|
Muscina Stabulans
''Muscina stabulans'' (formerly ''Curtonevra stabulans''), commonly known as the false stable fly, is a fly from the family Muscidae. Description As an adult, ''Muscina stabulans'' has partially reddish-brown legs, four characteristic dark stripes along the thorax region, and a pale spot above the thorax. These flies average 8 millimeters (0.3 inches) in length."False Stable Fly." North Carolina IPM. 20 Mar. 2009 The abdomen is either entirely black or black with red sides. Its head ranges in color from a dark-grey to a whitish hue."Fly Control In Confined Livestock And Poultry Production - Novartis Animal Health Inc." The Control Of Flies On Livestock And Poultry Farms - Novartis Animal Health Inc. 20 Mar. 2009 Circular spiracular plates can be found separated by about one plate's width in the posterior area. Larvae are dullish-white in colour, 6–7 mm long and 1–1.5 mm wide. They consist of 11 segments, with all but the last having a belt of small, well-de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Fredrik Fallén
Carl Fredrik Fallén (born 22 September 1764 in Kristinehamn – 26 August 1830) was a Swedish botanist and entomologist. Fallén taught at the Lund University. He wrote ''Diptera Sueciae'' (1814–27). Fallén described very many species of Diptera and Hymenoptera"ITIS" Taxon authorFallen/ref> He was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1810. Publications May be incomplete *''Monographia cimicum Sveciae''. Hafniae Copenhagen 124 p. (180*''Specimen entomologicum novam Diptera disponendi methodum exhibens''. Berlingianus, Lundae Lund 26 p. (1810) *Försök att bestämma de i Sverige funne Flugarter, som kunna föras till Slägtet ''Tachina''. ''K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handl.'' (2) 31: 253–87. (181*''Specimen Novam Hymenoptera Disponendi Methodum Exhibens''. Dissertation. Berling, Lund. pp. 1–41. 1 pl.(1813*Beskrifning öfver några i Sverige funna Vattenflugor (Hydromyzides). ''K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handl.'' (3) 1: 240–57. (181*181 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musca Domestica
The housefly (''Musca domestica'') is a fly of the suborder Cyclorrhapha. It is believed to have evolved in the Cenozoic Era, possibly in the Middle East, and has spread all over the world as a commensal of humans. It is the most common fly species found in houses. Adults are gray to black, with four dark, longitudinal lines on the thorax, slightly hairy bodies, and a single pair of membranous wings. They have red eyes, set farther apart in the slightly larger female. The female housefly usually mates only once and stores the sperm for later use. She lays batches of about 100 eggs on decaying organic matter such as food waste, carrion, or feces. These soon hatch into legless white larvae, known as maggots. After two to five days of development, these metamorphose into reddish-brown pupae, about long. Adult flies normally live for two to four weeks, but can hibernate during the winter. The adults feed on a variety of liquid or semi-liquid substances, as well as solid materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pondicherry
Pondicherry (), now known as Puducherry ( French: Pondichéry ʊdʊˈtʃɛɹi(listen), on-dicherry, is the capital and the most populous city of the Union Territory of Puducherry in India. The city is in the Puducherry district on the southeast coast of India and is surrounded by Bay of Bengal to the east and the state of Tamil Nadu, with which it shares most of its culture, heritage, and language. History Puducherry, formerly known as Pondicherry, gained its significance as “The French Riviera of the East” after the advent of the French colonialization in India. Puducherry is the Tamil interpretation of “new town” and mainly derived from “Poduke”, the name of the marketplace as the “Port town” for Roman trading in 1st century as mentioned in ‘The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea’. The settlement was once an abode of many learned scholars as evidently versed in the Vedas, hence also known as Vedapuri. The history of Puducherry can broadly be classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maggot
A maggot is the larva of a fly (order Diptera); it is applied in particular to the larvae of Brachycera flies, such as houseflies, cheese flies, and blowflies, rather than larvae of the Nematocera, such as mosquitoes and crane flies. Entomology "Maggot" is not a technical term and should not be taken as such; in many standard textbooks of entomology, it does not appear in the index at all. In many non-technical texts, the term is used for insect larvae in general. Other sources have coined their own definitions; for example: "The term applies to a grub when all trace of limbs has disappeared" and "Applied to the footless larvae of Diptera".Smith, John. BExplanation of terms used in entomology Brooklyn Entomological Society, 1906. Additionally, in ''Flies: The Natural History and Diversity of Diptera'', the author claims maggots "are larvae of higher Brachycera ( Cyclorrhapha)." Maggot-like fly larvae are of significance in ecology and medicine; among other roles, var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relatively small amount of metabolic waste products such as bacterially altered bilirubin, and dead epithelial cells from the lining of the gut. Feces are discharged through the anus or cloaca during defecation. Feces can be used as fertilizer or soil conditioner in agriculture. They can also be burned as fuel or dried and used for construction. Some medicinal uses have been found. In the case of human feces, fecal transplants or fecal bacteriotherapy are in use. Urine and feces together are called excreta. Skatole is the principal compound responsible for the unpleasant smell of feces. Characteristics The distinctive odor of feces is due to skatole, and thiols (sulfur-containing compounds), as well as amines and carboxylic acids. Skatole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
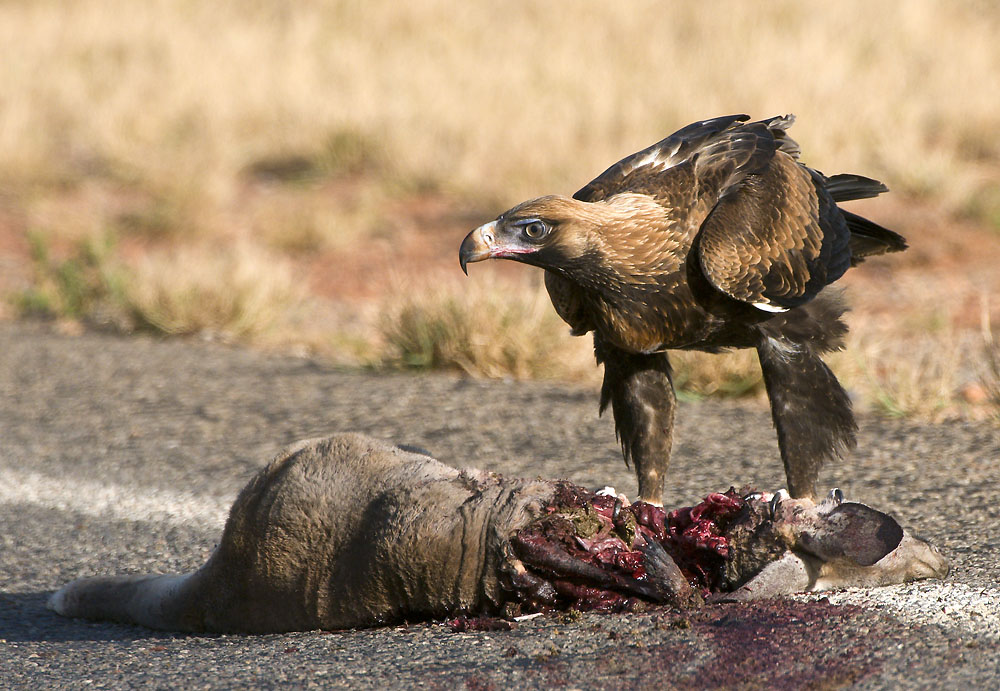
Carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh. Overview Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, condors, hawks, eagles, hyenas, Virginia opossum, Tasmanian devils, coyotes and Komodo dragons. Many invertebrates, such as the carrion and burying beetles, as well as maggots of calliphorid flies (such as one of the most important species in '' Calliphora vomitoria'') and flesh-flies, also eat carrion, playing an important role in recycling nitrogen and carbon in animal remains. Carrion begins to decay at the moment of the animal's death, and it will increasingly attract insects and breed bacteria. Not long after the animal has died, its body will begin to exude a foul odor caused by the presence of bacteria and the emission of cadaverine and putrescine. Some plants and fungi smell like decomposing carrion and attract insects that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decomposition
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is essential for recycling the finite matter that occupies physical space in the biosphere. Bodies of living organisms begin to decompose shortly after death. Animals, such as worms, also help decompose the organic materials. Organisms that do this are known as decomposers or detritivores. Although no two organisms decompose in the same way, they all undergo the same sequential stages of decomposition. The science which studies decomposition is generally referred to as ''taphonomy'' from the Greek word ''taphos'', meaning tomb. Decomposition can also be a gradual process for organisms that have extended periods of dormancy. One can differentiate abiotic decomposition from biotic decomposition (biodegradation). The former means "the degradation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucosal
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
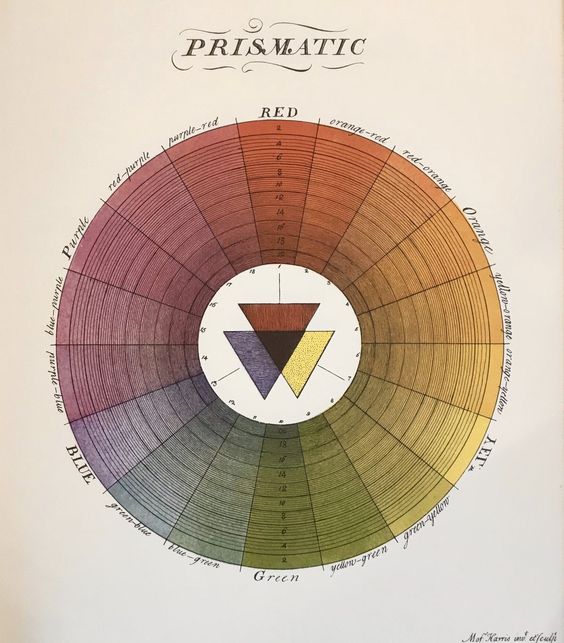
Moses Harris
Moses Harris (15 April 1730 – 1787) was an English entomologist and engraver. Life and work Harris was encouraged in entomology from a young age by his uncle, a member of the Society of the Aurelians. In 1762 he became secretary of a second Society of Aurelians. He was a skilled artist, displaying some of his insect drawings at the Royal Academy in 1785. He drew and engraved illustrations for books including Dru Drury's ''Illustrations of Natural History'' (3 volumes, 1770–1782) and John Coakley Lettsom's ''The Naturalist's and Traveller's Companion'' (1772). Colour theory In "The Natural System of Colours" published in 1766, Harris discussed the multitude of colours that can be created using three "grand or principle" colours: red, yellow and blue. As a naturalist and an engraver, Harris focussed on the relationships between colours and how they are coded and created. He explained how three colours can be íntermixed, tinted and shaded to create 660 colours "materially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)