|
Mugunghwa Train
The Mugunghwa-ho is a class of train operated by Korail, main railway operator of South Korea. Mugunghwa trains are Korail's slowest tier of trains stopping at a number of towns and villages, and operating over a number of lines that are not served by other trains. Journey times are generally well over double that of KTX trains and 25% longer than express trains. In 1980, new express train, named 우등 (Udeung, literally meaning Premium), was introduced. Soon it was renamed as Mugunghwa-ho, which was a name of an express train operated in the 1960s. Since train classes below Mugunghwa had been retired, thus Mugunghwa trains are now the cheapest class of trains to operate cross-country. Along rural lines such as the Gyeongbuk Line, they remain the only class of passenger train operating. They (and in some cases the Tonggeun) are the only trains to stop at many stations not served by Saemaeul-ho or KTX trains. Mugunghwa are built to accommodate large numbers of standing passen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Rail
Regional rail, also known as local trains and stopping trains, are passenger rail services that operate between towns and cities. These trains operate with more stops over shorter distances than inter-city rail, but fewer stops and faster service than commuter rail. Regional rail services operate beyond the limits of urban areas, and either connect similarly-sized smaller cities and towns, or cities and surrounding towns, outside or at the outer rim of a suburban belt. Regional rail normally operates with an even service load throughout the day, although slightly increased services may be provided during rush-hour. The service is less oriented around bringing commuters to the urban centers, although this may generate part of the traffic on some systems. Other regional rail services operate between two large urban areas but make many intermediate stops. In North America, "regional rail" is not recognized as a service classification between "commuter rail" and "inter-city rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
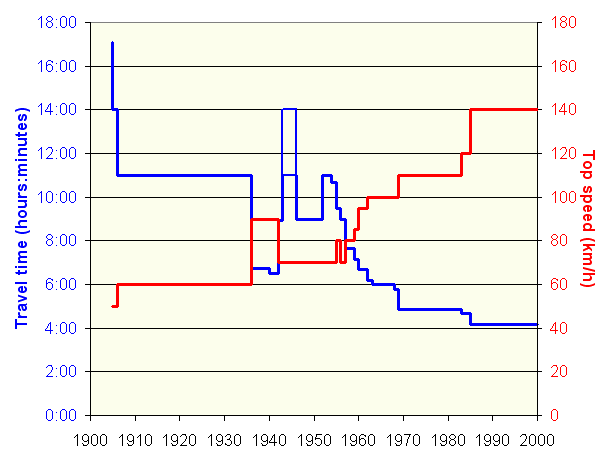
Gyeongbu Line
The Gyeongbu Line (''Gyeongbuseon'') is a railway line in South Korea and is considered to be the most important and one of the oldest ones in the country. It was constructed in 1905, connecting Seoul with Busan via Suwon, Daejeon, and Daegu. It is by far the most heavily travelled rail line in South Korea. All types of Korea Train Express, high-speed, express, local, and freight trains provide frequent service along its entire length. History In 1894–1895, the Empire of Japan and Qing Dynasty, Qing China fought the First Sino-Japanese War for influence over Korea. Following the war, Japan competed with the Russian Empire's railway expansion in Northeast Asia, which led it to seek the right from the Korean Empire to build a railway from Busan to Keijō. This railway line was intended by Japan to solidify its strategic positions against Russia, which it would later go to Russo-Japanese War, war. Surveying began in 1896, and in spite of local protests, the Korean Empire gav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Coaches Of South Korea
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles ( rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transportation In South Korea
Transportation in South Korea is provided by extensive networks of railways, highways, bus routes, ferry services and air routes that traverse the country. South Korea is the third country in the world to operate a maglev train, which is an automatically run people mover at Incheon International Airport. History Development of modern infrastructure began with the first Five-Year Development Plan (1962–66), which included the construction of 275 kilometers of railways and several small highway projects. Construction of the Gyeongbu Expressway, which connects the two major cities of Seoul and Busan, was completed on 7 July 1970. The 1970s saw increased commitment to infrastructure investments. The third Five-Year Development Plan (1972–76) added the development of airports, seaports. The Subway system was built in Seoul, the highway network was expanded by 487 km and major port projects were started in Pohang, Ulsan, Masan, Incheon and Busan. The railroad network experie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In South Korea
Rail transport in South Korea is a part of the transport network in South Korea and an important mode of the conveyance of people and goods, though railways play a secondary role compared to the road network. The network consists of of standard-gauge lines connecting all major cities with the exception of Jeju City on Jeju Island, which does not have railways; of the network, are double-tracked and are electrified. In 2018, rails carried 11.5 percent of all traffic in South Korea134.8million passengers and 30.9milliontonnes of freightwith roads carrying 88.3 percent. Passenger and freight services are primarily provided by the Korea Railroad Corporation, branded as Korail, a state-owned enterprise under the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, although some rail lines and services, including high-speed intercity rails and metropolitan rapid transit, are operated by private companies. The Korea National Railway (formerly the Korea Rail Network Authority), anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daegu Line
The Daegu Line is a railway line in South Korea. The line connects Gacheon station on the Gyeongbu Line in Daegu to Yeongcheon on the Jungang Line. The line is served by frequent passenger trains between Seoul (via the Gyeongbu Line), Dongdaegu, and Gyeongju, Pohang and Ulsan (via the Jungang and Donghae Nambu Lines). History The first section of the Daegu Line was opened in 1917, between Daegu and Hayang. The line was extended to the Haksan station in Pohang until 1919 as follows: A branch was opened from Gyeongju to Ulsan on October 25, 1921. The sections from Gyeongju to Pohang and Ulsan were integrated into the Donghae Nambu Line on December 16, 1935. On 1 July 1938 the reconstruction of the section Daegu–Yeongcheon was complete with the standard gauge. On 1 December 1938 the section Yeongcheon–Gyeongju became a part of the Gyeonggyeong Nambu Line (the southern part of the Jungang Line), which was established on April 1, 1942. At the same time the present s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donghae Line
The Donghae Line is a railway line connecting Busanjin station to Yeongdeok in South Korea. The literal meaning of its name, the "East Sea Line," reflects its position along the nation's East coast. It merged with the Donghae Nambu Line on December 30, 2016, and will merge with the Donghae Bukbu Line. Stations Major stations along the line include (in order): * Bujeon station, terminal station of the line and terminus of the Bujeon Line *Sinhaeundae station, a popular resort beach in eastern Busan * Gijang station * Taehwagang station (formerly Ulsan), major industrial city and terminus of the Jangsaengpo and Ulsanhang Lines * Singyeongju station, historic city * Pohang station, seaport and industrial city *BEXCO station, where the G-Star gaming event is held Services KTX Plans foresee direct KTX high-speed train service from Seoul to Pohang and Ulsan after the completion of the upgrades. From 2015, direct KTX trains are to reach Pohang from Seoul in 1 hour 50 minutes, cut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janghang Line
The Janghang Line is a railway line serving South Chungcheong Province in South Korea. The line connects Cheonan (on the Gyeongbu Line) to the railway junction city of Iksan. The Janghang Line is served by frequent Saemaeul-ho and Mugunghwa-ho passenger train services between Seoul and Iksan. There is also a link from Asan station to the KTX network at Cheonan-Asan station. History The original Janghang Line was opened along its full length between Cheonan and Janghang by the Chosen Gyeongnam Railway on June 1, 1922. Upgrade The entire Janghang Line is being electrified and double-tracked and upgraded for higher speeds with a straighter alignment. Work started in 1997 from Cheonan. By the end of 2008, the new alignment was in service from Cheonan via Asan and Hongseong to Sinseong, from Jupo to Nampo, and from Ganchi to Janghang, and electrification was put in service on the first 19.4 km between Cheonan and Sinchang, after Asan, on December 15, 2008. The 17.1&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taebaek Line
Taebaek Line is a single-track electrified railway mainline connecting Jecheon station to Baeksan station in South Korea. At its two ends, the Taebaek Line connects to the Jungang Line and Yeongdong Line. The line was originally two spur lines, which were built across difficult mountainous terrain in stages, before a connection was built. The line includes the steepest section of the South Korean network, a short parallel line that is operated as a second track on the section includes South Korea's longest spiral tunnel. The centerpiece of the last-built section west of Taebaek, is a tunnel that was the longest in South Korea at the time of its construction, and Chujeon Station at the eastern end of the tunnel is the highest altitude in South Korea at . In passenger traffic, the line is served by cross-country passenger trains connecting the capital Seoul with Korea's east coast. In freight traffic, while coal transport declined, the line carries significant cement transport. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeongdong Line
The Yeongdong Line is a line of Korail. It connects Yeongju in North Gyeongsang Province with Gangneung in Gangwon Province. From Yeongju, it crosses the Taebaek Mountains and reaches the Sea of Japan (East Sea) at Donghae, thence proceeding north to Gangneung. At Yeongju, the line connects with the Gyeongbuk and Jungang Lines. Some trains travel directly from one to the other, so that it is possible to travel directly from Seoul or Busan to Gangneung by rail. History Construction The first section of the line (Mukho Port–Dogye) was opened by the privately owned Samcheok Railway on 31 July 1940. The line was named Cheoram Line, which ran from Mukho, a port on Korea's east coast that became part of Donghae in 1980, to Cheoram in the Taebaek Mountains, to develop three coal fields. Between Simpo-ri and Tong-ri stations, the great height difference was scaled by a steep double-track railway. Freight railcars going up and down were connected to the same cable, passenge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyeongjeon Line
The Gyeongjeon Line (''Gyeongjeonseon'') is a railway line serving South Gyeongsang and South Jeolla Provinces in South Korea. It covers a total of 300.6 km, from Samnangjin Station in Miryang, South Gyeongsang, to Gwangju Songjeong Station in Gwangju, South Jeolla. History An east-west railway along Korea's southern shore was long seen as a strategic route, but it took a number of attempts to complete the line. The first section of the line was opened as a branch from the newly built Gyeongbu Line at Samnangjin to Masan in May 1905, which was named the Masan Line. On December 1, 1923, the Jinju Line opened from Masan to Jinju, extending the line to . A branch from Changwon on the ''Masan Line'' to Jinhae, the Jinhae Line, opened on November 11, 1926. Meanwhile, construction started in the opposite direction from Songjeong-ri (today Gwangju·Songjeong) on the Honam Line, the other end of the future Gyeongjeon Line, with the first to Gwangju opened in July 1922. The Gwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |