|
Molyneux Shuldham, 1st Baron Shuldham
Admiral Molyneux Shuldham, 1st Baron Shuldham ( – 30 September 1798) was an officer of the British Royal Navy. He served for a time as colonial governor of Newfoundland. Family and early life Molyneux Shuldham was born in Ireland c. 1717, and was the second son of the Reverend Lemuel Shuldham, by his wife Elizabeth, daughter of Daniel Molyneux of Ballymulvy, of County Longford. Molyneux entered the navy in 1732 as captain's servant on board , with Captain George Forbes (afterwards Earl of Granard and governor of County Longford). He afterwards served in with Captain Charles Fanshawe, and for upwards of four years in with Fitzroy Henry Lee. He passed his examination on 25 January 1739, being then described on his certificate as 'near twenty-two.' According to the statement in Charnock, he was not seventeen. On 31 August 1739 he was promoted to be lieutenant of , one of the ships which went out to the West Indies with Sir Chaloner Ogle, and took part in the unsuccessful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral (Royal Navy)
Admiral is a senior rank of the Royal Navy, which equates to the NATO rank code OF-9, outranked only by the rank of admiral of the fleet. Royal Navy officers holding the ranks of rear admiral, vice admiral and admiral of the fleet are sometimes considered generically to be admirals. The rank of admiral is currently the highest rank to which a serving officer in the Royal Navy can be promoted, admiral of the fleet being in abeyance except for honorary promotions of retired officers and members of the Royal Family. The equivalent rank in the British Army and Royal Marines is general; and in the Royal Air Force, it is air chief marshal. History The first admirals (1224 to 1523) King Henry III of England appointed the first known English Admiral Sir Richard de Lucy on 29 August 1224. De Lucy was followed by Sir Thomas Moulton in 1264, who also held the title of ''Keeper of the Sea and Sea Ports''. Moulton was succeeded by Sir William de Leybourne, (the son of Sir Roger de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Privateering allowed sovereigns to raise revenue for war by mobilizing privately owned armed ships and sailors to supplement state power. For participants, privateerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-pay
Half-pay (h.p.) was a term used in the British Army and Royal Navy of the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries to refer to the pay or allowance an officer received when in retirement or not in actual service. Past usage United Kingdom In the English Army the option of half-pay developed during the late 17th and early 18th centuries, at the same time as the system of purchasing commissions and promotions by officers took hold. Serving officers could go on half-pay voluntarily, or be obliged to do so if their services were not required. In both cases, they could be summoned back to their regiments if there was a sudden need for their services. As an example, during the Jacobite rising of 1715, all listed half-pay officers were recalled to the army. In the long period of peace that the reduced British Army experienced after the Napoleonic Wars, the half-pay system became a means by which arduous overseas service could be avoided. Well-to-do officers who were promoted through the pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Newspaper Archive
The British Newspaper Archive web site provides access to searchable digitized archives of British and Irish newspapers. It was launched in November 2011. History The British Library Newspapers section was based in Colindale in north London, until 2013, and is now divided between the St Pancras and Boston Spa sites. The library has an almost complete collection of British and Irish newspapers since 1840. This is partly because of the legal deposit legislation of 1869, which required newspapers to supply a copy of each edition of a newspaper to the library. London editions of national daily and Sunday newspapers are complete back to 1801. In total, the collection consists of 660,000 bound volumes and 370,000 reels of microfilm containing tens of millions of newspapers with 52,000 titles on 45 km of shelves. After the closure of Colindale in November 2013, access to the 750 million original printed pages was maintained via an automated and climate-controlled storage facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Foudroyant (1758)
The ''Foudroyant'' was an 80-gun ship of the line of the French Navy. She was later captured and served in the Royal Navy as the Third Rate HMS ''Foudroyant''. Following the Royal Navy tradition she is identified by the date of her introduction to the British navy (in this case post-dating the date of her construction). French Navy service and capture ''Foudroyant'' was built at Toulon to a design by François Coulomb, and was launched on 18 December 1750. She was present at the Battle of Minorca in 1756, where she engaged the British flagship HMS ''Ramillies''. She then formed part of a squadron under Jean-François de La Clue-Sabran, during which time she was captured during the Battle of Cartagena off Cartagena, Spain on 28 February 1758 by , and . The ''Monmouths Captain Arthur Gardiner was mortally wounded early in the fight, and his two lieutenants, led by Lt Robert Carkett, commanded the Monmouth for most of the battle. The captain of the ''Foudroyant'', the Marqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Pocock
Admiral Sir George Pocock or Pococke, KB (6 March 1706 – 3 April 1792) was a British officer of the Royal Navy. Family Pocock was born in Thames Ditton in Surrey, the son of Thomas Pocock, a chaplain in the Royal Navy. His great grandfather was Rev. Dr. Laurence Pocock, Rector of Brightwalton in Berkshire, and his ancestors had long been resident at adjoining Chieveley in the same county. Early career George Pocock entered the navy in 1718, serving aboard under the patronage of his maternal uncle, Captain Streynsham Master (1682–1724).Pocock, 2004 He became lieutenant in April 1725 and commander in 1733. In 1738 he was promoted to post-captain and granted command of the 20-gun . After serving in the West Indies he was sent to join the Commander-in-Chief, East Indies, Rear-Admiral Charles Watson, in 1754 as captain of the 58-gun . Watson's squadron co-operated with Clive in the conquest of Bengal. In 1755 Pocock became rear-admiral, and was promoted to vice-admiral in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Brydges Rodney, 1st Baron Rodney
Admiral George Brydges Rodney, 1st Baron Rodney, KB ( bap. 13 February 1718 – 24 May 1792), was a British naval officer. He is best known for his commands in the American War of Independence, particularly his victory over the French at the Battle of the Saintes in 1782. It is often claimed that he was the commander to have pioneered the tactic of breaking the line. Rodney came from a distinguished but poor background, and went to sea at the age of fourteen. His first major action was the Second Battle of Cape Finisterre in 1747. He made a large amount of prize money during the 1740s, allowing him to purchase a large country estate and a seat in the House of Commons of Great Britain. During the Seven Years' War, Rodney was involved in a number of amphibious operations such as the raids on Rochefort and Le Havre and the Siege of Louisbourg. He became well known for his role in the capture of Martinique in 1762. Following the Peace of Paris, Rodney's financial situation sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Royal
Fort-de-France (, , ; gcf, label= Martinican Creole, Fodfwans) is a commune and the capital city of Martinique, an overseas department and region of France located in the Caribbean. It is also one of the major cities in the Caribbean. History In 1638, Jacques Dyel du Parquet (1606–1658), nephew of Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc and first governor of Martinique, decided to have Fort Saint Louis built to protect the city against enemy attacks. The fort was soon destroyed, and rebuilt in 1669, when Louis XIV appointed the Marquis of Baas as governor general. Under his orders and those of his successors, particularly the Count of Blénac, the fort was built with a Vauban design. Originally named Fort-Royal, the administrative capital of Martinique was over-shadowed by Saint-Pierre, the oldest city in the island, which was renowned for its commercial and cultural vibrancy as "The Paris of the Caribbean". The name of Fort-Royal was changed to a short-lived "Fort-La-Republique" d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Guadeloupe (1759)
The British expedition against Guadeloupe was a military action from January to May 1759, as part of the Seven Years' War. A large British force had arrived in the West Indies, intending to seize French possessions. After a six-month-long battle to capture Guadeloupe they finally received the formal surrender of the island, just days before a large French relief force arrived under Admiral Maximin de Bompart. Though the island was eventually ceded back to the French, the capture of the island contributed to the Annus Mirabilis of 1759. Background To divert French troops from Germany, William Pitt decided the British should attack France wherever they could. British troops were sent on diversionary attacks on the French coast, at St. Malo and Cherbourg. An expedition to western Africa captured the French slaving station at Senegal. In North America, a force was dispatched to take Louisbourg and Quebec. In India Robert Clive won the Battle of Plassey. For 1759, Pitt direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir John Moore, 1st Baronet
Admiral Sir John Moore, 1st Baronet, KB (24 March 1718 – 2 February 1779) was a British officer of the Royal Navy during the War of the Austrian Succession and the Seven Years' War. He eventually rose to the rank of admiral. Childhood Moore was born on 24 March 1718, as the third son of Henry Moore, the rector of Malpas, Cheshire and the son of Henry Hamilton-Moore, 3rd Earl of Drogheda. John's mother, Catherine, was the daughter of Sir Thomas Knatchbull, baronet, and was also the widow of Sir George Rooke.Laughton, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' Moore was initially educated at the Whitchurch grammar school, Shropshire but by age 11 he appears on the books of HMS ''Lion'' for her voyage to the West Indies in 1729. ''Lion'' was at this time the flagship of Rear-Admiral Charles Stewart, a relative of Moore's. Early naval service Moore left ''Lion'' before it sailed however, transferring first to HMS ''Rupert'', and then to HMS ''Diamond''. ''Diamond'' came und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartel
A cartel is a group of independent market participants who collude with each other in order to improve their profits and dominate the market. Cartels are usually associations in the same sphere of business, and thus an alliance of rivals. Most jurisdictions consider it anti-competitive behavior and have outlawed such practices. Cartel behavior includes price fixing, bid rigging, and reductions in output. The doctrine in economics that analyzes cartels is cartel theory. Cartels are distinguished from other forms of collusion or anti-competitive organization such as corporate mergers. Etymology The word ''cartel'' comes from the Italian word '' cartello'', which means a "leaf of paper" or "placard", and is itself derived from the Latin ''charta'' meaning "card". The Italian word became ''cartel'' in Middle French, which was borrowed into English. In English, the word was originally used for a written agreement between warring nations to regulate the treatment and exchange of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poitiers
Poitiers (, , , ; Poitevin: ''Poetàe'') is a city on the River Clain in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and the historical centre of Poitou. In 2017 it had a population of 88,291. Its agglomeration has 130,853 inhabitants in 2016 and is the center of an urban area of 261,795 inhabitants. With more than 29,000 students, Poitiers has been a major university city since the creation of its university in 1431, having hosted René Descartes, Joachim du Bellay and François Rabelais, among others. A city of art and history, still known as "''Ville aux cent clochers''" the centre of town is picturesque and its streets include predominantly historical architecture and half-timbered houses, especially religious architecture, mostly from the Romanesque period ; including notably the Saint-Jean baptistery (4th century), the hypogeum of the Dunes (7th century), the Notre-Dame-la-Grande church (12th century), the Saint-Porchaire church (12th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
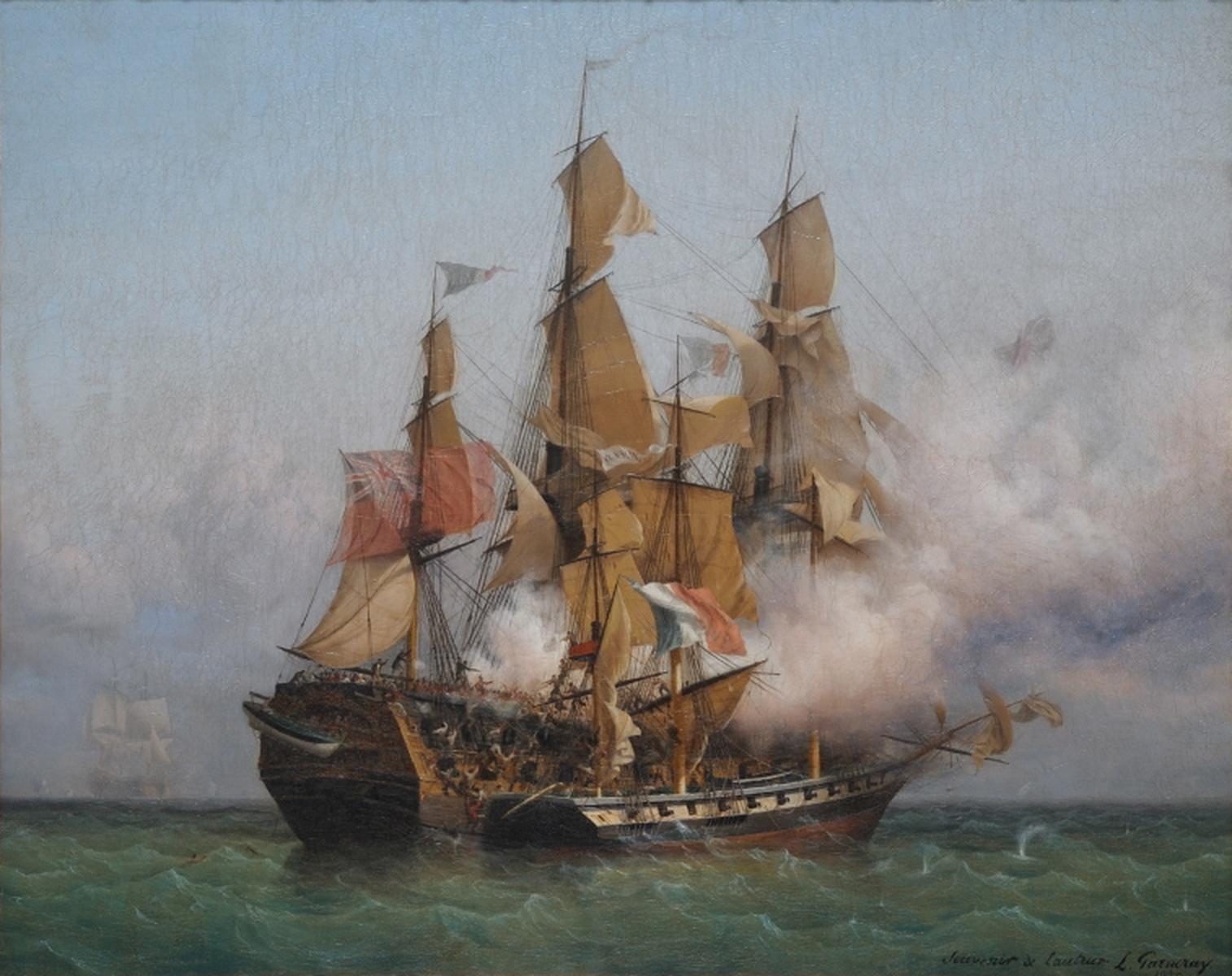




.jpg)