|
Moritz Rittinghausen
Moritz Rittinghausen (November 10, 1814, in Hückeswagen – December 29, 1890, in Ath, Belgium) was a German advocate and theorist of direct democracy, an early socialist and a politician. Rittinghausen lived in Belgium temporarily during the period before the March Revolution and emerged there as a leading thinker on social politics. He took an active part in the German revolutions of 1848–49 as a democrat. After leaving the country during the Reaction following the Revolution, he later returned to Germany and began to take a role in the labor movement. He was among the founders of the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Germany, before he was thrown out of the party over political differences. Early life and pre-Revolutionary Period He was born into an influential family in Hückeswagen, in the Rhineland. His grandfather already had been mayor; his grandmother was descended from the old, originally French de Blois family. His father also served as mayor and as a court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democratic Workers' Party Of Germany
The Social Democratic Workers' Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Arbeiterpartei Deutschlands, SDAP) was a Marxist socialist political party in the North German Confederation during unification. Founded in Eisenach in 1869, the SDAP endured through the early years of the German Empire. Often termed the Eisenachers, the SDAP was one of the first political organizations established among the nascent German labor unions of the 19th century. It officially existed under the name SDAP for only six years (1869–1875). However, through name changes and political partnerships, its lineage can be traced to the present-day Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD). Origins VDAV and ADAV The SDAP was one of the earliest organizations to arise from German workers' unionizing activity, but it was not the first. At the group's founding in 1869, the fast-growing working class of the Industrial Revolution had already established several notable associations for workers' advocacy. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bildungsbürgertum
''Bildungsbürgertum'' () is a social class that emerged in mid-18th-century Germany, as the educated social stratum of the bourgeoisie, men and women who had received an education based upon the metaphysical values of Idealism and Classical studies of the Graeco–Roman culture of Antiquity. In sociological contrast to the ''Kleinbürgertum'', the petite bourgeoisie of Germany, the ''Bildungsbürgertum'' were the intelligentsia and the upper economic-stratum of the German bourgeoisie. Term The term ''Bildungsbürgertum'' was coined in 1920s Germany, by the political right-wing to communicate anti-bourgeois sentiment, based upon the perceived incompatibility of temperament in a person who claims to being both a 'genuine' intellectual and a ''Bürger'', a bourgeois. In the German compound word ''Bildungsbürgertum'', the word ''Bildung'' denotes "culture" and "education" as defined in the Age of Enlightenment. ''Bildung'' also corresponds to the educational ideal presented in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutz, Cologne
The Cologne borough of Deutz (german: Köln-Deutz ; ), is a part of central Cologne, Germany, and was once an independent town. History Deutz was established under Roman Emperor Constantine I in 310 AD, when he established ''Castrum Divitia'', a military camp built on the banks of the Rhine across from Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium. Camp and city were linked via a bridge from the same time. During the Middle Ages, Deutz was an important centre of learning in medieval Germany. Up into the early Middle Ages it was known by the Latin name ''Divitia'', from the 10th century as ''Tuitium''. It was located on the right bank of the Rhine, opposite Cologne, which grew up on the left bank. In 1002, the old castle in Deutz was made a Benedictine monastery by Heribert, archbishop of Cologne, and the important abbey was home to many influential theologians, such as Rupert of Deutz. Permission to fortify the town was in 1230 granted to the citizens by the archbishop of Cologne, between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census Suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to vote is called active suffrage, as distinct from passive suffrage, which is the right to stand for election. The combination of active and passive suffrage is sometimes called ''full suffrage''. In most democracies, eligible voters can vote in elections of representatives. Voting on issues by referendum may also be available. For example, in Switzerland, this is permitted at all levels of government. In the United States, some states such as California, Washington, and Wisconsin have exercised their shared sovereignty to offer citizens the opportunity to write, propose, and vote on referendums; other states and the federal government have not. Referendums in the United Kingdom are rare. Suffrage is granted to everybody mentally capable, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First International
The International Workingmen's Association (IWA), often called the First International (1864–1876), was an international organisation An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states an ... which aimed at uniting a variety of different Left-wing politics, left-wing Socialism, socialist, Communism, communist and Anarchism, anarchist groups and trade unions that were based on the working class and class struggle. It was founded in 1864 in a workmen's meeting held in St. Martin's Hall, London. Its first congress was held in 1866 in Geneva. In Europe, a period of harsh reaction followed the widespread Revolutions of 1848. The next major phase of revolutionary activity began almost twenty years later with the founding of the IWA in 1864. At its peak, the IWA reported having 8 million m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
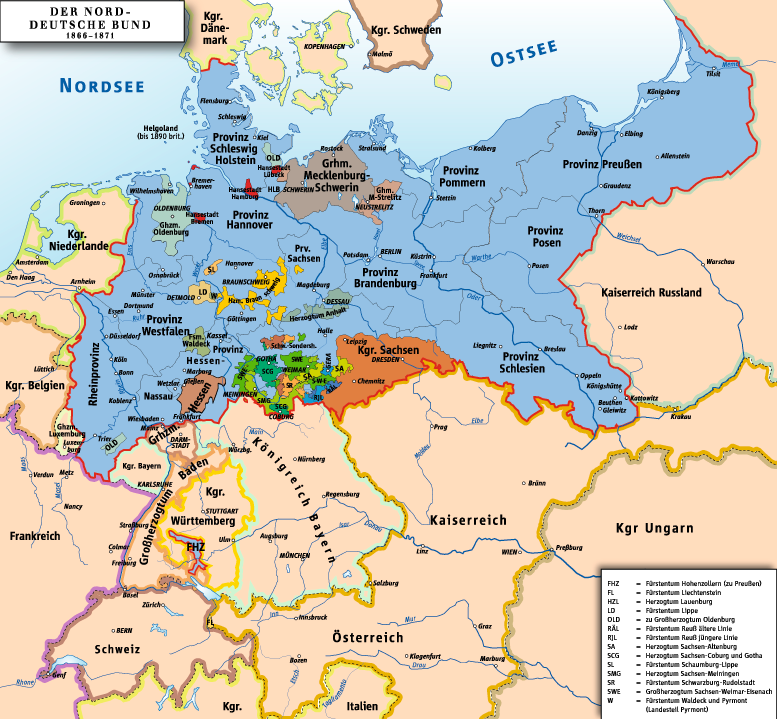
Reichstag (North German Confederation)
The Reichstag () of the North German Confederation was the federal state's lower house of parliament. The popularly elected Reichstag was responsible for federal legislation together with the Bundesrat, the upper house whose members were appointed by the governments of the individual states to represent their interests. Executive power lay with the Bundesrat and the king of Prussia acting as ''Bundespräsidium'', or head of state. The Reichstag debated and approved or rejected taxes and expenditures and could propose laws in its own right. To become effective, all laws required the approval of both the Bundesrat and the Reichstag. Voting rights in Reichstag elections were advanced for the time, granting universal, equal, and secret suffrage to men above the age of 25. When the German Empire was established in 1871, the North German Reichstag formed the basis of the new Reichstag of the German Empire. Background The draft constitution Following Prussia's victory in the 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General German Workers' Association
The General German Workers' Association (german: Allgemeiner Deutscher Arbeiter-Verein, ADAV) was a German political party founded on 23 May 1863 in Leipzig, Kingdom of Saxony by Ferdinand Lassalle. It was the first organized mass working-class party in European history. The organization existed by this name until 1875, when it combined with the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Germany (SDAP) to form the Socialist Workers' Party of Germany. This unified organization was renamed soon thereafter the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), which presently remains in existence and dates its origins to the founding of the ADAV. Its Austrian part would become the SPÖ. The ADAV was the first German Labour Party, formed in Prussia prior to the establishment of the German Empire. It was active in the German Confederation, which included the Austrian Empire. Organizational history Establishment The ADAV was founded in Leipzig by Ferdinand Lassalle and twelve delegates from so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Era (Prussia)
The New Era (German: ''Neue Ära'') was the term for the government policy in the Kingdom of Prussia between Autumn 1858 and Spring 1862. It followed the Era of Reaction under Frederick William IV. Overview The New Era began with the regency of Wilhelm I on October 7, 1858, who became King Wilhelm I in 1861. After the Era of Reaction of the 1850s, which had emphasized the preservation of the old conservative prerogatives, the new Regent tried to enforce reforms by calling together a conservative-liberal coalition government. However, the reforms were blocked by the deputies from the Junker Junker ( da, Junker, german: Junker, nl, Jonkheer, en, Yunker, no, Junker, sv, Junker ka, იუნკერი (Iunkeri)) is a noble honorific, derived from Middle High German ''Juncherre'', meaning "young nobleman"Duden; Meaning of Junke ... nobility, which led the Prussian House of Lords. References {{reflist 1858 establishments in Prussia 1862 disestablishments in Prussia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the Flemish Region (from which it is List of capitals outside the territories they serve, separate) and Belgium. The City of Brussels is also the administrative centre of the European Union, as it hosts a number of principal Institutions of the European Union, EU institutions in its Brussels and the European Union#European Quarter, European Quarter. Besides the central historic town located within the Pentagon (Brussels), Pentagon, the City of Brussels covers some of the city's immediate outskirts within the greater Brussels-Capital Region, namely Haren, Belgium, Haren, Laeken, and Neder-Over-Heembeek to the north, as well as the Avenue Louise, Avenue Louise/Louizalaan and the Bois de la Cambre, Bois de la Cambre/Ter Kamer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew of Napoleon I, he was the last monarch to rule over France. Elected to the presidency of the Second Republic in 1848, he seized power by force in 1851, when he could not constitutionally be reelected; he later proclaimed himself Emperor of the French. He founded the Second Empire, reigning until the defeat of the French Army and his capture by Prussia and its allies at the Battle of Sedan in 1870. Napoleon III was a popular monarch who oversaw the modernization of the French economy and filled Paris with new boulevards and parks. He expanded the French overseas empire, made the French merchant navy the second largest in the world, and engaged in the Second Italian War of Independence as well as the disastrous Franco-Prussian War, dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankfurt Parliament
The Frankfurt Parliament (german: Frankfurter Nationalversammlung, literally ''Frankfurt National Assembly'') was the first freely elected parliament for all German states, including the German-populated areas of Austria-Hungary, elected on 1 May 1848 (see German federal election, 1848). The session was held from 18 May 1848 to 31 May 1849, in the Paulskirche at Frankfurt am Main. Its existence was both part of and the result of the "March Revolution" within the states of the German Confederation. After long and controversial debates, the assembly produced the so-called Frankfurt Constitution (''Paulskirchenverfassung'' or St. Paul's Church Constitution, officially the ''Verfassung des Deutschen Reiches'') which proclaimed a German Empire based on the principles of parliamentary democracy. This constitution fulfilled the main demands of the liberal and nationalist movements of the Vormärz and provided a foundation of basic rights, both of which stood in opposition to Metterni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1975%2C_MiNr_2050.jpg)
.jpg)