|
Mother Ship (aviation)
A mother ship, mothership or mother-ship is a large vehicle that leads, serves, or carries other smaller vehicles. A mother ship may be a maritime ship, aircraft, or spacecraft. Examples include bombers converted to carry experimental aircraft to altitudes where they can conduct their research (such as the B-52 carrying the X-15), or ships that carry small submarines to an area of ocean to be explored (such as the Atlantis II carrying the Alvin). A mother ship may also be used to recover smaller craft, or go its own way after releasing them. A smaller vessel serving or caring for ''larger'' craft is usually called a tender. Etymology In many Asian languages, such as Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Indonesian, the word ''mothership'' (, ja, 母艦, ko, 모함, id, Kapal induk, literally "mother" + "(war)ship") typically refers to an aircraft carrier, which is translated as "aircraft/aviation mothership" (, ja, 航空母艦, ko, 항공모함, ms, Kapal induk pesawat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-52B With X43
B5, B05, B-5 may refer to: Biology * ATC code B05 (''Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions''), a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System * Cytochrome ''b''5, ubiquitous electron transport hemoproteins ** Cytochrome b5, type A, a human microsomal cytochrome b5 * HLA-B5, an HLA-B serotype * Pantothenic acid (a.k.a. vitamin B5), a water-soluble vitamin * Procyanidin B5, a B type proanthocyanidin Entertainment * Alekhine's Defence (ECO code B5), a chess opening beginning with the moves e4 Nf6 * B5 (band), an R&B boy band ** ''B5'' (album), B5's self-titled debut album * ''Babylon 5'', an American science fiction television series Transport * Amadeus (airline) (IATA code: B5), an airline based in Germany (1996–2004) * B5 and B5 DOHC, models of the Mazda B engine series * B-5, the manufacturer's model number for the Blackburn Baffin biplane * B5 platform, the series designator for Audi A4 from 1994–2001 * Bundesstraße 5, a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Language
Korean ( South Korean: , ''hangugeo''; North Korean: , ''chosŏnmal'') is the native language for about 80 million people, mostly of Korean descent. It is the official and national language of both North Korea and South Korea (geographically Korea), but over the past years of political division, the two Koreas have developed some noticeable vocabulary differences. Beyond Korea, the language is recognised as a minority language in parts of China, namely Jilin Province, and specifically Yanbian Prefecture and Changbai County. It is also spoken by Sakhalin Koreans in parts of Sakhalin, the Russian island just north of Japan, and by the in parts of Central Asia. The language has a few extinct relatives which—along with the Jeju language (Jejuan) of Jeju Island and Korean itself—form the compact Koreanic language family. Even so, Jejuan and Korean are not mutually intelligible with each other. The linguistic homeland of Korean is suggested to be somewhere in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
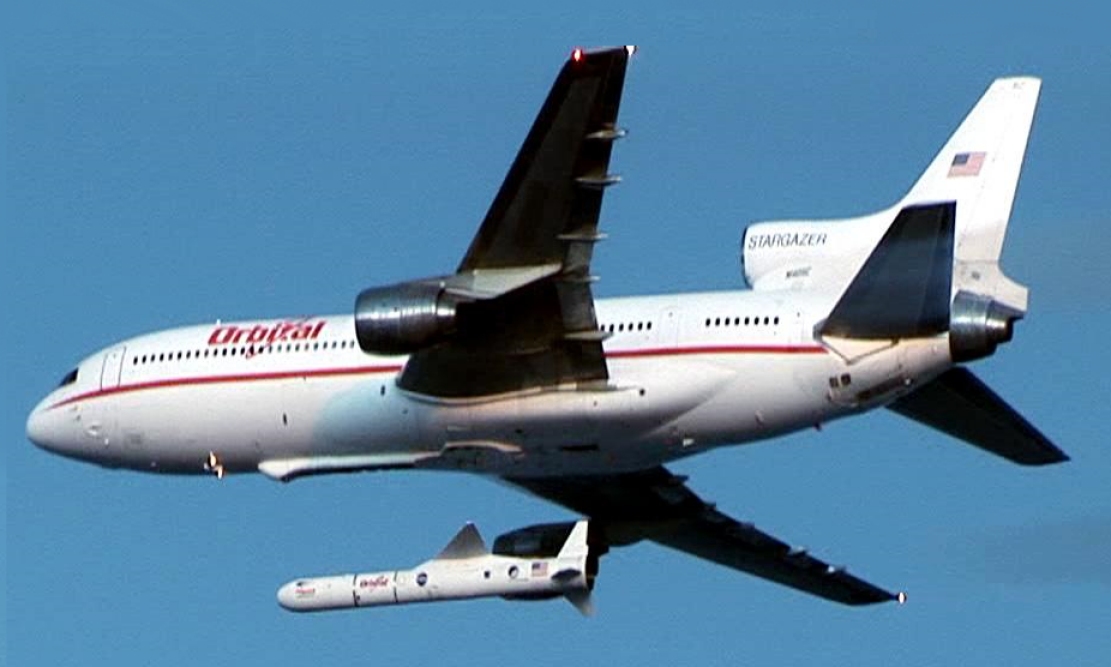
Composite Aircraft
A composite aircraft is made up of multiple ''component'' craft. It takes off and flies initially as a single aircraft, with the components able to separate in flight and continue as independent aircraft.Harper (1937) Typically the larger aircraft acts as a ''carrier aircraft'' or ''mother ship'', with the smaller sometimes called a ''parasite'' or ''jockey'' craft. The first composite aircraft flew in 1916, during World War I, when the British launched a Bristol Scout from a Felixstowe Porte Baby flying boat. Between the World Wars, American experiments with airship/biplane composites led to the construction of two airborne aircraft carriers, while the British Short Mayo seaplane composite demonstrated successful transatlantic mail delivery. During the Second World War some composites saw operational use including the Mistel ("mistletoe"), the larger unmanned component of a composite aircraft configuration developed in Germany during the later stages of World War II, in effect a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite Aircraft
A parasite aircraft is a component of a composite aircraft which is carried aloft and air launched by a larger carrier aircraft or mother ship to support the primary mission of the carrier. The carrier craft may or may not be able to later recover the parasite during flight. The first parasite aircraft flew in 1916, when the British launched a Bristol Scout from a Felixstowe Porte Baby flying boat. The idea eventually developed into jet bombers carrying fully capable parasite fighters. With the advent of long-range fighters equipped with air-to-air missiles, and aerial refueling, parasite fighters fell out of use. Parasite fighters Until the middle of the 20th century there was military interest in parasite fighters – fighter aircraft intended to be carried into a combat zone by a larger aircraft, such as a bomber. If the bomber were threatened, the parasite would be released to defend it. Parasite fighters have never been highly successful and have seldom been used in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Launch
Air launching is the practice of releasing a rocket, missile, parasite aircraft or other aircraft payload from a mother ship or launch aircraft. The payload craft or missile is often tucked under the wing of the larger mother ship and then "dropped" while in flight. It may also be stored within a bomb bay, beneath the main fuselage or even on the back of the carrier aircraft, as in the case of the D-21 drone. Air launching provides several advantages over ground launching, giving the smaller craft an altitude and range boost, while saving it the weight of the fuel and equipment needed to take off on its own. History One of the earliest uses of air launching used an airship as a carrier and docking station for biplane parasite fighters. These planes would connect to their mothership through a trapeze-like rig, mounted to the top of the upper wing, that attached to a hook dangling from the bottom of the dirigible above. Fighters could be both launched and retrieved this way, gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airborne Aircraft Carrier
An airborne aircraft carrier is a type of mother ship aircraft which can carry, launch, retrieve and support other smaller parasite aircraft. The only dedicated examples to have been built were airships, although existing heavier-than-air aircraft have been modified for use in similar roles, and airborne aircraft carriers of various types appear in fiction, such as ''Cloudbase'' in Gerry Anderson's ''Captain Scarlet and the Mysterons'', the Helicarrier from Marvel Comics, the ''Valiant'' from series 3 of ''Doctor Who,'' and an unnamed one in ''Sky Captain and the World of Tomorrow''. Airship projects In July 1917, experiments were made with aircraft slung under HM Airship No. 23, in hopes that they could defend the airship. First an unmanned, then a manned, Sopwith Camel fighters were launched successfully. The experiment was successfully completed with two other manned Camels. The British Imperial Airship Scheme of 1924 initially envisaged an airship that could carry five fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. Etymology The word ''aviation'' was coined by the French writer and former naval officer Gabriel La Landelle in 1863. He derived the term from the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
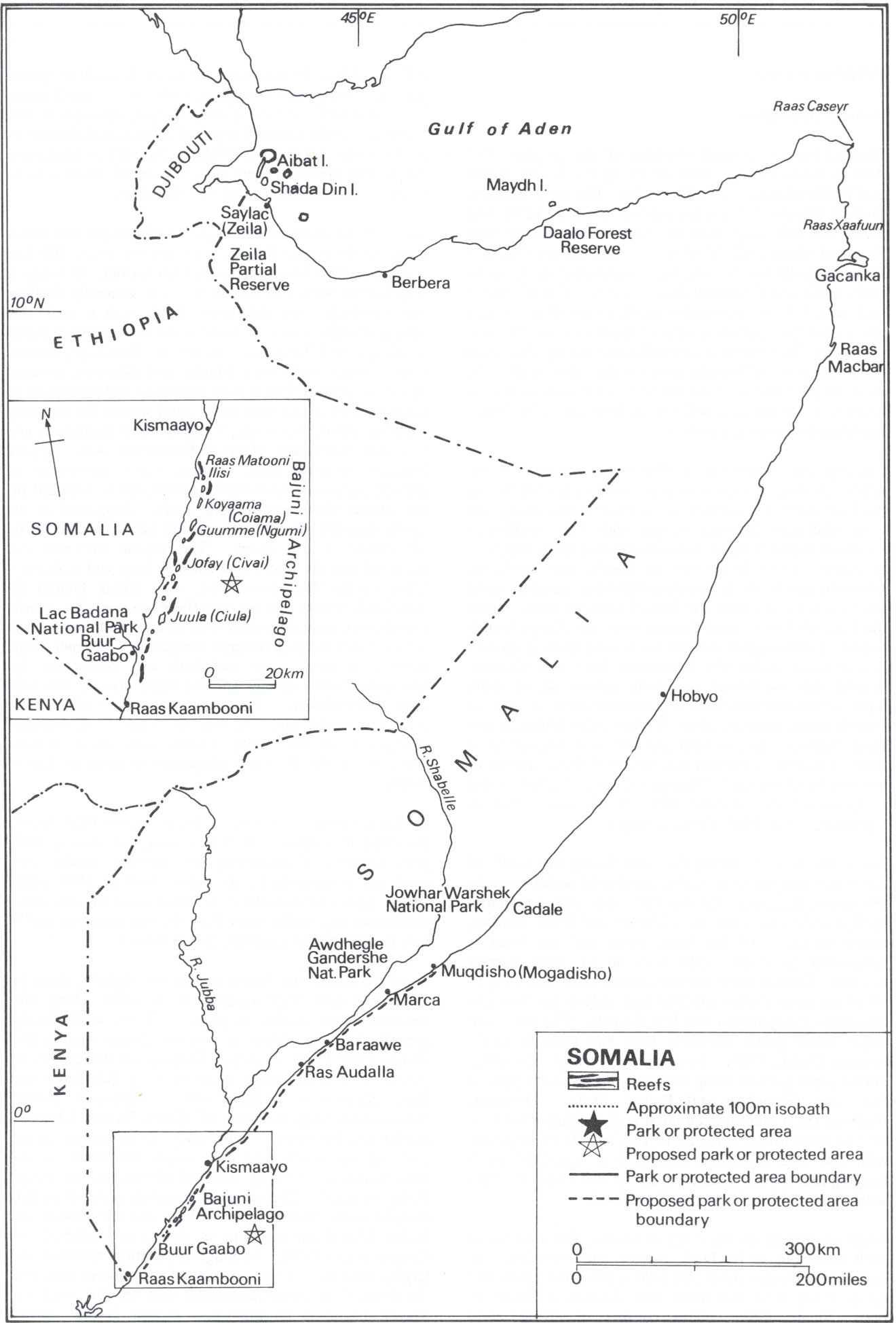
Piracy In Somalia
Piracy off the coast of Somalia occurs in the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel and Somali Sea, in Somali territorial waters and other surrounding areas and has a long and troubled history with different perspectives from different communities. It was initially a threat to international fishing vessels, expanding to international shipping since the Consolidation of states within Somalia (1998–2006), consolidation of states phase of the Somali Civil War around 2000. Somali waters have high fisheries production potential, but the sustainability of those fisheries is compromised by the presence of foreign fishing vessels, many of them fishing illegally. The Somali domestic fishing sector is small and poorly developed, whereas foreign vessels have fished in Somali waters for at least seven decades. Some foreign vessels and their crew have been viewed by Somali artisanal fishers as a threat to their traditional livelihoods. Many foreign vessels directly compete for fish, reducing fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submersible
A submersible is a small watercraft designed to operate underwater. The term "submersible" is often used to differentiate from other underwater vessels known as submarines, in that a submarine is a fully self-sufficient craft, capable of independent cruising with its own power supply and air renewal system, whereas a submersible is usually supported by a nearby ship, surface vessel, very large floating structure, platform, shore team or sometimes a larger submarine. In common usage by the general public, however, the word "submarine" may be used to describe a craft that is by the technical definition actually a submersible. There are many types of submersibles, including both crewed and uncrewed craft, otherwise known as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) or unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). Submersibles have many uses worldwide, such as oceanography, underwater archaeology, ocean exploration, adventure, equipment maintenance and recovery, and underwater videography. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare role (commerce raiding) and enforcing a naval blockade against enemy shipping. The primary targets of the U-boat campaigns in both wars were the merchant convoys bringing supplies from Canada and other parts of the British Empire, and from the United States, to the United Kingdom and (during the Second World War) to the Soviet Union and the Allied territories in the Mediterranean. German submarines also destroyed Brazilian merchant ships during World War II, causing Brazil to declare war on both Germany and Italy on 22 August 1942. The term is an anglicised version of the German word ''U-Boot'' , a shortening of ''Unterseeboot'' ('under-sea-boat'), though the German term refers to any submarine. Austro-Hungarian Navy submarines were also kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Type XIV Submarine
The Type XIV U-boat was a modification of the Type IXD, designed to resupply other U-boats, being the only submarine tenders built which were not surface ships. It was nicknamed the "''Milchkuh/Milchkühe (pl.)''" (milk cows) or ''U-Tanker''. Design German Type XIV submarines were shortened and deepened versions of the Type IXDs. The boats had a displacement of when at the surface and while submerged. The U-boats had a total length of , a pressure hull length of , a beam of , a height of , and a draught of . The submarines were powered by two Germaniawerft supercharged four-stroke, six-cylinder diesel engines producing a total of for use while surfaced, two Siemens-Schuckert 2 GU 345/38-8 double-acting electric motors producing a total of for use while submerged. They had two shafts and two propellers. The boats were capable of operating at depths of up to . The submarines had a maximum surface speed of and a maximum submerged speed of . When submerged, the boats co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |