|
Mushulatubbee
Mushulatubbee ( Choctaw ', "Determined to Kill") (born c. 1750–1770, died c. 1838) was the chief of the Choctaw ''Okla Tannap'' ("Lower Towns"), one of the three major Choctaw divisions during the early 19th century. When the Principal Chief Greenwood LeFlore stayed in Mississippi at the time of removal, Mushulatubbee was elected as principal chief, leading the tribe to Indian Territory. In 1812 he had led his warriors to assist General Andrew Jackson in the war against the Creek Red Sticks, known as the Creek Wars. In December 1824 Mushulatubbee was one of three principal chiefs leading a Choctaw delegation to Washington to seek help against encroaching European-American settlers. Pushmataha and Apuckshunubbee were the other chiefs; Apuckshunubbee, age 80, died before they reached Washington, and Pushmataha died of smallpox in the capital soon after their meeting with the government. On 26 September 1830, together with the Principal Chief Greenwood LeFlore and others, Mush ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apuckshunubbee
Apuckshunubbee (c. 1740 – October 18, 1824) was one of three principal chiefs of the Choctaw Native American tribe in the early nineteenth century, from before 1800. He led the western or ''Okla Falaya'' ("Long People") District of the Choctaw, of which the eastern edge ran roughly southeast from modern Winston County to Lauderdale County, then roughly southwest to Scott County, then roughly south-southeast to the western edge of Perry County. His contemporaries were Pushmataha and Moshulatubbee, who respectively led the southern district ''Okla Hannali'' ("Six Towns People") and the north-eastern district ''Okla Tannap'' ("People on the Other Side"). During the early 1800s, Apuckshunubbee and the other two division chiefs signed several treaties with the United States, ceding land to settlers in the hope of ending their encroachment on Choctaw territory. On his way to Washington, DC in 1824 with the other two division chiefs and a Choctaw delegation to meet with US offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushmataha
Pushmataha (c. 1764 – December 24, 1824; also spelled Pooshawattaha, Pooshamallaha, or Poosha Matthaw), the "Indian General", was one of the three regional chiefs of the major divisions of the Choctaw in the 19th century. Many historians considered him the "greatest of all Choctaw chiefs". Pushmataha was highly regarded among Native Americans, Europeans, and white Americans, for his skill and cunning in both war and diplomacy. Rejecting the offers of alliance and reconquest proffered by Tecumseh, Pushmataha led the Choctaw to fight on the side of the United States in the War of 1812. He negotiated several treaties with the United States. In 1824, he traveled to Washington to petition the Federal government against further cessions of Choctaw land; he met with John C. Calhoun and Marquis de Lafayette, and his portrait was painted by Charles Bird King. He died in the capital city and was buried with full military honors in the Congressional Cemetery in Washington, D.C. Name T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Catlin
George Catlin (July 26, 1796 – December 23, 1872) was an American adventurer, lawyer, painter, author, and traveler, who specialized in portraits of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans in the Old West. Traveling to the Western United States, American West five times during the 1830s, Catlin wrote about and painted portraits that depicted the life of the Plains Indians. His early work included engravings, drawn from nature, of sites along the route of the Erie Canal in New York State. Several of his renderings were published in one of the first printed books to use lithography, Cadwallader D. Colden's ''Memoir, Prepared at the Request of a Committee of the Common Council of the City of New York, and Presented to the Mayor of the City, at the Celebration of the Completion of the New York Canals'', published in 1825, with early images of the Buffalo, New York, City of Buffalo. Background and education George Catlin was born in 1796 in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwood LeFlore
Greenwood LeFlore or Greenwood Le Fleur (June 3, 1800 – August 31, 1865) served as the elected Principal Chief of the Choctaw in 1830 before removal. Before that, the nation was governed by three district chiefs and a council of chiefs. A wealthy and regionally influential Choctaw of mixed-race, who belonged to the Choctaw elite due to his mother's rank, LeFlore had many connections in state and federal government. In 1830 LeFlore led other chiefs in signing the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek, which ceded the remaining Choctaw lands in Mississippi to the US government and agreed to removal to Indian Territory. It also provided that Choctaw who chose to stay in Mississippi would have reserved lands, but the United States government failed to follow through on this provision. While many leaders argued that removal was inevitable, others opposed the treaty and made death threats against LeFlore. Ousted by the tribal council in a coup, he stayed in Mississippi, where he settled in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes: the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, and Jena Band of Choctaw Indians in Louisiana. The Choctaw were first noted by Europeans in French written records of 1675. Their mother mound is Nanih Waiya, a great earthwork platform mound located in central-east Mississippi. Early Spanish explorers of the mid-16th century in the Southeast encountered ancestral Mississippian culture villages and chiefs. The Choctaw coalesced as a people in the 17th century and developed at least three distinct political and geographical divisions: eastern, western, and southern. These different groups sometimes created distinct, independent alliances with nearby European powers. These i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
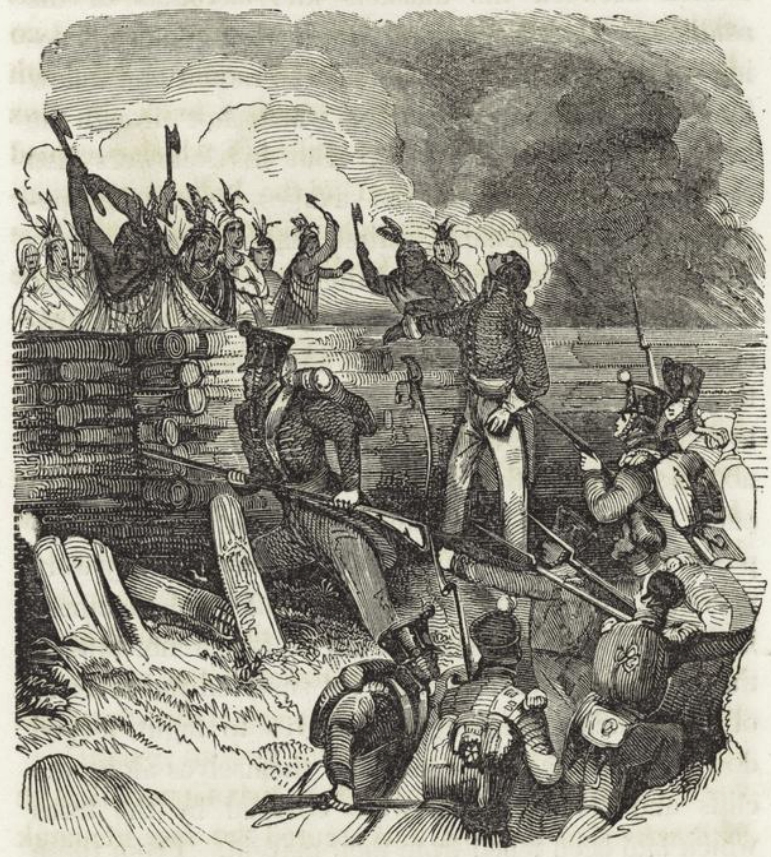
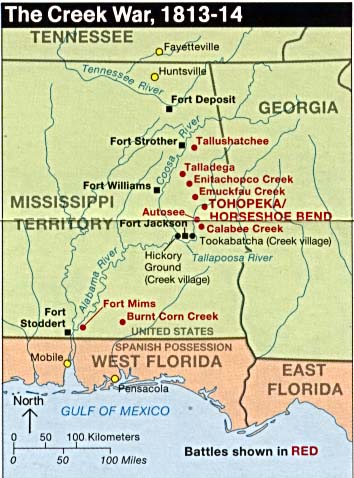
Creek Wars
The Creek War (1813–1814), also known as the Red Stick War and the Creek Civil War, was a regional war between opposing Indigenous American Creek factions, European empires and the United States, taking place largely in modern-day Alabama and along the Gulf Coast. The major conflicts of the war took place between state militia units and the "Red Stick" Creeks. The United States government formed an alliance with the Choctaw Nation and Cherokee Nation (the traditional enemies of the Creeks), along with the remaining Creeks to put the rebellion down. According to historian John K. Mahon, the Creek War "was as much a civil war among Creeks as between red and white, and it pointed up the separation of Creeks and Seminoles". The war was also part of the centuries-long American Indian Wars. It is usually considered part of the War of 1812 because it was influenced by Tecumseh's War in the Old Northwest, was concurrent with the American-British portion of the war and involved m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creek War
The Creek War (1813–1814), also known as the Red Stick War and the Creek Civil War, was a regional war between opposing Indigenous American Creek factions, European empires and the United States, taking place largely in modern-day Alabama and along the Gulf Coast. The major conflicts of the war took place between state militia units and the "Red Stick" Creeks. The United States government formed an alliance with the Choctaw Nation and Cherokee Nation (the traditional enemies of the Creeks), along with the remaining Creeks to put the rebellion down. According to historian John K. Mahon, the Creek War "was as much a civil war among Creeks as between red and white, and it pointed up the separation of Creeks and Seminoles". The war was also part of the centuries-long American Indian Wars. It is usually considered part of the War of 1812 because it was influenced by Tecumseh's War in the Old Northwest, was concurrent with the American-British portion of the war and involved m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
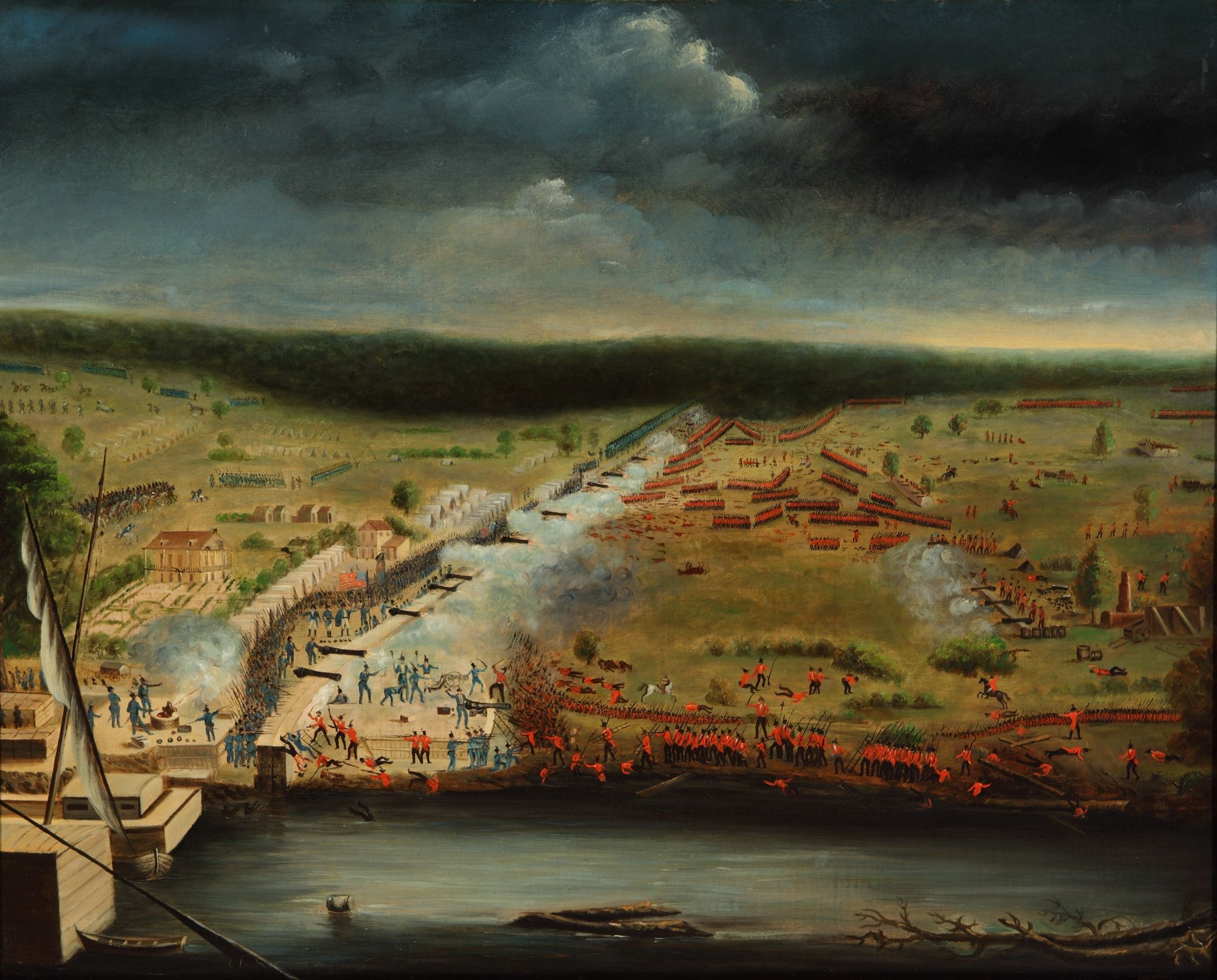
Battle Of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815 between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of the French Quarter of New Orleans, in the current suburb of Chalmette, Louisiana. The battle was the climax of the five-month Gulf Campaign (September 1814 to February 1815) by Britain to try to take New Orleans, West Florida, and possibly Louisiana Territory which began at the First Battle of Fort Bowyer. Britain started the New Orleans campaign on December 14, 1814, at the Battle of Lake Borgne and numerous skirmishes and artillery duels happened in the weeks leading up to the final battle. The battle took place 15 days after the signing of the Treaty of Ghent, which formally ended the War of 1812, on December 24, 1814, though it would not be ratified by the United States (and therefore did not take effect) until February 16, 1815, as news of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscogee
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern WoodlandsTranscribed documents Sequoyah Research Center and the American Native Press Archives in the . Their original homelands are in what now comprises southern , much of , western |
Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean and the Western United States, with the Midwestern and Northeastern United States to its north and the Gulf of Mexico and Mexico to its south. Historically, the South was defined as all states south of the 18th century Mason–Dixon line, the Ohio River, and 36°30′ parallel.The South . ''Britannica.com''. Retrieved June 5, 2021. Within the South are different subregions, such as the |
Tecumseh
Tecumseh ( ; October 5, 1813) was a Shawnee chief and warrior who promoted resistance to the expansion of the United States onto Native American lands. A persuasive orator, Tecumseh traveled widely, forming a Native American confederacy and promoting intertribal unity. Even though his efforts to unite Native Americans ended with his death in the War of 1812, he became an iconic folk hero in American, Indigenous, and Canadian popular history. Tecumseh was born in what is now Ohio, at a time when the far-flung Shawnees were reuniting in their Ohio Country homeland. During his childhood, the Shawnees lost territory to the expanding American colonies in a series of border conflicts. Tecumseh's father was killed in battle against American colonists in 1774. Tecumseh was thereafter mentored by his older brother Cheeseekau, a noted war chief who died fighting Americans in 1792. As a young war leader, Tecumseh joined Shawnee Chief Blue Jacket's armed struggle against further Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tecumseh's War
Tecumseh's War or Tecumseh's Rebellion was a conflict between the United States and Tecumseh's Confederacy, led by the Shawnee leader Tecumseh in the Indiana Territory. Although the war is often considered to have climaxed with William Henry Harrison's victory at the Battle of Tippecanoe in 1811, Tecumseh's War essentially continued into the War of 1812 and is frequently considered a part of that larger struggle. The war lasted for two more years, until 1813, when Tecumseh and his second-in-command, Roundhead, died fighting Harrison's Army of the Northwest at the Battle of the Thames in Upper Canada, near present-day Chatham, Ontario, and his confederacy disintegrated. Tecumseh's War is viewed by some academic historians as the final conflict of a longer-term military struggle for control of the Great Lakes region of North America, encompassing a number of wars over several generations, referred to as the Sixty Years' War. Background The two principal adversaries in the confli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |