|
Munc-13
Munc-13 (an acronym for mammalian uncoordinated-13) is a protein which complexes with RIM and likely comprises part of cellular structure which anchors synaptic vesicle In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulse ...s. Its activation by DAG seems to be important for maintaining high rate of synaptic release during prolonged repetitive stimulation. References Proteins Secretory vesicles Neurophysiology {{Protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
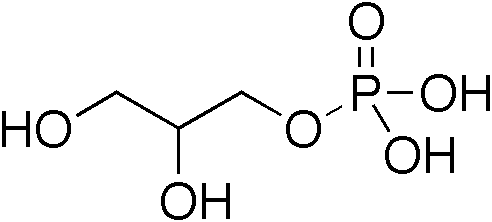
Diglyceride
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oils or animal fats. Food additive Diglycerides, generally in a mix with monoglycerides (E471), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acronym
An acronym is a word or name formed from the initial components of a longer name or phrase. Acronyms are usually formed from the initial letters of words, as in ''NATO'' (''North Atlantic Treaty Organization''), but sometimes use syllables, as in ''Benelux'' (short for ''Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg''). They can also be a mixture, as in ''radar'' (''Radio Detection And Ranging''). Acronyms can be pronounced as words, like ''NASA'' and ''UNESCO''; as individual letters, like ''FBI'', ''TNT'', and ''ATM''; or as both letters and words, like '' JPEG'' (pronounced ') and ''IUPAC''. Some are not universally pronounced one way or the other and it depends on the speaker's preference or the context in which it is being used, such as '' SQL'' (either "sequel" or "ess-cue-el"). The broader sense of ''acronym''—the meaning of which includes terms pronounced as letters—is sometimes criticized, but it is the term's original meaning and is in common use. Dictionary and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Vesicle
In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell. The area in the axon that holds groups of vesicles is an axon terminal or "terminal bouton". Up to 130 vesicles can be released per bouton over a ten-minute period of stimulation at 0.2 Hz. In the visual cortex of the human brain, synaptic vesicles have an average diameter of 39.5 nanometers (nm) with a standard deviation of 5.1 nm. Structure Synaptic vesicles are relatively simple because only a limited number of proteins fit into a sphere of 40 nm diameter. Purified vesicles have a protein:phospholipid ratio of 1:3 with a lipid composition of 40% phosphatidylcholine, 32% phosphatidylethanolamine, 12% phosphatidylserine, 5% phosphatidylinositol, and 10% chole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
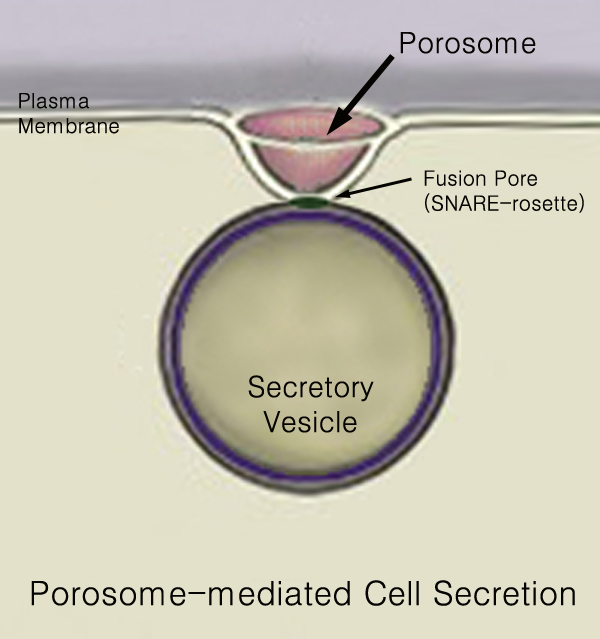
Secretory Vesicles
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |