|
Mollo Culture
The Mollo culture existed in Bolivia's altiplano area after the collapse of the Tiwanaku culture during the period of AD 1000 to 1500; it predated the Inca civilization. While the Mollo showed a continuity with Late Tiwanaku culture in both domestic and village architecture, they left no pyramids. Mollo worshiped the jaguar. Archaeology One of the best representations of the Mollo are the ruins northeast of Lake Titicaca at Iskanwaya, on the Cordillera Real, above the Rio Llica (). Iskanwaya, in Muñecas Province, is from La Paz, Bolivia. Dated from 1145 to 1425, the city was built on platforms and was notable for its running water. More than one hundred buildings, streets and plazas still survive. Mollo streets ran in east-west direction. Their houses were rectangular and grouped around patios. Agriculture patterns included terracing and irrigation. Other Mollo sites, such as Piniqo and Khargi, exhibit the same settlement characteristics as Iskanwaya, Wamán is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
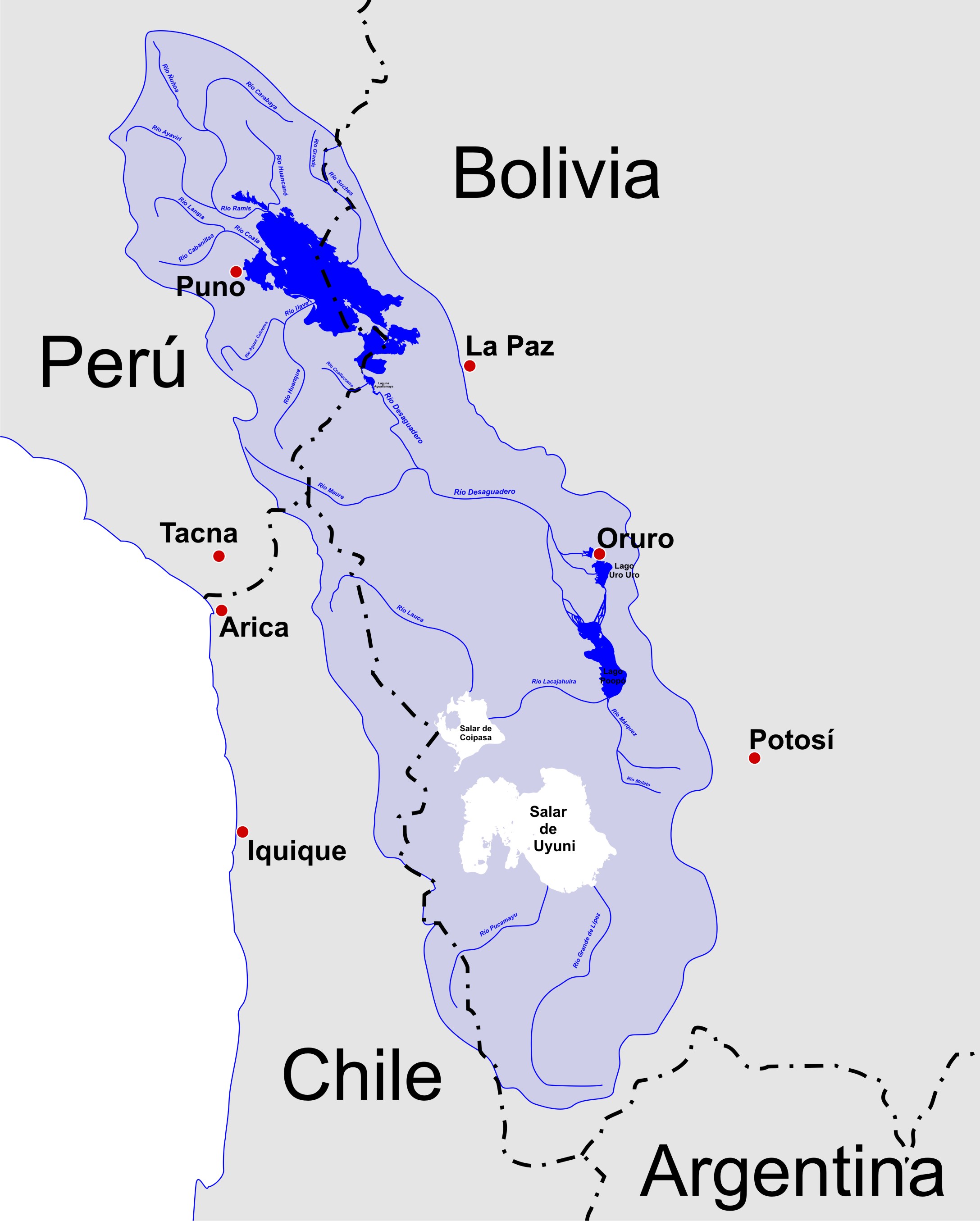
Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Bolivia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistory Of Bolivia
Pre-Columbian Bolivia covers the historical period between 10,000 BCE, when the Upper Andes region was first populated and 1532, when Spanish conquistadors invaded Inca empire. The Andes region of Pre-Columbian South America was dominated by the Tiwanaku civilization until about 1200, when the regional kingdoms of the Aymara emerged as the most powerful of the ethnic groups living in the densely populated region surrounding Lake Titicaca. Power struggles continued until 1450, when the Incas incorporated upper Bolivia into their growing empire. Based in present-day Peru, the Incas instituted agricultural and mining practices that rivaled those put in place many years later by European conquerors. They also established a strong military force, and centralized political power. Despite their best efforts however, the Incas never completely controlled the nomadic tribes of the Bolivian lowlands, nor did they fully assimilate the Aymara kingdoms into their society. These internal divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
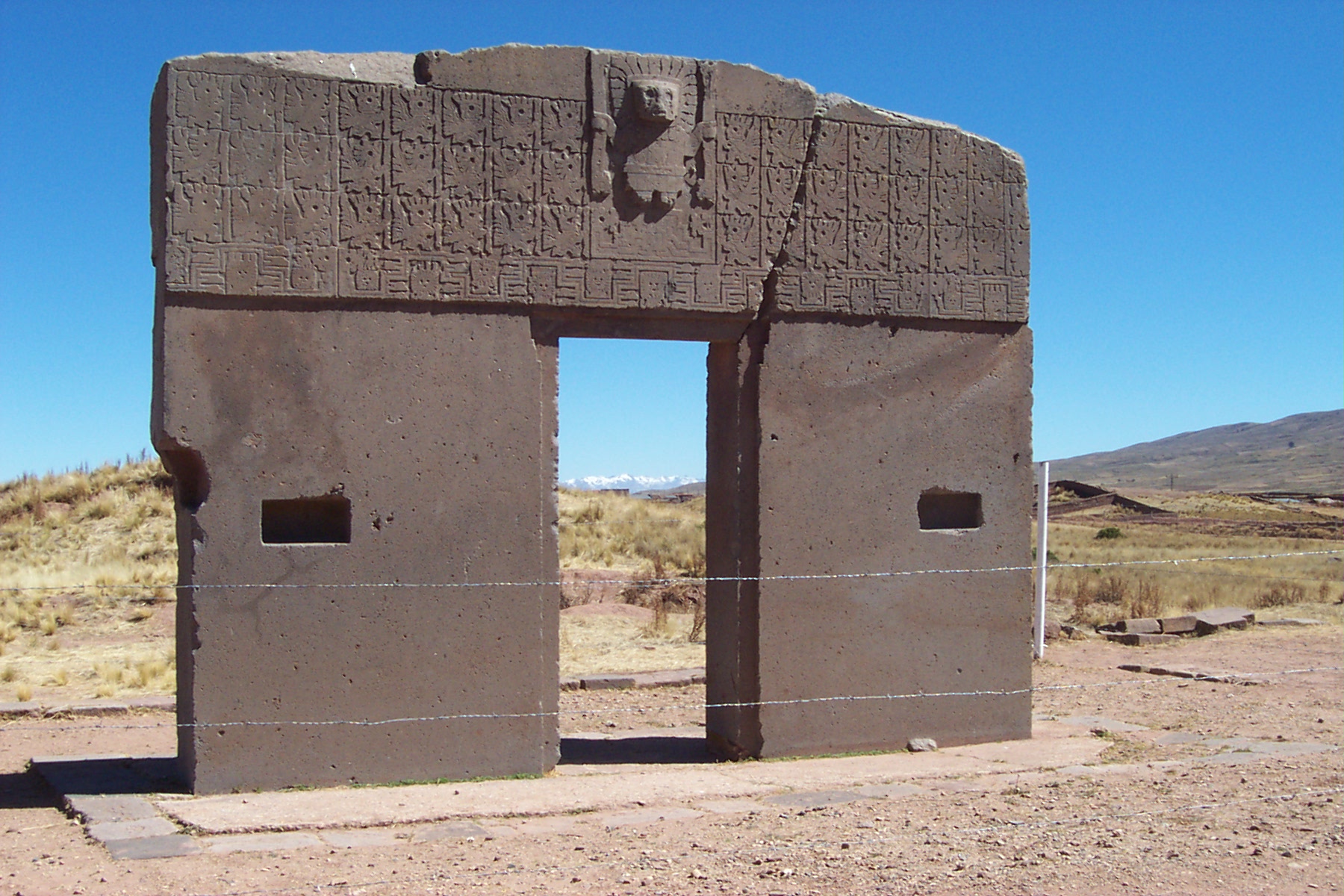
Andean Civilizations
The Andean civilizations were civilization, complex societies of many Indigenous peoples of South America, cultures and peoples mainly developed in the river valleys of the coastal deserts of Peru. They stretched from the Andes of southern Colombia southward down the Andes to Chile and northwest Argentina. Archaeologists believe that Andean civilizations first developed on the narrow coastal plain of the Pacific Ocean. The Norte Chico civilization, Caral or Norte Chico civilization of Peru is the oldest known civilization in the Americas, dating back to 3200 BCE. Despite severe environmental challenges, the Andean civilizations domesticated a wide variety of crops, some of which became of worldwide importance. The Andean civilizations were also noteworthy for monumental architecture, textile weaving, and many unique characteristics of the societies they created. Less than a century prior to the arrival of the Spanish Empire, Spanish conquerors, the Inca Empire, Incas, from their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chullpa
A ''chullpa'' is an ancient Aymara funerary tower originally constructed for a noble person or noble family. ''Chullpas'' are found across the Altiplano in Peru and Bolivia. The tallest are about high. The tombs at Sillustani are most famous. Recent research has focused on the connection between ''chullpas'' and the ritual pathways etched into the landscape around Nevado Sajama, as well as possible patterns within ''chullpa'' sites. Description Corpses in each tomb were typically placed in a fetal position along with some of their belongings, including clothing and common equipment. In virtually all cases, the only opening to the tomb faces the rising sun in the east. The construction of the ''chullpa'' varied with ethnic group: in general, those of the north Altiplano are circular and constructed with stone, while those of the south are rectangular and constructed with adobe. Some are unadorned, while others have intricate carvings. At Sillustani, many of the ''chull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate oceanic climate, with relatively warm summers and chilly winters. Prague is a political, cultural, and economic hub of central Europe, with a rich history and Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque architectures. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Bohemia and residence of several Holy Roman Emperors, most notably Charles IV (r. 1346–1378). It was an important city to the Habsburg monarchy and Austro-Hungarian Empire. The city played major roles in the Bohemian and the Protestant Reformations, the Thirty Years' War and in 20th-century history as the capital of Czechoslovakia between the World Wars and the post-war Communist era. Prague is home to a number of well-known cultural attractions, many of which survived the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Náprstek Museum
The Náprstek Museum is a museum of Asian, African and Native American art located in Bethlehem Square ( cs, Betlemske namesti) in Prague, Czech Republic. It is one of several permanent exhibitions of the National Museum. The museum is situated in the former brewing and wine-making compound of U Halanku in the Prague Old Town. History The museum, originally private, was founded in 1874 by Czech national revivalist politician Vojtěch Náprstek in his former family brewery, as the Czech Industrial Museum. After his death the museum became the Ethnographic Museum, and since World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ... it has been focused on non-European cultures. In the 19th century the museum was one of the cultural and educational centres of the Czech intell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
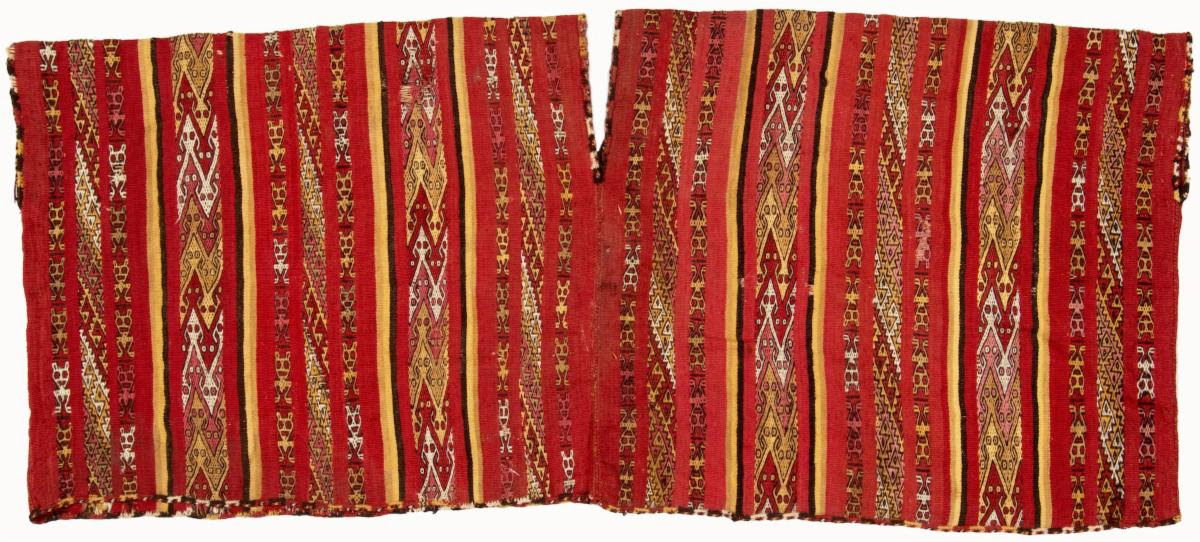
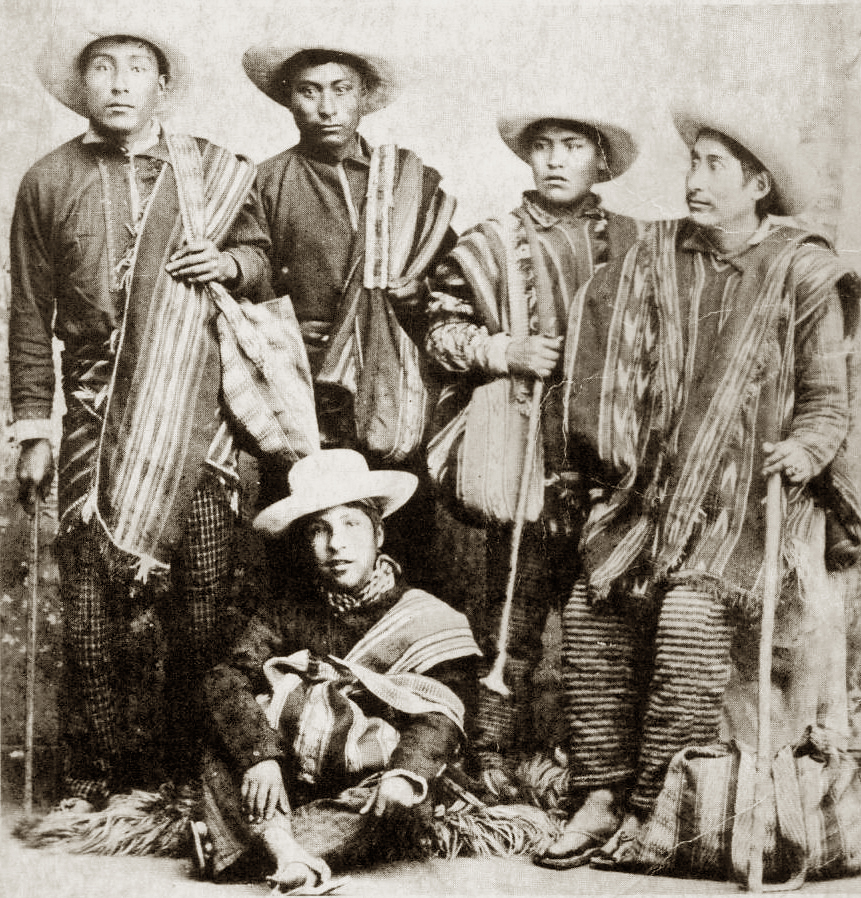
Kallawaya People
The Kallawaya are an indigenous group living in the Andes of Bolivia. They live in the Bautista Saavedra Province and Muñecas Province of the La Paz Department but are best known for being an itinerant group of traditional healers that travel on foot to reach their patients. Hannß, Katja. "The Etymology of Kallawaya". Journal of Language Contact (10), 2017, p. 219-263 According to the UNESCO Safeguarding Project, the Kallawaya can be traced to the pre-Inca period as direct descendants of the Tiwanaku and Mollo cultures, meaning their existence has lasted approximately 1,000 years.They are known to have performed complex procedures like brain surgery alongside their continuous use of medicinal plants as early as 700 AD. Most famously, they are known to have helped to save thousands of lives during the construction of the Panama Canal, in which they used traditional plant remedies to treat the malaria epidemic. Some historical sources even cite the Kallawayas as the first to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
512-Sillustani
51 may refer to: * 51 (number) * The year ** 51 BC ** AD 51 ** 1951 ** 2051 * ''51'' (film), a 2011 American horror film directed by Jason Connery * "Fifty-One "Fifty-One" is the fourth episode of the fifth season of the American television crime drama series ''Breaking Bad'', and the 50th overall episode of the series. Written by Sam Catlin and directed by Rian Johnson, it originally aired on AMC in th ...", an episode of the American television drama series ''Breaking Bad'' * ''51'' (album), a 2012 mixtape by rapper Kool A.D. * "Fifty One", a song by Karma to Burn from the album '' V'', 2011 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallku Janalaya
Mallku is a title roughly translating as "prince" or "leader" in the Aymara language of South America. They recognise an Apu Mallku as their "supreme leader" or "king". There is also an institution called the ''Council of Mallkus and Amautas'' which acts rather like an upper house of the indigenous parliament of the Andes region and consists of four delegates from each of the modern Latin American states that comprise the Greater Collasuyu Qullasuyu (Quechua and Aymara spelling, ; Hispanicized spellings: ''Collasuyu, Kholla Suyu'') was the southeastern provincial region of the Inca Empire. Qullasuyu is the region of the Qulla and related specifically to the native Qulla Quechuas wh ... region. Aymara Titles {{SouthAm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



