|
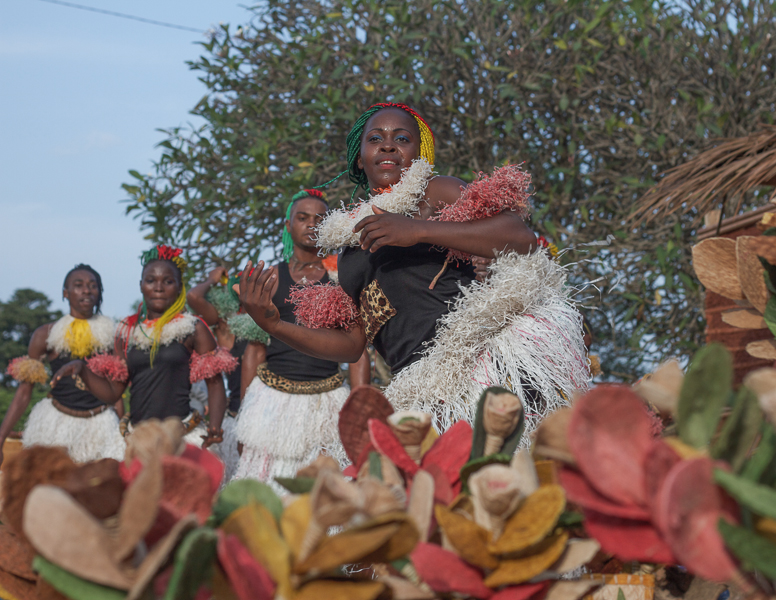
Mvet
The mvet is a stringed musical instrument, a type of stick zither, Hornbostel-Sachs (311) of the Fang people of Gabon, Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, São Tomé and Equatorial Guinea. Somewhat resembling the Mande kora, but larger and simpler, it consists of a tubular stick of palm-raffia or bamboo, between one and two metres long, with usually three calabash resonators. A central vertical bridge divides four or five gut or metal strings, played both sides of the bridge. The instrument is held horizontally on the chest to close or open the central resonator with a movement of the arms. It may be played solo or may accompany song or poetry that includes epics, battle-songs, ritual, philosophy and knowledge of the world. In the late twentieth century the mvet became a key instrument of bikutsi music. File:Mvet (MDMB 679).jpg, Mvet with multiple gourd resonators File:Musée africain de Gunsbach-Mvett.jpg file:GuitareTraditionelle.jpg See also *Bwiti *List of mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stick Zither
Bar zither is class of musical instruments (subset of zither) within the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system for a type of simple chordophone (stringed instrument), in which the body of the instrument is shaped like a bar. In the system, bar zithers are made up of musical bows and stick zithers. Musical bows have flexible ends, stick zithers are rigid or have only one flexed end. Bar zithers, whether musical bow or stick zithers, often have some form of resonator. Examples of resonators include the player's mouth, an attached gourd or an inflated balloon or bladder. According to Sachs,Sachs, Curt (1940). ''The History of Musical Instruments'', p.463. W. W. Nortan & Company, Inc. Instruments may be monochords (single stringed) or polychord (multiple stinged). They may also be idiochords (string made from the bar or stick) or heterchords (string made of separate substance from the bar or stick. File:Richard Nunns 22.jpg, Man playing a heterochord musical bow, using his m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Musical Instruments Of Cameroon
This article is a list of traditional musical instruments in Cameroon, based primarily on the research of Roger Blench (2009). Idiophones Idiophones of Cameroon include percussion instruments, untuned idiophones, tuned idiophones (xylophones), concussion instruments, and other instruments. Percussion *Slit gongs: historically used for long-distance communication, and often mimic tones in languages. Common throughout much of Africa, the tropical Americas, and Oceania. Called ''egyʉ̂k'' in Ejagham, and also played by the Oroko people and by Tunen speakers. Untuned idiophones *Struck plaques **Lithophones: played by the Mofu of northern Cameroon, and also in Central Nigeria and throughout the world. Women of the Noni and other nearby ethnic groups in Bui Division play flat lithophones. The Noni lithophone consists of a ''ncéw'' (large flat stone) struck by a pair of ''ncùy'' (smaller stones). **Struck iron plaque: a pair of sticks is used to strike a triangular plaque mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonator
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a resonator can be either electromagnetic or mechanical (including acoustic). Resonators are used to either generate waves of specific frequencies or to select specific frequencies from a signal. Musical instruments use acoustic resonators that produce sound waves of specific tones. Another example is quartz crystals used in electronic devices such as radio transmitters and quartz watches to produce oscillations of very precise frequency. A cavity resonator is one in which waves exist in a hollow space inside the device. In electronics and radio, microwave cavities consisting of hollow metal boxes are used in microwave transmitters, receivers and test equipment to control frequency, in place of the tuned circuits which are used at lower freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatoguinean Musical Instruments
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoriale, pt, link=no, República da Guiné Equatorial), *french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoriale * pt, link=no, República da Guiné Equatorial is a country on the west coast of Central Africa, with an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name evokes its location near both the Equator and the Gulf of Guinea. , the country had a population of 1,468,777. Equatorial Guinea consists of two parts, an insular and a mainland region. The insular region consists of the islands of Bioko (formerly ''Fernando Pó'') in the Gulf of Guinea and Annobón, a small volcanic island which is the only part of the country south of the equator. Bioko Island is the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea and is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West African Musical Instruments
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב maarav 'west' from עֶרֶב erev 'evening'. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigation (in a place where magnetic north is the same dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroonian Music
The music of the Cameroon includes diverse traditional and modern musical genres. The best-known contemporary genre is makossa, a popular style that has gained fans across Africa, and its related dance craze bikutsi. The pirogue sailors of Douala are known for a kind of singing called ngoso which has evolved into a kind of modern music accompanied by zanza, balafon, and various percussion instruments. Traditional music The ethnicities of Cameroon include an estimated 250 distinct ethnic groups in five regional-cultural divisions. An estimated 38% of the population are Western highlanders–Semi-Bantu or grassfielders including the Bamileke, Bamum, and many smaller Tikar groups in the northwest. 12% are coastal tropical forest peoples, including the Bassa, Duala, and many smaller groups in the southwest. The southern tropical forest peoples (18%) include the Beti-Pahuin and their sub-groups the Bulu and Fang, the Maka and Njem, as well as, the Baka pygmies. In the semi-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabonese Music
Gabon's music includes several folk styles and pop. Gabonese pop artist Patience Dabany, who now lives in the US, produces albums recorded in Los Angeles with a distinctively Gabonese element; they are popular throughout Francophone Africa. Other musicians include guitarists Georges Oyendze, La Rose Mbadou and Sylvain Avara, and the singer Oliver N'Goma. Imported rock and hip hop from the US and UK are popular in Gabon, as are rumba, makossa and soukous. National music The national anthem of Gabon is "La Concorde", written and composed by Georges Aleka Damas and adopted in 1960 upon independence. Traditional music Gabon's population, estimated at 1,640,286, of whom 42% are minors (July 2013 est.), include four major Bantu groupings; the Fang, the Punu, the Nzebi and the Obamba. Gabon, to the French ethnographer Barabe, "is to Africa what Tibet is to Asia, the spiritual center of religious initiations", due to the sacred music of the Bwiti, the dominant religious doctrine o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinnari Vina
The ''kinnari vina'' (Sanskrit: किन्नरी वीणा) is a historical veena, a tube zither with gourds attached to act as resonators and frets. It was played in India into the late 19th century and was documented by two European artists. The instrument dates back into medieval times (documented in the 13th century) and possibly as far back as 500 C.E. It is closely related to the Alapini Vina and Eka-tantri Vina, the instruments having coexisted in medieval times. Along with the ''alapini vina'' and ''eka-tantri vina'', the ''kinnari vina'' was mentioned by Śārṅgadeva in his Sangita Ratnakara (written 1210 - 1247 C.E.) By the late 19th century, the ''kinnari vina'' survived as a "folk instrument," in South Kanara and Mysore, India, and in the modern ''bīn'' or ''rudra vina''. The instrument shares its name with the kinnara, Buddhist and Hindu mythological creatures that are pictured playing stick zithers or tube zithers. The kinnari vina is traditionally carved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bwiti
Bwiti is a spiritual discipline of the forest-dwelling Punu people and Mitsogo peoples of Gabon (where it is recognized as one of three official religions) and by the Fang people of Gabon and Cameroon. Modern Bwiti incorporates animism, ancestor worship, and in some cases, Christianity, into a syncretistic belief system. Bwiti practitioners use the psychedelic, dissociative root bark of the ''Tabernanthe iboga'' plant, specially cultivated for the religion, to promote radical spiritual growth, to stabilize community and family structure, to meet religious requirements, and to resolve pathological problems. The root bark has been consumed for hundreds of years in a Bwiti rite of passage ceremony, as well as in initiation rites and acts of healing. The experience yields complex visions and insights anticipated to be valuable to the initiate and the chapel. Liturgy Intoxicants in liturgy Taking Iboga brings both open and closed-eye visions which can be made stronger by darkness, ambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bikutsi
Bikutsi is a musical genre from Cameroon. It developed from the traditional styles of the Beti, or Ewondo, people, who live around the city of Yaoundé. It was popular in the middle of the 20th century in West Africa. It is primarily dance music. Etymology The word 'bikutsi' literally means 'beat the earth' or 'let's beat the earth' (''bi''- indicates a plural, -''kut''- means 'to beat' and -''chi'' means 'earth'.) The name indicates a dance that is accompanied by stomping the feet on the ground. Description Bikutsi is characterised by an intense rhythm (3+3, with a strong "two" feel), though it is occasionally and its tempo is usually quarternote. it is played at all sorts of Beti gatherings, including parties, funerals and weddings. Beti gatherings fall into two major categories: * Ekang phase: the time when imaginary, mythological and spiritual issues are discussed * Bikutsi phase: when real-life issues are discussed A double sided harp with calabash amplification call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calabash
Calabash (; ''Lagenaria siceraria''), also known as bottle gourd, white-flowered gourd, long melon, birdhouse gourd, New Guinea bean, Tasmania bean, and opo squash, is a vine grown for its fruit. It can be either harvested young to be consumed as a vegetable, or harvested mature to be dried and used as a utensil, container, or a musical instrument. When it is fresh, the fruit has a light green smooth skin and white flesh. Calabash fruits have a variety of shapes: they can be huge and rounded, small and bottle-shaped, or slim and serpentine, and they can grow to be over a metre long. Rounder varieties are typically called calabash gourds. The gourd was one of the world's first cultivated plants grown not primarily for food, but for use as containers. The bottle gourd may have been carried from Asia to Africa, Europe, and the Americas in the course of human migration, or by seeds floating across the oceans inside the gourd. It has been proven to have been globally domesticated (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(3042092768).jpg)

