|
Monastery Of The Holy Trinity, Vilnius
Monastery of the Holy Trinity ( uk, ą£ąŠąĮą░čüčéąĖčĆ ąĪą▓čÅčéąŠčŚ ąóčĆč¢ą╣čåč¢, lt, Vienuolynas ir ┼Āv. Trejyb─Śs cerkv─Ś, pl, monaster ┼øw. Tr├│jcy ) is a monastery built in Vilnius by the Ruthenian Uniate Church and Grand Hetman of Lithuania Konstanty Ostrogski as a thanksgiving to the God for the victory in Battle of Orsha. It belongs to the Order of Saint Basil the Great and the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church. The church is dedicated to the Holy Trinity. Beside this church, the monastery compound contains a fortified entrance gate, a university, a hotel complex for visitors, monastic cells including the Konrad's cell. The church is surrounded by adjoining four towers at each corner. This monastery is associated with the Union of Brest personalities like Josaphat Kuntsevych, Archbishop of Polatsk who took vows here and spent first years of his monastic life, as well as a prominent reformer of the Basilian Order, Veliamyn Rutsky. History The church According to a legend, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Catholic Church Of Holy Trinity In Vilnius 01(js)
Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek. **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC). **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000ŌĆō330 BC. **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity. **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople. **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD). *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language. *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church. *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity. *Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD. Other uses * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic nation born from several united Baltic tribes from Auk┼Ītaitija. The Grand Duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Lithuania, Belarus and parts of Ukraine, Latvia, Poland, Russia and Moldova. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multi-ethnic and multiconfessional state, with great diversity in languages, religion, and cultural heritage. The consolidation of the Lithuanian lands began in the late 13th century. Mindaugas, the first ruler of the Grand Duchy, was crowned as Catholic King of Lithuania in 1253. The pagan state was targeted in a religious crusade by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilnius University
Vilnius University ( lt, Vilniaus universitetas) is a public research university, oldest in the Baltic states and in Northern Europe outside the United Kingdom (or 6th overall following foundations of Oxford, Cambridge, St. Andrews, Glasgow and Aberdeen). Today it is Lithuania's leading academic institution, ranked among the top 400 ( QS) or top 800 ( ARWU) universities worldwide. As of 2022 QS ranks VU as 8th in CEE (ex. Russia); an ARWU equivalent would be 11th. The university was founded in 1579 as the Jesuit Academy (College) of Vilnius by Stephen B├Īthory, Grand Duke of Lithuania and King of Poland. It was the third oldest university (after the Cracow Academy and the Albertina) in the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth. Due to the failure of the November Uprising (1830ŌĆō1831), the university was closed down and suspended its operation until 1919. In the aftermath of World War I, the university saw failed attempts to restart it by the local Polish Society of Friends of Scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Mickiewicz
Adam Bernard Mickiewicz (; 24 December 179826 November 1855) was a Polish poet, dramatist, essayist, publicist, translator and political activist. He is regarded as national poet in Poland, Lithuania and Belarus. A principal figure in Polish Romanticism, he is one of Poland's "Three Bards" ( pl, Trzej Wieszcze) and is widely regarded as Poland's greatest poet. He is also considered one of the greatest Slavic and European poets and has been dubbed a "Slavic bard". A leading Romantic dramatist, he has been compared in Poland and Europe to Byron and Goethe. He is known chiefly for the poetic drama ''Dziady'' (''Forefathers' Eve'') and the national epic poem '' Pan Tadeusz''. His other influential works include '' Konrad Wallenrod'' and '' Gra┼╝yna''. All these served as inspiration for uprisings against the three imperial powers that had partitioned the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth out of existence. Mickiewicz was born in the Russian-partitioned territories of the former G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate period from 1800 to 1850. Romanticism was characterized by its emphasis on emotion and individualism, clandestine literature, paganism, idealization of nature, suspicion of science and industrialization, and glorification of the past with a strong preference for the medieval rather than the classical. It was partly a reaction to the Industrial Revolution, the social and political norms of the Age of Enlightenment, and the scientific rationalization of nature. It was embodied most strongly in the visual arts, music, and literature, but had a major impact on historiography, education, chess, social sciences, and the natural sciences. It had a significant and complex effect on politics, with romantic thinkers influencing conservatism, libe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilian Monks
Basilian monks are Roman Catholic monks who follow the rule of Basil the Great, bishop of Caesarea (330ŌĆō379). The term 'Basilian' is typically used only in the Catholic Church to distinguish Greek Catholic monks from other forms of monastic life in the Catholic Church. In the Eastern Orthodox Church, as all monks follow the Rule of Saint Basil, they do not distinguish themselves as 'Basilian'. The monastic rules and institutes of Basil are important because their reconstruction of monastic life remains the basis for most Eastern Orthodox and some Greek Catholic monasticism. Benedict of Nursia, who fulfilled much the same function in the West, took his ''Regula Benedicti'' from the writings of Basil and other earlier church fathers. Rule of St. Basil Under the name of Basilians are included all the religious that follow the Rule of St. Basil. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michał Kazimierz Pac
Micha┼é Kazimierz Pac (; 1624 ŌĆō 4 April 1682 in Vok─Ś near Vilnius) of the Gozdawa Coat of Arms, was a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman and a member of the Pac family. He was a son of Piotr Pac (c. 1570-19 July 1640, Lithuanian Court Treasurer 1635-42, Voivode of Trakai 1640-42); and a cousin of Krzysztof Zygmunt Pac, the Chancellor of Lithuania. Biography Micha┼é Kazimierz Pac joined the army as a young man and steadily rose through its ranks. In 1663, during the Second Northern War (Deluge), when the territory of the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth was occupied by Russian and Swedish soldiers, Pac was appointed as the Field Hetman of Lithuania and voivode of Smolensk. He was further promoted to Great Hetman in 1667 and voivode of Vilnius in 1669. Pac opposed election of Michael Korybut Wi┼øniowiecki (ruled 1669ŌĆō1673) to the throne of the Commonwealth. In 1673, Pac fought in the Battle of Khotyn against the Turks. After the death of Wi┼øniowiecki, he opposed election of John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Hetman Of Lithuania
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements * Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size * Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent People * List of people known as "the Great" *Artel Great (born 1981), American actor Other uses * ''Great'' (1975 film), a British animated short about Isambard Kingdom Brunel * ''Great'' (2013 film), a German short film * Great (supermarket), a supermarket in Hong Kong * GReAT, Graph Rewriting and Transformation, a Model Transformation Language * Gang Resistance Education and Training Gang Resistance Education And Training, abbreviated G.R.E.A.T., provides a school-based, police officer instructed program that includes classroom instruction and various learning activities. Their intention is to teach the students to avoid gang ..., or GREAT, a school-based and police officer-instructed program * Global Research and Analysis Team (GReAT), a cybersecurity team at Kaspersky Lab *'' Great!'', a 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgomaster
Burgomaster (alternatively spelled burgermeister, literally "master of the town, master of the borough, master of the fortress, master of the citizens") is the English form of various terms in or derived from Germanic languages for the chief magistrate or executive of a city or town. The name in English was derived from the Dutch ''burgemeester''. In some cases, Burgomaster was the title of the head of state and head of government of a sovereign (or partially or de facto sovereign) city-state, sometimes combined with other titles, such as Hamburg's First Mayor and President of the Senate). Contemporary titles are commonly translated into English as ''mayor''. Historical use * The title "burgermeister" was first used in the early 13th century. *In history (sometimes until the beginning of the 19th century) in many free imperial cities (such as Bremen, Hamburg, L├╝beck etc.) the function of burgomaster was usually held simultaneously by three persons, serving as an executive co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rafajil Korsak
Rafajil Nikolai Korsak ( be, ąĀą░čäą░ą╗ ą£č¢ą║ą░ą╗ą░ą╣ ąÜąŠčĆčüą░ą║, uk, ąĀą░čäą░茹╗ ąÜąŠčĆčüą░ą║, pl, Rafa┼é Miko┼éaj Korsak) (c. 1599 – 28 August 1640) was the " Metropolitan of Kiev, Galicia and all Ruthenia" in the Ruthenian Uniate Church ŌĆö a ''sui juris'' Eastern Catholic Church in full communion with the Holy See. He reigned from 1637 until his death in 1640. Life Mikalai Korsak was born near Navahrudak from a noble Calvinist family. Primaries sources disagree on his birth year, which anyway can be fixed into a range from 1598 to 1601. He studied by the Jesuits in Niasvi┼Š and in Vilnius, and later in Papal Missionary College in Braniewo and by the Jesuits in Prague. By the Jesuits he converted to the Latin Church and later, supported by Metropolitan Jazep Velamin-Rutski, he joined the Greek-Catholic Church. In 1620 he entered in the Order of Saint Basil the Great taking the religious name of Rafajil (Rafael) and he passed his year of novitiate in the monast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople. The canonical hours are very long and complicated, lasting about eight hours (longer during Great Lent) but are abridged outside of large Monastery, monasteries. An iconostasis, a partition covered with icons, separates Sanctuary#Sanctuary as area around the altar, the area around the altar from the nave. The Sign of the cross#Eastern Orthodoxy, sign of the cross, accompanied by bowing, is made very frequently, e.g., more than a hundred times during the Divine Liturgy#Byzantine Rite, divine liturgy, and there is prominent veneration of icons, a general acceptance of the congregants freely moving within the church and interacting with each other, and distinctive traditions of liturgical chanting. Some traditional practices are falling out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
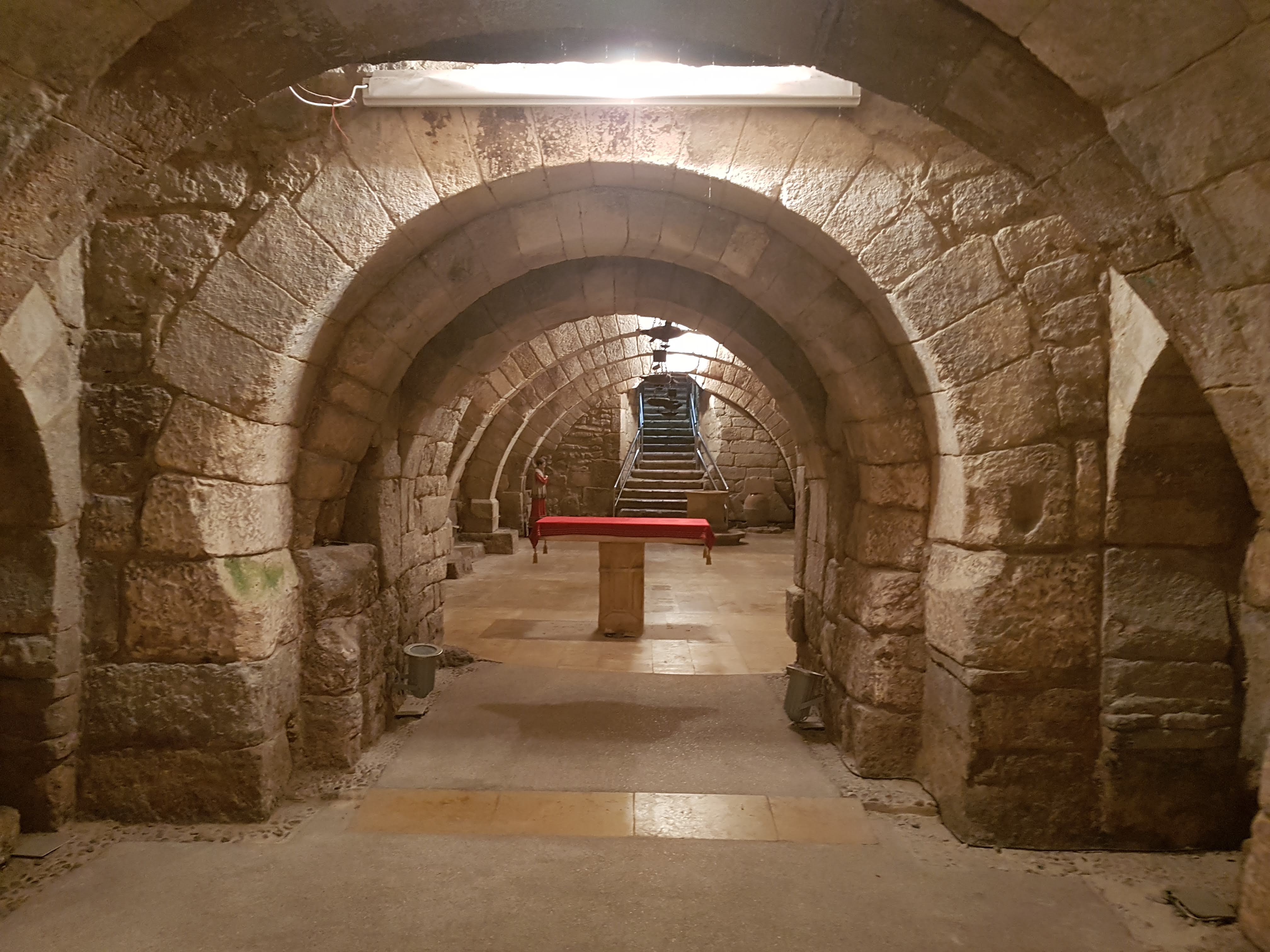
Crypt
A crypt (from Latin ''crypta'' "vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, sarcophagi, or religious relics. Originally, crypts were typically found below the main apse of a church, such as at the Abbey of Saint-Germain en Auxerre, but were later located beneath chancel, naves and transepts as well. Occasionally churches were raised high to accommodate a crypt at the ground level, such as St Michael's Church in Hildesheim, Germany. Etymology The word "Crypt" developed as an alternative form of the Latin "vault" as it was carried over into Late Latin, and came to refer to the ritual rooms found underneath church buildings. It also served as a vault for storing important and/or sacred items. The word "Crypta", however, is also the female form of ''crypto'' "hidden". The earliest known origin of both is in the Ancient Greek '' ╬║ŽüŽŹŽĆŽäŽē'' (krupto/krypto), the first person singular indicative of the verb "to conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)

