|
Monocoupe Monocoach H
The Lambert Twin Monocoach was a light, twin-engined U.S. aircraft, designed to carry three or four passengers. Initially it was fitted with economical, low-powered engines but even given a large increase of power it failed to attract customers. Design The Lambert Corporation got into financial difficulties and failed during 1936, the year that the Monocoach first flew. As a result, the earliest pre-World War II accounts of it use the Lambert name and later ones, like Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1938 refer to it as the Monocoupe Monocoach after the succeeding company. Although it was designated the Type H from the start, it has also been referred to as the Lambert or Monocoupe Twin Monocoach to distinguish it from the earlier Lambert Monocoach, a single-engine aircraft. The Monocoach H had a low, one-piece wooden wing, built around two box- spars with girder-type ribs and fabric covering. In plan the very low aspect ratio (5.6) wing was rectangular out to semi-elliptica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambert R-266
Lambert may refer to People *Lambert (name), a given name and surname * Lambert, Bishop of Ostia (c. 1036–1130), became Pope Honorius II *Lambert, Margrave of Tuscany ( fl. 929–931), also count and duke of Lucca *Lambert (pianist), stage-name of German pianist and composer Paul Lambert Places United States *Lambert, Mississippi, a town *Lambert, Missouri, a village *St. Louis Lambert International Airport, St. Louis, Missouri *Lambert, Montana, a rural town in Montana *Lambert, Oklahoma, a town *Lambert Township, Red Lake County, Minnesota *Lambert Castle, a mansion in Paterson, New Jersey * Lambert Creek, San Mateo County, California Elsewhere * Lambert Gravitational Centre, the geographical centre of Australia * Lambert (lunar crater), named after Johann Heinrich Lambert *Lambert (Martian crater), named after Johann Heinrich Lambert Transportation *Lambert (automobile), a defunct American automobile brand *Lambert (cyclecar), British three-wheeled cyclecar *''Lambert'', on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailplane
A tailplane, also known as a horizontal stabiliser, is a small lifting surface located on the tail (empennage) behind the main lifting surfaces of a fixed-wing aircraft as well as other non-fixed-wing aircraft such as helicopters and gyroplanes. Not all fixed-wing aircraft have tailplanes. Canards, tailless and flying wing aircraft have no separate tailplane, while in V-tail aircraft the vertical stabiliser, rudder, and the tail-plane and elevator are combined to form two diagonal surfaces in a V layout. The function of the tailplane is to provide stability and control. In particular, the tailplane helps adjust for changes in position of the centre of pressure or centre of gravity caused by changes in speed and attitude, fuel consumption, or dropping cargo or payload. Tailplane types The tailplane comprises the tail-mounted fixed horizontal stabiliser and movable elevator. Besides its planform, it is characterised by: *Number of tailplanes - from 0 ( tailless or canard) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight Engine
The straight or inline engine is an internal combustion engine with all cylinders aligned in one row and having no offset. Usually found in four, six and eight cylinder configurations, they have been used in automobiles, locomotives and aircraft, although the term in-line has a broader meaning when applied to aircraft engines, see Inline engine (aviation). Design A straight engine is considerably easier to build than an otherwise equivalent horizontally opposed or V engine, because both the cylinder bank and crankshaft can be milled from a single metal casting, and it requires fewer cylinder heads and camshafts. In-line engines are also smaller in overall physical dimensions than designs such as the radial, and can be mounted in any direction. Straight configurations are simpler than their V-shaped counterparts. Although six-cylinder engines are inherently balanced, the four-cylinder models are inherently off balance and rough, unlike 90-degree V fours and horizontally oppos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menasco D-4
The Menasco Motors Company was an American aircraft engine and component manufacturer. History The company was organized by Albert S. Menasco in 1926 to convert World War I surplus Salmson Z-9 water-cooled nine-cylinder radials into air-cooled engines for private use. His association with John K. (Jack) Northrop and his flying wing project in the late 1920s convinced him of the need for a new configuration of aircraft engine: an inverted in-line air-cooled layout that would have the propeller shaft on top for better ground clearance and improved pilot vision. In 1929, Menasco designed his own engine, the 4-A, the first of what was to become Menasco's main product line, the inverted, in-line engine. Menasco designed and built a variety of four- and six-cylinder inverted air-cooled aircraft engines, some with supercharging. During WWII, Menasco manufactured aircraft landing gear for North American, Lockheed, Republic, General Dynamics, and others. After WWII, aircraft landin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Absorber
A shock absorber or damper is a mechanical or hydraulic device designed to absorb and damp shock impulses. It does this by converting the kinetic energy of the shock into another form of energy (typically heat) which is then dissipated. Most shock absorbers are a form of dashpot (a damper which resists motion via viscous friction). Description Pneumatic and hydraulic shock absorbers are used in conjunction with cushions and springs. An automobile shock absorber contains spring-loaded check valves and orifices to control the flow of oil through an internal piston (see below). One design consideration, when designing or choosing a shock absorber, is where that energy will go. In most shock absorbers, energy is converted to heat inside the viscous fluid. In hydraulic cylinders, the hydraulic fluid heats up, while in air cylinders, the hot air is usually exhausted to the atmosphere. In other types of shock absorbers, such as electromagnetic types, the dissipated energy can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
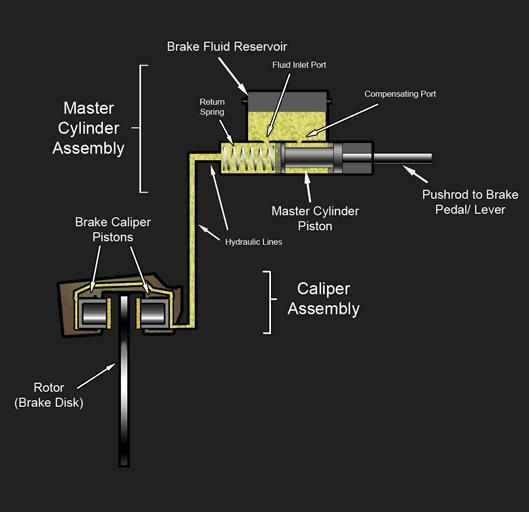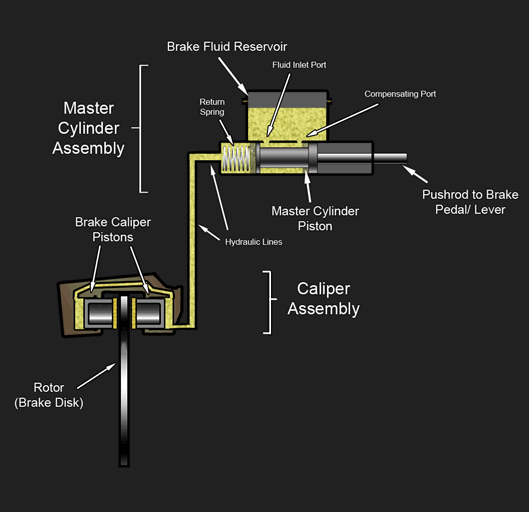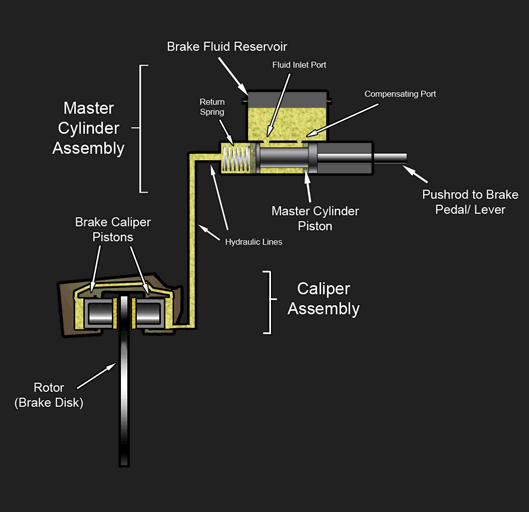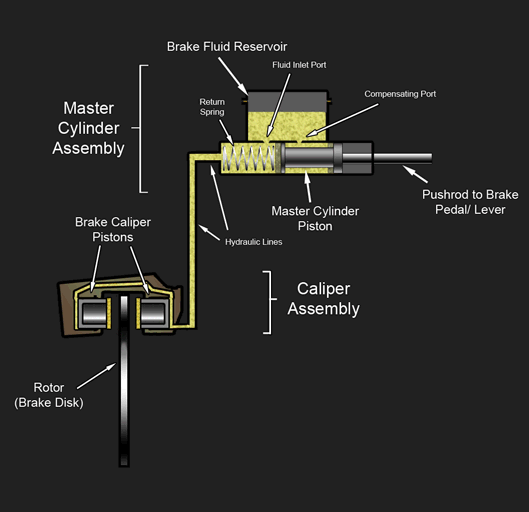
Hydraulic Brake
A hydraulic brake is an arrangement of braking mechanism which uses brake fluid, typically containing glycol ethers or diethylene glycol, to transfer pressure from the controlling mechanism to the braking mechanism. History During 1904, Frederick George Heath (Heath Hydraulic Brake Co., Ltd.), Redditch, England devised and fitted a hydraulic (water/glycerine) brake system to a cycle using a handlebar lever and piston. He obtained patent GB190403651A for “Improvements in hydraulic actuated brakes for cycles and motors”, as well as subsequently for improved flexible rubber hydraulic pipes. In 1908, Ernest Walter Weight of Bristol, England devised and fitted a four-wheel hydraulic (oil) braking system to a motor car. He patented it in Great Britain (GB190800241A) in December 1908, later in Europe and the USA and then exhibited it at the 1909 London Motor Show. His brother, William Herbert Weight improved the patent (GB190921122A) and both were assigned to the Weight Patent Autom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landing Gear
Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for takeoff or landing. For aircraft it is generally needed for both. It was also formerly called ''alighting gear'' by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Martin Company. For aircraft, Stinton makes the terminology distinction ''undercarriage (British) = landing gear (US)''. For aircraft, the landing gear supports the craft when it is not flying, allowing it to take off, land, and taxi without damage. Wheeled landing gear is the most common, with skis or floats needed to operate from snow/ice/water and skids for vertical operation on land. Faster aircraft have retractable undercarriages, which fold away during flight to reduce drag. Some unusual landing gear have been evaluated experimentally. These include: no landing gear (to save weight), made possible by operating from a catapult cradle and flexible landing deck: air cushion (to enable operation over a wide range of ground obstacles and wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trim Tab
Trim tabs are small surfaces connected to the trailing edge of a larger control surface on a boat or aircraft, used to control the trim of the controls, i.e. to counteract hydro- or aerodynamic forces and stabilise the boat or aircraft in a particular desired attitude without the need for the operator to constantly apply a control force. This is done by adjusting the angle of the tab relative to the larger surface. Changing the setting of a trim tab adjusts the neutral or resting position of a control surface (such as an elevator or rudder). As the desired position of a control surface changes (corresponding mainly to different speeds), an adjustable trim tab will allow the operator to reduce the manual force required to maintain that position—to zero, if used correctly. Thus the trim tab acts as a servo tab. Because the center of pressure of the trim tab is farther away from the axis of rotation of the control surface than the center of pressure of the control surface, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanced Rudder
Balanced rudders are used by both ships and aircraft. Both may indicate a portion of the rudder surface ahead of the hinge, placed to lower the control loads needed to turn the rudder. For aircraft the method can also be applied to elevators and ailerons; all three aircraft control surfaces may also be mass balanced, chiefly to avoid aerodynamic flutter. Ships A balanced rudder is a rudder in which the axis of rotation of the rudder is behind its front edge. This means that when the rudder is turned, the pressure of water caused by the ship's movement through the water acts upon the forward part to exert a force which increases the angle of deflection, so counteracting the pressure acting on the after part, which acts to reduce the angle of deflection. A degree of semi-balance is normal to avoid rudder instability i.e. the area in front of the pivot is less than that behind. This allows the rudder to be moved with less effort than is necessary with an unbalanced rudder. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nacelle
A nacelle ( ) is a "streamlined body, sized according to what it contains", such as an engine, fuel, or equipment on an aircraft. When attached by a pylon entirely outside the airframe, it is sometimes called a pod, in which case it is attached with a pylon or strut and the engine is known as a podded engine. In some cases—for instance in the typical "Farman" type "pusher" aircraft, or the World War II-era P-38 Lightning—an aircraft cockpit may also be housed in a nacelle, rather than in a conventional fuselage. Etymology Like many aviation terms, the word comes from French, in this case from a word for a small boat. Development The development of the Arado Ar 234, merging the four nacelles into two The Arado Ar 234 was one of the first operational jet aircraft with engines mounted in nacelles. During its development, the four jet engines were merged from having four distinct nacelles, all of which contained their own landing gear wheel, to two nacelles with two engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Fairing
An aircraft fairing is a structure whose primary function is to produce a smooth outline and reduce drag.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, Third Edition'', page 206. Aviation Supplies & Academics Inc, Newcastle Washington, 1997. These structures are covers for gaps and spaces between parts of an aircraft to reduce form drag and interference drag, and to improve appearance.Bingelis, Tony: ''The Sportplane Builder'', pages 261-265. Experimental Aircraft Association Aviation Foundation, 1979. Types On aircraft, fairings are commonly found on: ; Belly fairing : Also called a "ventral fairing", it is located on the underside of the fuselage between the main wings. It can also cover additional cargo storage or fuel tanks. ; Cockpit fairing : Also called a "cockpit pod", it protects the crew on ultralight trikes. Commonly made from fiberglass, it may also incorporate a windshield.Cliche, Andre: ''Ultralight Aircraft Shopper's Guide'' 8th Edition, page C-17. Cybair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |