|
Moses Norton
Moses Norton (29 December 1773) was a Hudson's Bay Company administrator who was chief factor of Fort Prince of Wales from 1762 until his death in 1773. A controversial figure throughout his life, he notably commissioned explorer Samuel Hearne's three expeditions in 1769–1772, which led to the first European discovery of the Coppermine River and the northern coast of Canada. Early life Moses Norton was born at Prince of Wales Fort around 1735, the son of Richard Norton and Sunannah Dupeer. Career After being indentured to HBC ship captain George Spurrell in 1744, he first served aboard an HBC sloop for several years before becoming an assistant to Ferdinand Jacobs, the then-chief factor of Fort Prince of Wales, in present-day Churchill, Manitoba. He later served as a mate on the Company's vessel ''Churchill''. In 1762, Norton was appointed to the position of chief factor of Fort Prince of Wales. In 1769, he commissioned English explorer Samuel Hearne to embark on a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business division is Hudson's Bay, commonly referred to as The Bay ( in French). After incorporation by English royal charter in 1670, the company functioned as the ''de facto'' government in parts of North America for nearly 200 years until the HBC sold the land it owned (the entire Hudson Bay drainage basin, known as Rupert's Land) to Canada in 1869 as part of the Deed of Surrender, authorized by the Rupert's Land Act 1868. At its peak, the company controlled the fur trade throughout much of the English- and later British-controlled North America. By the mid-19th century, the company evolved into a mercantile business selling a wide variety of products from furs to fine homeware in a small number of sales shops (as opposed to trading posts) acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor (agent)
A factor is a type of trader who receives and sells goods on commission, called factorage. A factor is a mercantile fiduciary transacting business in his own name and not disclosing his principal. A factor differs from a commission merchant in that a factor takes possession of goods (or documents of title representing goods, such as a bill of lading) on consignment, but a commission merchant sells goods not in his possession on the basis of samples. Most modern factor business is in the textile field, but factors are also used to a great extent in the shoe, furniture, hardware, and other industries, and the trade areas in which factors operate have increased. In the United Kingdom, most factors fall within the definition of a mercantile agent under the Factors Act 1889 and therefore have the powers of such. A factor has a possessory lien over the consigned goods that covers any claims against the principal arising out of the factor's activity. A debt factor, whether a perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
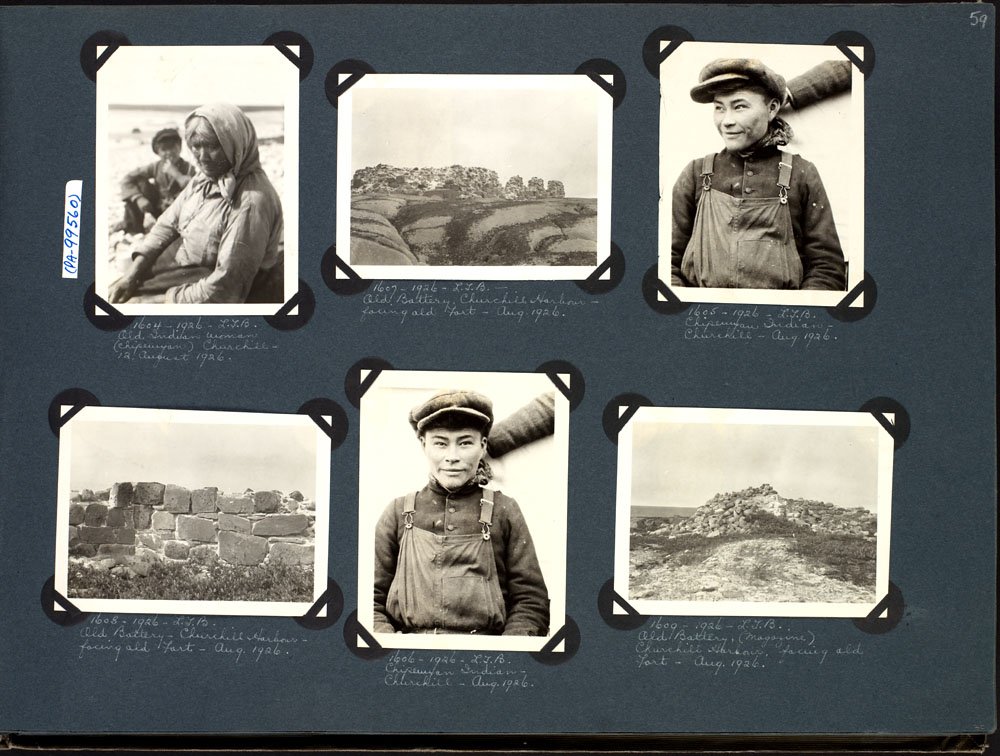
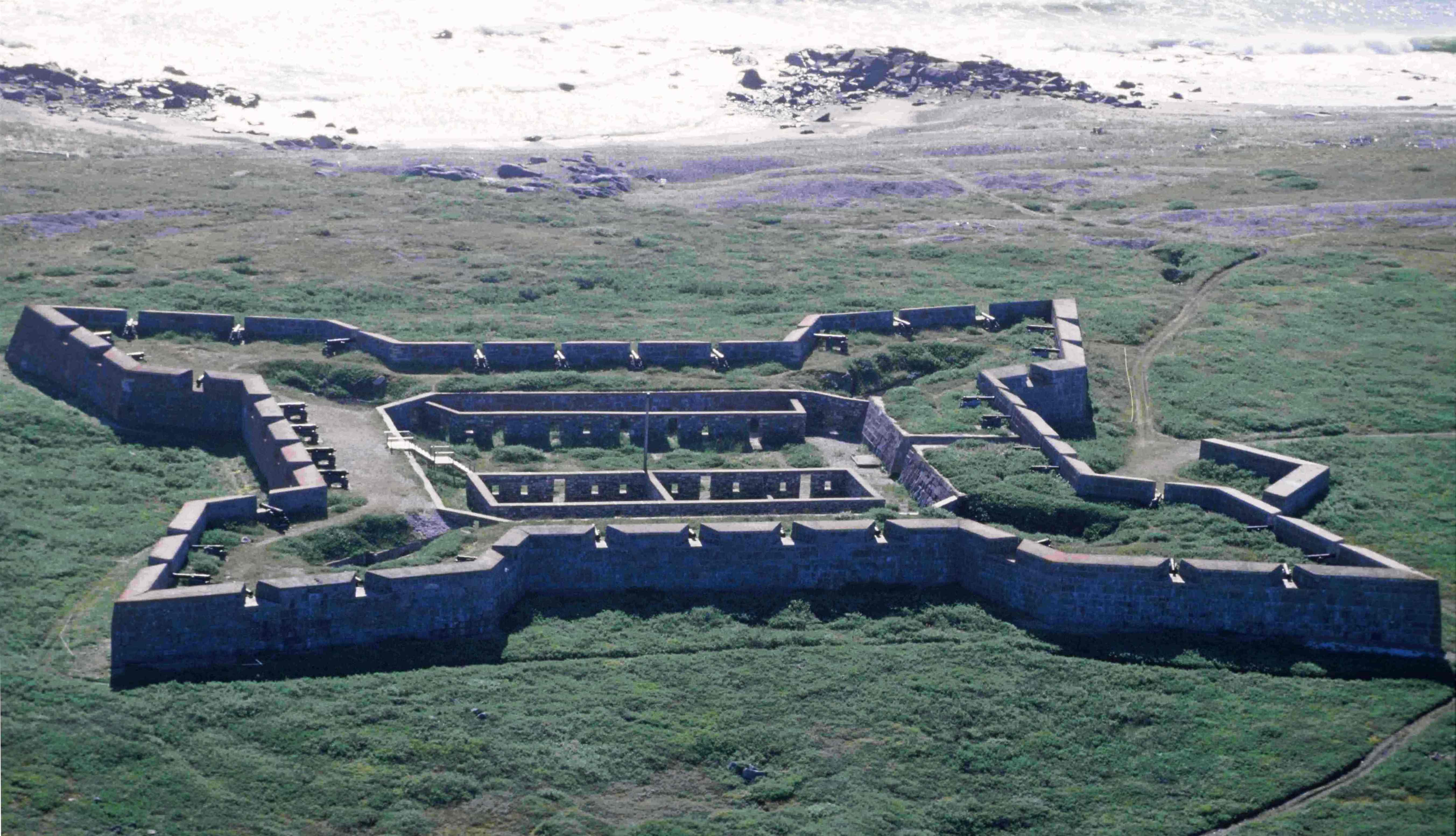
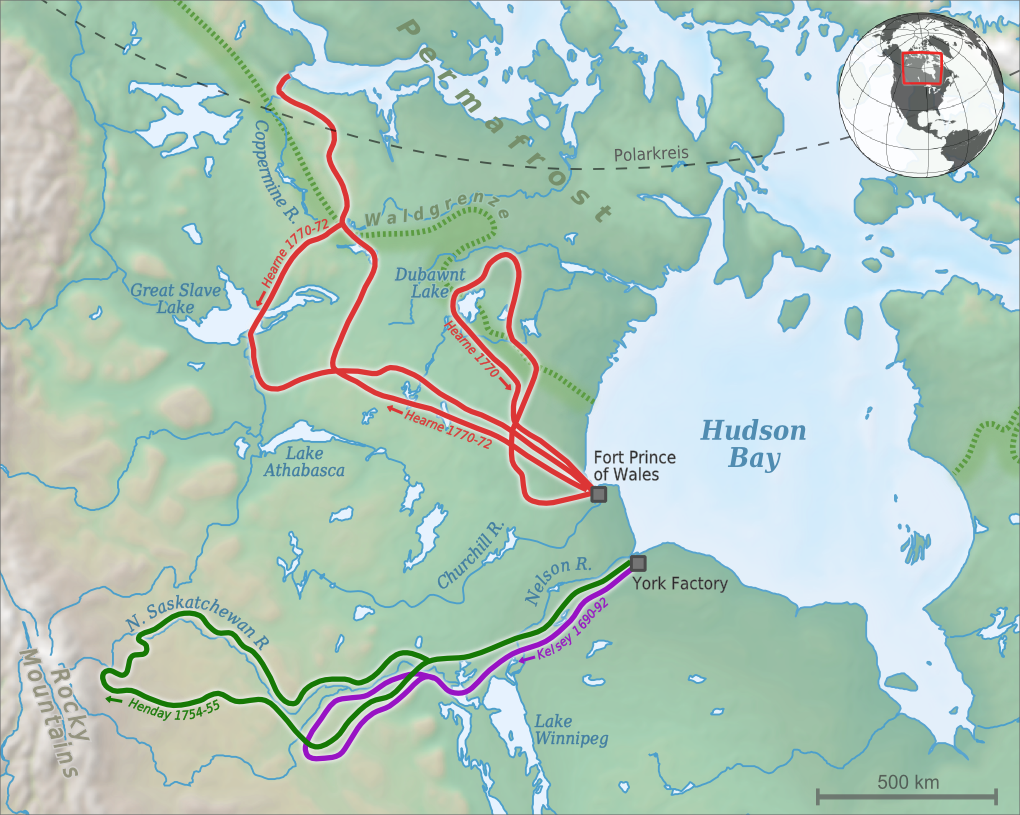
Fort Prince Of Wales
The Prince of Wales Fort is a historic bastion fort on Hudson Bay across the Churchill River from Churchill, Manitoba, Canada. History The European history of this area starts with Henry Hudson sailing into Hudson Bay in 1610. The area was recognized as important in the fur trade and of potential importance for other discoveries. The fort is built in a star shape. Original (wood) fort This fort began as a log fort built in 1717 by James Knight of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) and was originally called the Churchill River Post. In 1719, the post was renamed Prince of Wales Fort. It was located on the west bank of the Churchill River to protect and control the HBC's interests in the fur trade. Construction of the present stone fort The original wooden fort was replaced by a massive stone fort, probably to abide by the Royal Charter which required that Rupert's Land should be fortified. Construction of this fort was started in 1731 near what was then called Eskimo Point. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Hearne
Samuel Hearne (February 1745 – November 1792) was an English explorer, fur-trader, author, and naturalist. He was the first European to make an overland excursion across northern Canada to the Arctic Ocean, actually Coronation Gulf, via the Coppermine River. In 1774, Hearne built Cumberland House for the Hudson's Bay Company, its second interior trading post after Henley House and the first permanent settlement in present Saskatchewan. Biography Samuel Hearne was born in February 1745 in London. Hearne's father was Secretary of the Waterworks of London Bridge, who died in 1748. His mother's name was Diana, and his sister's name was Sarah, three years younger than Samuel. Samuel Hearne joined the British Royal Navy in 1756 at the age of 11 as midshipman under the fighting captain Samuel Hood. He remained with Hood during the Seven Years' War, seeing considerable action during the conflict, including the bombardment of Le Havre. At the end of the Seven Years' War, having serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coppermine River
The Coppermine River is a river in the North Slave and Kitikmeot regions of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut in Canada. It is long. It rises in Lac de Gras, a small lake near Great Slave Lake, and flows generally north to Coronation Gulf, an arm of the Arctic Ocean. The river freezes in winter but may still flow under the ice. The community of Kugluktuk (formerly Coppermine) is located at the river's mouth. The river was named for the copper ores which are located along the river, by Samuel Hearne in 1771. Hearne found only one lump of copper and commercial mining was not considered viable. Bloody Falls, part of the Kugluk/Bloody Falls Territorial Park, is located from Kugluktuk, and was home to the Kogluktogmiut a sub-group of the Copper Inuit. It is the site of the Bloody Falls Massacre, when Matonabbee, Samuel Hearne's guide, and his fellow Chipewyan warriors ambushed and massacred the local Inuit. Gallery See also *List of longest rivers of Canada Among the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of Wales Fort
The Prince of Wales Fort is a historic bastion fort on Hudson Bay across the Churchill River from Churchill, Manitoba, Canada. History The European history of this area starts with Henry Hudson sailing into Hudson Bay in 1610. The area was recognized as important in the fur trade and of potential importance for other discoveries. The fort is built in a star shape. Original (wood) fort This fort began as a log fort built in 1717 by James Knight of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) and was originally called the Churchill River Post. In 1719, the post was renamed Prince of Wales Fort. It was located on the west bank of the Churchill River to protect and control the HBC's interests in the fur trade. Construction of the present stone fort The original wooden fort was replaced by a massive stone fort, probably to abide by the Royal Charter which required that Rupert's Land should be fortified. Construction of this fort was started in 1731 near what was then called Eskimo Point. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indentured Servitude
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an "indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensation or debt repayment, or it may be imposed as a judicial punishment. Historically, it has been used to pay for apprenticeships, typically when an apprentice agreed to work for free for a master tradesman to learn a trade (similar to a modern internship but for a fixed length of time, usually seven years or less). Later it was also used as a way for a person to pay the cost of transportation to colonies in the Americas. Like any loan, an indenture could be sold; most employers had to depend on middlemen to recruit and transport the workers so indentures (indentured workers) were commonly bought and sold when they arrived at their destinations. Like prices of slaves, their price went up or down depending on supply and demand. When the indenture (loan) was paid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Jacobs
Ferdinand Jacobs ( – November 1783) was a Hudson's Bay Company chief factor. He joined the company's outpost in Prince of Wales's Fort (now Churchill, Manitoba Churchill is a town in northern Manitoba, Canada, on the west shore of Hudson Bay, roughly from the Manitoba–Nunavut border. It is most famous for the many polar bears that move toward the shore from inland in the autumn, leading to the nickname ...) in 1732. In 1752 he was promoted to chief factor of the trading post. External links * 1710s births 1783 deaths Hudson's Bay Company people {{Canada-business-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchill, Manitoba
Churchill is a town in northern Manitoba, Canada, on the west shore of Hudson Bay, roughly from the Manitoba–Nunavut border. It is most famous for the many polar bears that move toward the shore from inland in the autumn, leading to the nickname "Polar Bear Capital of the World" that has benefited its burgeoning tourism industry. Geography Churchill is located on Hudson Bay, at the mouth of the Churchill River on the 58th parallel north, far above most Canadian populated areas. Churchill is far from any other towns or cities, with Thompson, approximately to the south, being the closest larger settlement. Manitoba's provincial capital, Winnipeg, is approximately south of Churchill. While not part of the city, Eskimo Point and Eskimo Island are located across river with the former site of the Prince of Wales Fort. History A variety of nomadic Arctic peoples lived and hunted in this region. The Thule people arrived around the year 1000 from the west, the ancestors of the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chipewyan
The Chipewyan ( , also called ''Denésoliné'' or ''Dënesųłı̨né'' or ''Dënë Sųłınë́'', meaning "the original/real people") are a Dene Indigenous Canadian people of the Athabaskan language family, whose ancestors are identified with the Taltheilei Shale archaeological tradition. They are part of the Northern Athabascan group of peoples, and come from what is now Western Canada. Terminology The term ''Chipewyan'' (ᒌᐘᔮᐣ) is a Cree exonym meaning ''pointed hides'', referring to the design of their parkas. The French-speaking missionaries to the northwest of the Red River Colony referred to the Chipewyan people as Montagnais in their documents written in French. Montagnais simply means "mountain people" or "highlanders" in French and has been applied to many unrelated nations across North America over time. For example the Neenolino Innu of northern Quebec are also called "Montagnais". Demographics Chipewyan peoples live in the region spanning the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Disease
Gastrointestinal diseases (abbrev. GI diseases or GI illnesses) refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum, and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Oral disease The oral cavity is part of the gastrointestinal system and as such the presence of alterations in this district can be the first sign of both systemic and gastrointestinal diseases. By far the most common oral conditions are plaque-induced diseases (e.g., gingivitis, periodontitis, dental caries). Oral symptoms can be similar to lesions occurring elsewhere in the digestive tract, with a pattern of swelling, inflammation, ulcers, and fissures. If these signs are present, then patients are more likely to also have anal and esophageal lesions and experience other extra-intestinal disease manifestations. Some diseases which involve other parts of the GI tract can manifest in the mouth, alone or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


