|
Molly Verney
Mary Verney (1675 - February 1696) known also as ''Molly'', & ''Mall Klenyg'' was a British noblewoman best known for having the first instance of recorded use of the word Japan as a verb in English in 1683. Biography Verney was born in 1675 to Mary Abell (1641-1715) and Edmund Verney (1636-1688), the granddaughter of Mary Blacknall (1616-1650) and Ralph Verney (1613-1696). She had two brothers, Ralph (d.1686) and Edmund Verney (d.1690) who upon their deaths, made Verney heiress to the West Claydon estate. As early as 1679, the family would spend lavish amounts of money on Verney dressing her in silk frocks.The Verneys: A True Story of Love, War and Madness in Seventeenth-Century England, Adrian Tinniswood, 2006, pp.471-473 In 1682 she travelled with her father Edmund Verney to London to be engaged at Gorges School upon her request; Gorges being a boarding school for upper-class women (knocked down in 1762) which stood on the Cheyne Walk; where she took dancing and handcraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. On 12 July 927, the various Anglo-Saxon kings swore their allegiance to Æthelstan of Wessex (), unifying most of modern England under a single king. In 1016, the kingdom became part of the North Sea Empire of Cnut the Great, a personal union between England, Denmark and Norway. The Norman conquest of England in 1066 led to the transfer of the English capital city and chief royal residence from the Anglo-Saxon one at Winchester to Westminster, and the City of London quickly established itself as England's largest and principal commercial centre. Histories of the kingdom of England from the Norman conquest of 1066 conventionally distinguish periods named after successive ruling dynasties: Norman (1066–1154), Plantagenet (1154–1485), Tudor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
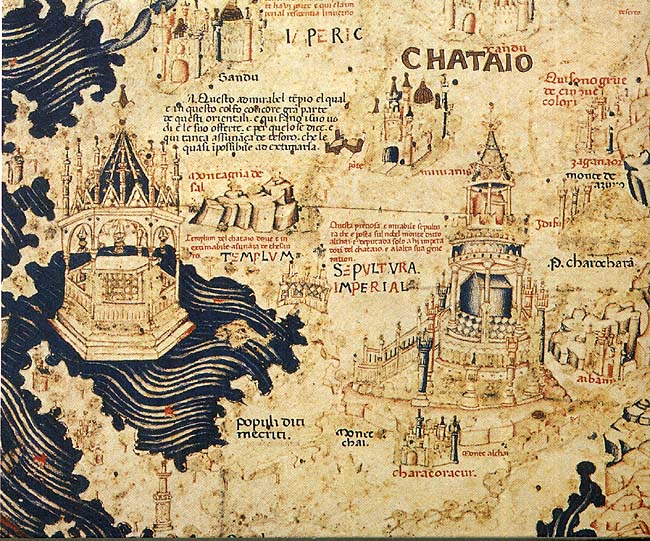
Cathay
Cathay (; ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from China, which was a reference to southern China. As knowledge of East Asia increased, Cathay came to be seen as the same polity as China as a whole. The term ''Cathay'' became a poetic name for China. The name ''Cathay'' originates from the word '' Khitan'', a name of a para-Mongolic nomadic people who ruled the Liao dynasty in northern China from 916 to 1125, and who later migrated west after they were overthrown by the Jin dynasty to form the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty) for another century thereafter. Originally, this name was the name applied by Central and Western Asians and Europeans to northern China; the name was also used in Marco Polo's book on his travels in Yuan dynasty China (he referred to southern China as '' Mangi''). Odoric of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Pope
Alexander Pope (21 May 1688 O.S. – 30 May 1744) was an English poet, translator, and satirist of the Enlightenment era who is considered one of the most prominent English poets of the early 18th century. An exponent of Augustan literature, Pope is best known for his satirical and discursive poetry including '' The Rape of the Lock'', ''The Dunciad'', and ''An Essay on Criticism,'' and for his translation of Homer. After Shakespeare, Pope is the second-most quoted author in ''The Oxford Dictionary of Quotations'', some of his verses having entered common parlance (e.g. "damning with faint praise" or " to err is human; to forgive, divine"). Life Alexander Pope was born in London on 21 May 1688 during the year of the Glorious Revolution. His father (Alexander Pope, 1646–1717) was a successful linen merchant in the Strand, London. His mother, Edith (1643–1733), was the daughter of William Turner, Esquire, of York. Both parents were Catholics. His mother's sister was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary II
Mary II (30 April 166228 December 1694) was Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland, co-reigning with her husband, William III & II, from 1689 until her death in 1694. Mary was the eldest daughter of James, Duke of York, and his first wife Anne Hyde. Mary and her sister Anne were raised as Anglicans at the behest of their uncle, King Charles II, although their parents both converted to Roman Catholicism. Charles lacked legitimate children, making Mary second in the line of succession. She married her first cousin, William of Orange, a Protestant, in 1677. Charles died in 1685 and James took the throne, making Mary heir presumptive. James's attempts at rule by decree and the birth of his son from a second marriage, James Francis Edward (later known as "the Old Pretender"), led to his deposition in the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and the adoption of the English Bill of Rights. William and Mary became king and queen regnant. Mary mostly deferred to her husband – a renowne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kakiemon
is a style of Japanese porcelain, with overglaze decoration called "enameled" ceramics. It was originally produced at the factories around Arita, in Japan's Hizen province (today, Saga Prefecture) from the Edo period's mid-17th century onwards. The style shares much in common with the Chinese "Famille Verte" style. The quality of its decoration was highly prized in the West and widely imitated by major European porcelain manufacturers during the Rococo period. Kakiemon is a term that generates some confusion, being the name of a family, one or more kilns, and a brightly-coloured overglaze style broadly imitating Chinese wares. The style originated with the family, whose kilns were the main producers of it, but other kilns also made it, and the Kakiemon kilns made other styles. Both the palette and style, and very probably the kiln, were in place by the 1680s. The style is a sub-type of what is called in the West Imari ware, the overglaze coloured variety of the broader grouping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannah Woolley
Hannah Woolley, sometimes spelled Wolley, (1622 – c.1675) was an English writer who published early books on household management; she was probably the first person to earn a living doing this. Life Her mother and elder sisters were all skilled in "Physick and Chirurgery" and she learned from them. Nothing is known of her father.Considine, John; Wolley, Hannah (b. 1622?, d. in or after 1674)Oxford Dictionary of National Biography Oxford University Press, 2004 From 1639 to 1646 Woolley worked as a servant for an unnamed woman, almost certainly Anne, Lady Maynard (d. 1647), during which time she learned about medical remedies and recipes. She married Jerome Woolley, a schoolmaster, in 1646 and together with him ran a free grammar school at Newport, in Essex. This is very near the Maynard family's house at Little Easton. In the school she put into practice her skills at "physick". A few years later, the Woolleys opened a school in Hackney, London. She had at least four sons an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Sphere
The private sphere is the complement or opposite to the public sphere. The private sphere is a certain sector of societal life in which an individual enjoys a degree of authority, unhampered by interventions from governmental or other institutions. Examples of the private sphere are family and home. In public-sphere theory, on the bourgeois model, the private sphere is that domain of one's life in which one works for oneself. In that domain, people work, exchange goods, and maintain their families; it is therefore, in that sense, separate from the rest of society. Shifting boundaries The parameters separating public and private spheres are not fixed but vary both in (cultural) space and in time. In the classical world, economic life was the prerogative of the household, only matters which could not be dealt with by the household alone entered the public realm of the polis. In the modern world, the public economy permeates the home, providing the main access to the public sphere fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engelbert Kaempfer
Engelbert Kaempfer (16 September 16512 November 1716) was a German naturalist, physician, explorer and writer known for his tour of Russia, Persia, India, Southeast Asia, and Japan between 1683 and 1693. He wrote two books about his travels. ''Amoenitatum exoticarum'', published in 1712, is important for its medical observations and the first extensive description of Japanese plants (''Flora Japonica''). His ''History of Japan'', published posthumously in 1727, was the chief source of Western knowledge about the country throughout the 18th and mid-19th centuries, when it was closed to foreigners. Early life Kaempfer was born at Lemgo in the Principality of Lippe, within the Holy Roman Empire. His father was a pastor and his mother helped support the congregation. He studied at Hameln, Lüneburg, Hamburg, Lübeck and Danzig (Gdańsk), and after graduating at Kraków, spent four years at Königsberg in Prussia, studying medicine and natural science. Travels and studies Persi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marvels of the World '' and ''Il Milione'', ), a book that described to Europeans the then mysterious culture and inner workings of the Eastern world, including the wealth and great size of the Mongol Empire and China in the Yuan Dynasty, giving their first comprehensive look into China, Persia, India, Japan and other Asian cities and countries. Born in Venice, Marco learned the mercantile trade from his father and his uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, who travelled through Asia and met Kublai Khan. In 1269, they returned to Venice to meet Marco for the first time. The three of them embarked on an epic journey to Asia, exploring many places along the Silk Road until they reached Cathay (China). They were received by the royal court of Kublai Khan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trade duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinoiserie
(, ; loanword from French ''wikt:chinoiserie#French, chinoiserie'', from ''wikt:chinois#French, chinois'', "Chinese"; ) is the European interpretation and imitation of China, Chinese and other East Asia, East Asian artistic traditions, especially in the decorative arts, garden design, architecture, literature, theatre, and music. The aesthetic of Chinoiserie has been expressed in different ways depending on the region. Its acknowledgement derives from the current of Orientalism, which studied Far East cultures from a historical, philological, anthropological, philosophical and religious point of view. First appearing in the 17th century, this trend was popularized in the 18th century due to the rise in trade with China and the rest of East Asia. As a style, chinoiserie is related to the Rococo style. Both styles are characterized by exuberant decoration, asymmetry, a focus on materials, and stylized nature and subject matter that focuses on leisure and pleasure. Chinoiserie focu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_wife_of_Sir_Ralph_Verney%2C_1636.jpg)



.jpg)

