|
Mount Olympus (Euboea)
Mount Olympus ( el, Όλυμπος, Ólympos) is a mountain in the east central part of the island of Euboea, Greece. Its maximum elevation is 1,172 m. It is not the highest mountain of Euboea, that is 1,743 m high Dirfi, 16 km to the north. Olympus is 10 km north of Amarynthos, 11 km northeast of Eretria and 24 km east of the city of Chalcis Chalcis ( ; Ancient Greek & Katharevousa: , ) or Chalkida, also spelled Halkida (Modern Greek: , ), is the chief town of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from .... There are forests on the northern slopes while most of the mountain range is covered with grassland and bushes. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Olympus Mountains of Central Greece Landforms of Euboea (regional unit) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euboea
Evia (, ; el, Εύβοια ; grc, Εὔβοια ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (Μάκρις) and ''Doliche'' (Δολίχη) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'', ''Aonia'' and ''Abantis'' from the tribes inhabiting it. Its ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands. The country consists of nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilization, being the birthplace of Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirfi
Dirfi ( el, Δίρφη, older form Δίρφυς - ''Dirfys'') is a mountain in the central part of the island of Euboea, Greece. At 1,743 m elevation, it is the highest mountain of Euboea. The Dirfi gave its name to the municipal unit Dirfys. Its summit is 4 km west of Stropones, 5 km north of Steni Dirfyos and 28 km northeast of the city of Chalcis. There are forests on the lower slopes while most of the mountain is covered with grassland and in winter with permafrost and snow. Gallery File:Trekking path (Dirfi).JPG, A part of the trekking path located on Dirfi mountain. File:Dirfi river.JPG, A tiny river flowing by the Dirfi mountain. File:Dirfi Mountain.JPG, One of the peaks of Dirfi mountain. See also * List of European ultra prominent peaks This is a list of all the mountains in Europe with ultra-prominent peaks with topographic prominence greater than . The column "Col" denotes the highest elevation to which one must descend from a peak in order to reach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarynthos
Amarynthos (Greek: Αμάρυνθος, , also called Βάθεια ''Váthia''), is a coastal town and a former municipality in Euboea, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Eretria, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 109.909 km2. In 2011 its population was 3,672 for the town and 6,723 for the municipal unit. The Amarynthos is 8 km east of Eretria, 27 km southeast of Chalcis, 63 km northwest of Karystos and 10 km north of Kalamos, across the gulf. The Greek National Road 44 ( Thebes - Chalcis - Karystos) passes through the town. History The area of Amarynthos, along with the region of Eretria, has a long and rich history. Many scientists place Eretria of the Mycenaean period in the location of the present town of Amarynthos. The archaeological artifacts testify a permanent settlement in this location since the Late Neolithic period, around 3000 BC, which was one of the most important H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
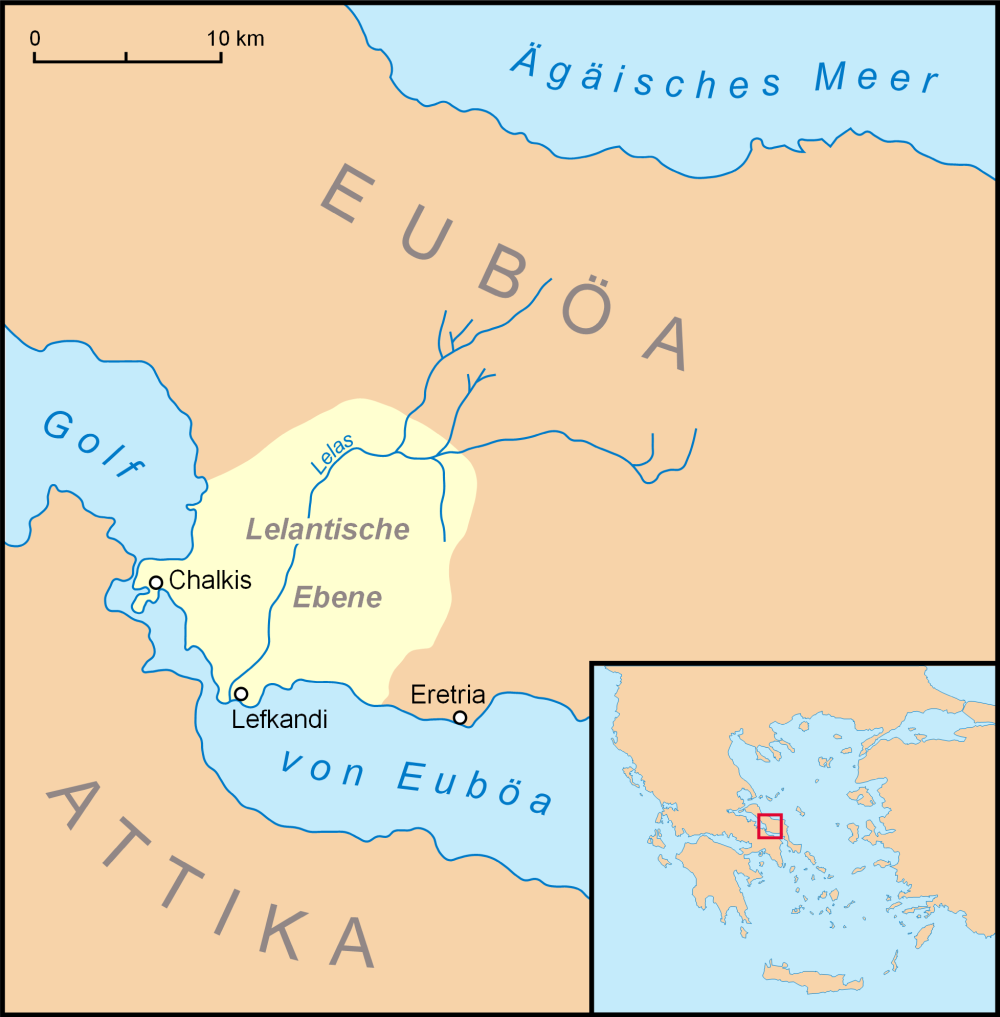
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcis
Chalcis ( ; Ancient Greek & Katharevousa: , ) or Chalkida, also spelled Halkida (Modern Greek: , ), is the chief town of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from antiquity and is derived from the Greek χαλκός (copper, bronze), though there is no trace of any mines in the area. In the Late Middle Ages, it was known as Negropont(e), an Italian name that has also been applied to the entire island of Euboea. History Ancient Greece The earliest recorded mention of Chalcis is in the Iliad, where it is mentioned in the same line as its rival Eretria. It is also documented that the ships set for the Trojan War gathered at Aulis, the south bank of the strait near the city. Chamber tombs at Trypa and Vromousa dated to the Mycenaean period were excavated by Papavasiliou in 1910. In the 8th and 7th centuries BC, colonists from Chalcis founded thirty townships on the peninsula of Chalcidice and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Central Greece
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |