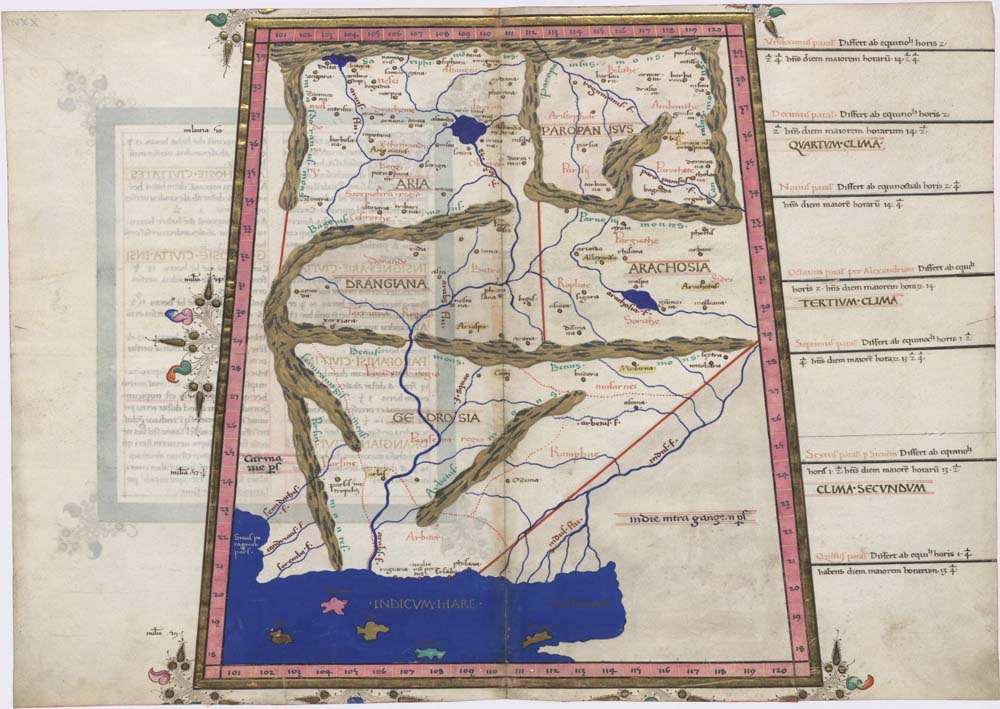
|
Mozaffarid
The Muzaffarid dynasty ( fa, مظفریان) was a Muslim dynasty which came to power in Iran following the breakup of the Ilkhanate in the 14th century. At their zenith, they ruled a kingdom comprising Iranian Azerbaijan, Central Persia, and Persian Iraq. The Muzaffarids were known for their support of Arabic literature. Shah Shoja was a poet and wrote in both Arabic and Persian and was said to be capable of memorizing eight verses of Arabic poetry after hearing them read once. While the Muzaffarid ruler of Kirman, Shah Yahya, commissioned the scholar Junyad bin Mahmud Al-Umari to compile an anthology of Arabic poetry and prose for him Rise to power The Muzaffarids were originally from Arabia and had settled in Khorasan from the beginning of Caliphal rule there. They have been described as an Arab, Iranian, and Persian dynasty.http://referenceworks.brillonline.com/entries/encyclopaedia-of-islam-1/muzaffarids-SIM_4963, ”a Persian dynasty. Their ancestors came from Arabia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meybod
Meybod ( fa, Meybod) is a city in and capital of Meybod County, Yazd Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 58,295, in 15,703 families. Meybod is a major desert city in Yazd Province, Iran, with a population of about 75,000 making it the second major city in Yazd. History It is an ancient city that goes back to the pre-Islamic era and, hence, is the home to many ancient points of interests. The Historical City of Maybod is part of the Tentative List, in order to qualify for inclusion in the World Heritage List. It was the capital of Iran during the period of the Mozaffarids. The Mozaffarid kingdom originated from Meybod where the first king, Mubariz al-Din Muhammad, was born. One of the oldest castles in Iran is Narin ghaleh in Meybod, which dates back to the Achaemenid and Sassanid periods. Chaparkhaneh and Karvansaraye Abbasi are some other examples of the historical buildings from Safavid era. The town was sacked and massacred by the Mongols and later th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Shoja Mozaffari
Shah Shoja ( fa, شاه شجاع, Shāh Shojā, lit. "the brave shah"), was the ruler of the Mozaffarids from 1358 to 1384. He was the son and successor of Mubariz al-Din Muhammad. During the lengthy reign of Shah Shoja, his kingdom reached its zenith of power, stretching from Balochistan to Arran. Early life Shah Shoja was born in 10 March 1333—he was the son of the Muzaffarid ruler Mubariz al-Din Muhammad and a woman named Khatun Qotlogh Beg, better known as Makhdum Shah, daughter of the Mongol ruler Qutb al-Din Shah Jahan. After Mubariz al-Din Muhammad's conquest of Kerman in 1341, he organized a marriage between Shah Shoja and a daughter of one of the tribal Mongol chieftains who roamed the region. Shah Shoja later prevented his father from having the tomb of the prominent Persian poet Saadi Shirazi demolished, whom Mubariz al-Din Muhammad had condemned for his poems on religious factors. In 1358, Shah Shoja blinded and imprisoned his cruel father, and thus succeeded him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mubariz Al-Din Muhammad
Mubariz al-Din Muhammad (1301-1363) ( fa, مبارز الدین محمد), was the founder of the Muzaffarid dynasty, ruling from 1314 to 1358. He was a Persian of Yemeni origins, which settled in Khurasan during the Islamic conquest. He was the son of Sharaf al-Din Muzaffar, a servant of the Ilkhanids and on his father's death in 1314 Mubariz inherited his father's offices. Mubariz al-Din lived at the court of Ilkhanid ruler Öljaitü until the latter's death. After Öljaitü's death, Mubariz al-Din left for Maibud, and in 1319, he captured Yazd from Hajji Shah ibn Yusuf Shah, the Atabeg of Yazd, thus putting an end to the Atabeg rule over Yazd. Sometime later, the people of Sistan rebelled against the Ilkhanids, and Mubariz al-Din was ordered to subdue the province, which he did. However, the people of Sistan shortly rebelled, and Mubariz al-Din was once again to forced to fight them; he reportedly fought the rebels in 21 battles until the province was finally subdued. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Mansur (Muzaffarid)
Shah Mansur was the last of the Muzaffarid rulers of Southern Iran. He ruled from Isfahan and was killed by the forces of Timur in 29 March 1393.TÜRKLER ANSİKLOPEDİSİ CİLT 8 Life Mansur was the brother of Shah Yahya and Shah Hosein. His uncle was Shah Shoja, with whom he fought against in battle. With support from the Jalayirid Sultanate, Mansur established himself as an independent ruler in Shushtar. Mansur's grave is located in the eastern part of Shiraz, in an area known as ''Gowd-e-Shahzadeh'' (Prince Mansur's Tomb). References Sources *Jackson, Peter. "Muzaffarids." '' Encyclopaedia of Islam, Volume VII (Mif-Naz).'' New ed. 1993. *M. Ismail Marcinkowski, ''Persian Historiography and Geography: Bertold Spuler on Major Works Produced in Iran, the Caucasus, Central Asia, India and Early Ottoman Turkey, with a foreword by Professor Clifford Edmund Bosworth'', member of the British Academy The British Academy is the United Kingdom's national academy for the hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerman
Kerman ( fa, كرمان, Kermân ; also romanization of Persian, romanized as Kermun and Karmana), known in ancient times as the satrapy of Carmania, is the capital city of Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2011 census, its population was 821,394, in 221,389 households, making it the 10th most populous city of Iran. It is the largest and most developed city in Kerman Province and one of the most important cities in the southeast of Iran. It is also one of the largest cities of Iran in terms of area. Kerman is famous for its long history and strong cultural heritage. The city is home to many historic mosques and Zoroastrian fire temples. Kerman became the capital city of Iranian dynasties several times during its history. It is located on a large, flat plain, 800 km (500 mi) south-east of Tehran, the capital of Iran. History Kerman was founded as a defensive outpost, with the name Veh-Ardashir, by Ardashir I, founder of the Sasanian Empire, in the 3rd century AD. After th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Il-Khan
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm, officially known as ''Iranzamin'' (), was ruled by the Mongols, Mongol House of Hulagu. Hulagu Khan, the son of Tolui and grandson of Genghis Khan, inherited the Middle Eastern part of the Mongol Empire after his brother Möngke Khan died in 1260. Its core territory lies in what is now part of the countries of Iran, Azerbaijan, and Turkey. At its greatest extent, the Ilkhanate also included parts of modern Iraq, Syria, Armenia, Georgia (country), Georgia, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Pakistan, part of modern Dagestan, and part of modern Tajikistan. Later Ilkhanate rulers, beginning with Ghazan in 1295, converted to Islam. In the 1330s, the Ilkhanate was ravaged by the Black Death. Its last khan Abu Sa'id (Ilkhanid dynasty), Abu Sa'id died in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Sa'id (Ilkhanid Dynasty)
Abu Sa'id Bahadur Khan (June 2, 1305 – December 1, 1335) (Persian, Arabic: ), also spelt Abusaid Bahador Khan, Abu Sa'id Behauder ( mn, , ''Busayid Baghatur Khan'', ''Бусайд баатар хаан'' / ''Busaid baatar khaan'', in modern Mongolian), was the ninth ruler (c. 1316 – 1335) of the Ilkhanate, a division of the Mongol Empire that encompassed the present day countries of Iran, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Armenia, as well as portions of Iraq, Turkey, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. Early life He was born on 2 June 1305, near Ujan, Tabriz to Öljaitü and Hajji Khatun. He became his father's heir after deaths of his elder brothers. He was assigned to govern Khorasan and Mazandaran in 1315 with Uyghur noble Amir Sevinch as his guardian. Reign He was brought back to Soltaniyeh by Sevinch in December, 1316. But his coronation was delayed until April, May, July or August 1317 due to a conflict between Chupan and Sevinch. Abu Said employed Rashid-al-Din Hamadani and T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kartid
The Kart dynasty, also known as the Kartids ( fa, آل کرت), was a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Tajik origin closely related to the Ghurids, that ruled over a large part of Khorasan during the 13th and 14th centuries. Ruling from their capital at Herat and central Khorasan in the Bamyan, they were at first subordinates of ''Sultan Abul-Fateh'' Ghiyāṣ-ud-din Muhammad bin Sām, Sultan of the Ghurid Empire, to whom they were related,M.J. Gohari, ''Taliban: Ascent to Power'', (Oxford University Press, 2000), 4. and then as vassal princes within the Mongol Empire.C.E. Bosworth, ''The New Islamic Dynasties'', (Columbia University Press, 1996), 263. Upon the fragmentation of the Ilkhanate in 1335, Mu'izz-uddin Husayn ibn Ghiyath-uddin worked to expand his principality. The death of Husayn b. Ghiyath-uddin in 1370 and the invasion of Timur in 1381, ended the Kart dynasty's ambitions. Vassals of the Ghurid dynasty The Karts trace their lineage to a Tajuddin Uthman Marghini, whose bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injuids
The House of Inju (Injuids, Injus, or Inju'ids) was an Iranian dynasty of Persian origin that came to rule over the cities of Shiraz and Isfahan during the 14th century. Its members became de facto independent rulers following the breakup of the Ilkhanate until their defeat in 1357. Before the breakup of the Ilkhanate The Injuids gained control of parts of Iran, mostly Fars, in 1304 at the beginning of the reign of the Ilkhan Öljeitü. The Ilkhan had given Sharaf al-Din Mahmud Shah control of the ''injü'' (or ''inji''; the Mongol word for the royal estates). Sharaf al-Din was reportedly descended from ' Abd-Allah Ansari, an 11th-century mystic of Herat. His son, Amir Ghiyas al-Din Kai-Khusrau, assisted another family, the Muzaffarids, in their takeover of Yazd. By 1325 Sharaf al-Din had gained nearly an absolute grip on the region. His power displeased Öljeitü's successor Abu Sa'id, who ordered Sharaf al-Din removed and sent a Sheikh Hussein ibn Juban to replace him. Kai-K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safēd Kōh'') in the fertile valley of the Hari River in the western part of the country. An ancient civilization on the Silk Road between the Middle East, Central and South Asia, it serves as a regional hub in the country's west. Herat dates back to Avestan times and was traditionally known for its wine. The city has a number of historic sites, including the Herat Citadel and the Musalla Complex. During the Middle Ages Herat became one of the important cities of Khorasan, as it was known as the ''Pearl of Khorasan''. After the conquest of Tamerlane, the city became an important center of intellectual and artistic life in the Islamic world. Under the rule of Shah Rukh the city served as the focal point of the Timurid Renaissance, whose glor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
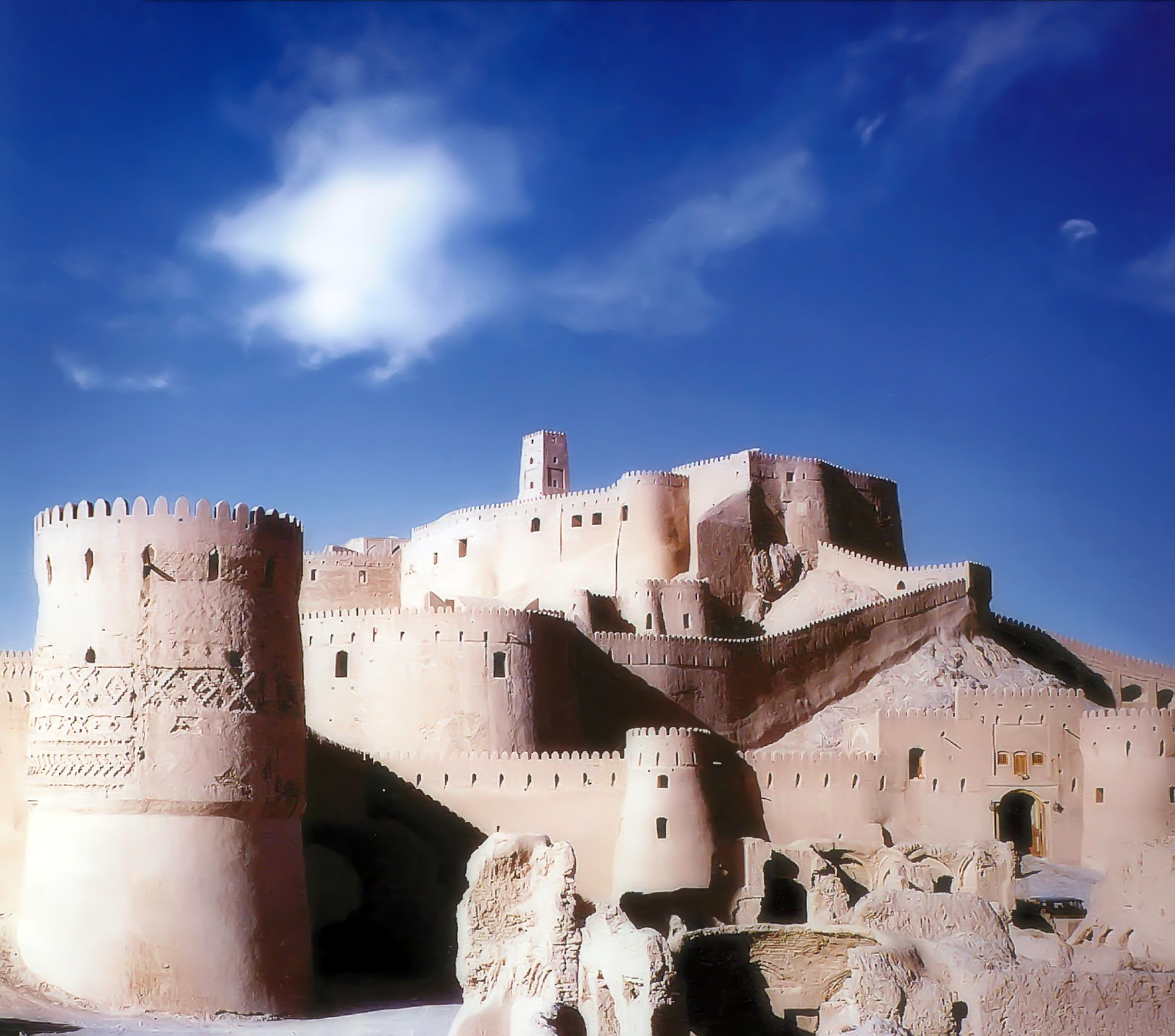
Bam, Iran
Bam ( fa, بم) is a city and capital of Bam County, Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 73,823, in 19,572 families. The modern Iranian city of Bam surrounds the Bam citadel. Before the 2003 earthquake the official population count of the city was roughly 43,000. There are various opinions about the date and reasons for the foundation of the citadel. Economically and commercially, Bam occupied a very important place in the region and was famous for its textiles and clothes. Ibn Hawqal (943–977), the Arab traveller and geographer, wrote of Bam in his book ''Surat-ul-'ard'' (''The Earth-figure''): :''Over there they weave excellent, beautiful and long-lasting cotton cloths which are sent to places all over the world There they also make excellent clothes, each of which costs around 30 dinars; these are sold in Khorasan, Iraq and Egypt.'' History The ancient citadel of Arg-é Bam has a history dating back around 2,000 years ago, to the Parth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |