|
Multiway Data Analysis
Multiway data analysis is a method of analyzing large data sets by representing a collection of observations as a multiway array, \in^. The proper choice of data organization into ''(C+1)''-way array, and analysis techniques can reveal patterns in the underlying data undetected by other methods. History The study of multiway data analysis was first formalized as the result of a conference held in 1988. The result of this conference was the first text specifically addressed to this field, Coppi and Bolasco's ''Multiway Data Analysis''. At that time, the application areas for multiway analysis included statistics, econometrics and psychometrics. In recent years, applications have expanded to include chemometrics, agriculture, social network analysis and the food industry. Composition of multiway data analysis Multiway data Multiway data analysts use the term ''way'' to refer to the number sources of data variation while reserving the word ''mode'' for the methods or model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application for computation, organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets were developed as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The program operates on data entered in cells of a table. Each cell may contain either numeric or text data, or the results of formulas that automatically calculate and display a value based on the contents of other cells. The term ''spreadsheet'' may also refer to one such electronic document. Spreadsheet users can adjust any stored value and observe the effects on calculated values. This makes the spreadsheet useful for "what-if" analysis since many cases can be rapidly investigated without manual recalculation. Modern spreadsheet software can have multiple interacting sheets and can display data either as text and numerals or in graphical form. Besides performing basic arithmetic and mathematical functions, modern spreadsheets provide built-in functions for common financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
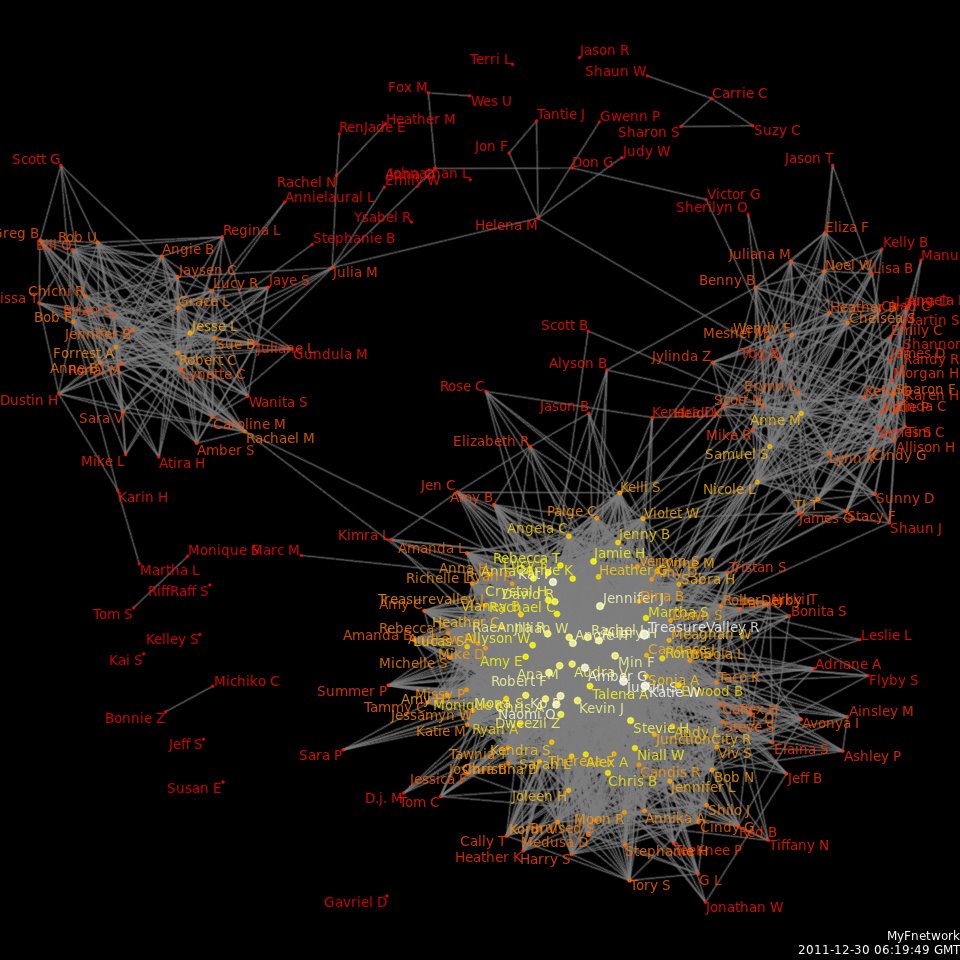
Social Network Analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of ''nodes'' (individual actors, people, or things within the network) and the ''ties'', ''edges'', or ''links'' (relationships or interactions) that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, memes spread, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, social networks, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through '' sociograms'' in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attribute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Analysis
Process analysis is a form of technical writing and expository writing "designed to convey to the reader how a change takes place through a series of stages". While the traditional process analysis and a set of instructions are both organized chronologically, the reader of a process analysis is typically interested in understanding the chronological components of a system that operates largely without the reader's direct actions (such as how the body digests an apple), while the reader of a set of instructions intends to use the instructions in order to accomplish a specific, limited task (such as how to bake an apple pie). By contrast, the reader of a mechanism description is more interested in an object in space (such as the form and nutritional value of a particular kind of apple). References {{Reflist See also * Process mining Process mining is a family of techniques relating the fields of data science and process management to support the analysis of operational proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the science, scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a Multidisciplinary approach, multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and Mathematical Modeling, mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the Biology, biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular biology, molecular and cell biology, cellular studies of indivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroanalytical Chemistry
Electroanalytical methods are a class of techniques in analytical chemistry which study an analyte by measuring the potential (volts) and/or current (amperes) in an electrochemical cell containing the analyte. These methods can be broken down into several categories depending on which aspects of the cell are controlled and which are measured. The four main categories are potentiometry (the difference in electrode potentials is measured), amperometry (electric current is the analytical signal), coulometry (charge passed during a certain time is recorded), and voltammetry (the cell's current is measured while actively altering the cell's potential). Potentiometry Potentiometry passively measures the potential of a solution between two electrodes, affecting the solution very little in the process. One electrode is called the reference electrode and has a constant potential, while the other one is an indicator electrode whose potential changes with the sample's composition. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Vision
Computer vision is an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the human visual system can do. Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the forms of decisions. Understanding in this context means the transformation of visual images (the input of the retina) into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory. The scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute () (RPI) is a private research university in Troy, New York, with an additional campus in Hartford, Connecticut. A third campus in Groton, Connecticut closed in 2018. RPI was established in 1824 by Stephen Van Rensselaer and Amos Eaton for the "application of science to the common purposes of life" and is the oldest technological university in the English-speaking world and the Western Hemisphere. Built on a hillside, RPI's campus overlooks the city of Troy and the Hudson River, and is a blend of traditional and modern architecture. The institute operates an on‑campus business incubator and the Rensselaer Technology Park. RPI is organized into six main schools which contain 37 departments, with emphasis on science and technology. It is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities: Very High Research Activity" and many of its engineering programs are highly ranked. As of 2017, RPI's faculty and alumni included 6 members of the National I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (mathematics And Physics)
In mathematics and physics, vector is a term that refers colloquially to some quantities that cannot be expressed by a single number (a scalar), or to elements of some vector spaces. Historically, vectors were introduced in geometry and physics (typically in mechanics) for quantities that have both a magnitude and a direction, such as displacements, forces and velocity. Such quantities are represented by geometric vectors in the same way as distances, masses and time are represented by real numbers. The term ''vector'' is also used, in some contexts, for tuples, which are finite sequences of numbers of a fixed length. Both geometric vectors and tuples can be added and scaled, and these vector operations led to the concept of a vector space, which is a set equipped with a vector addition and a scalar multiplication that satisfy some axioms generalizing the main properties of operations on the above sorts of vectors. A vector space formed by geometric vectors is called a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Amsterdam
The University of Amsterdam (abbreviated as UvA, nl, Universiteit van Amsterdam) is a public research university located in Amsterdam, Netherlands. The UvA is one of two large, publicly funded research universities in the city, the other being the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam (VU). Established in 1632 by municipal authorities and later renamed for the city of Amsterdam, the University of Amsterdam is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, third-oldest university in the Netherlands. It is one of the largest research universities in Europe with 31,186 students, 4,794 staff, 1,340 PhD students and an annual budget of €600 million. It is the List of universities in the Netherlands, largest university in the Netherlands by enrollment. The main campus is located in Amsterdam-Centrum, central Amsterdam, with a few faculties located in adjacent Government of Amsterdam, boroughs. The university is organised into seven faculties: Humanities, Social science, Social an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Industry
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditional, family-run activities that are highly labor-intensive, to large, capital-intensive and highly mechanized industrial processes. Many food industries depend almost entirely on local agriculture, produce, or fishing. It is challenging to find an inclusive way to cover all aspects of food production and sale. The UK Food Standards Agency describes it as "the whole food industry – from farming and food production, packaging and distribution, to retail and catering." The Economic Research Service of the USDA uses the term ''food system'' to describe the same thing, stating: "The U.S. food system is a complex network of farmers and the industries that link to them. Those links include makers of farm equipment and chemicals as well as fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(cropped).png)



