 9S-lipoxygenase contains nonheme iron. References External links * {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no EC 1.13.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PD-L1
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CD274'' gene. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a 40kDa type 1 transmembrane protein that has been speculated to play a major role in suppressing the adaptive arm of immune systems during particular events such as pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune disease and other disease states such as hepatitis. Normally the adaptive immune system reacts to antigens that are associated with immune system activation by exogenous or endogenous danger signals. In turn, clonal expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells and/or CD4+ helper cells is propagated. The binding of PD-L1 to the inhibitory checkpoint molecule PD-1 transmits an inhibitory signal based on interaction with phosphatases (SHP-1 or SHP-2) via Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Switch Motif (ITSM). This reduces the proliferation of antigen-specific T-cells in lymph nod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively. In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The cofactor is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction, also with H+, forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD38
CD38 (cluster of differentiation 38), also known as cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase is a glycoprotein found on the surface of many immune cells (white blood cells), including CD4+, CD8+, B lymphocytes and natural killer cells. CD38 also functions in cell adhesion, signal transduction and calcium signaling. In humans, the CD38 protein is encoded by the CD38 gene which is located on chromosome 4. CD38 is a paralog of CD157, which is also located on chromosome 4 (4p15) in humans. History CD38 was first identified in 1980 as a surface marker (cluster of differentiation) of thymus cell lymphocytes. In 1992 it was additionally described as a surface marker on B cells, monocytes, and natural killer cells (NK cells). About the same time, CD38 was discovered to be not simply a marker of cell types, but an activator of B cells and T cells. In 1992 the enzymatic activity of CD38 was discovered, having the capacity to synthesize the calcium-releasing second messengers cyclic ADP-ribose (cA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |