|
Models From Melbourne
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , . Models can be divided into physical models (e.g. a ship model or a fashion model) and abstract models (e.g. a set of mathematical equations describing the workings of the atmosphere for the purpose of weather forecasting). Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science. In scholarly research and applied science, a model should not be confused with a theory: while a model seeks only to represent reality with the purpose of better understanding or predicting the world, a theory is more ambitious in that it claims to be an explanation of reality. Types of model ''Model'' in specific contexts As a noun, ''model'' has specific meanings in certain fields, derived from its original meaning of "structural design or layout": * Model (art), a pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Role Model
A role model is a person whose behaviour, example, or success serves as a model to be emulated by others, especially by younger people. The term ''role model'' is credited to sociologist Robert K. Merton, who hypothesized that individuals compare themselves with reference groups of people who occupy the social role to which the individual aspires, an example of which is the way young fans may idolize and imitate professional athletes or entertainment artists. In the second half of the twentieth century, U.S. advocates for workplace equity popularized the term and concept of role models as part of a larger social capital lexicon—which also includes terms such as glass ceiling, networking, mentoring, and gatekeeper—serving to identify and address the problems barring non-dominant groups from professional success. Mainstream business literature subsequently adopted the terms and concepts, promoting them as pathways to success for all career climbers. In 1970 these terms we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Object
In natural language and physical science, a physical object or material object (or simply an object or body) is a contiguous collection of matter, within a defined boundary (or surface), that exists in space and time. Usually contrasted with abstract objects and mental objects. Also in common usage, an object is not constrained to consist of the same collection of matter. Atoms or parts of an object may change over time. An object is usually meant to be defined by the simplest representation of the boundary consistent with the observations. However the laws of physics only apply directly to objects that consist of the same collection of matter. In physics, an object is an identifiable collection of matter, which may be constrained by an identifiable boundary, and may move as a unit by translation or rotation, in 3-dimensional space. Each object has a unique identity, independent of any other properties. Two objects may be identical, in all properties except position, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , . Models can be divided into physical models (e.g. a ship model or a fashion model) and abstract models (e.g. a set of mathematical equations describing the workings of the atmosphere for the purpose of weather forecasting). Abstract or conceptual models are central to philosophy of science. In scholarly research and applied science, a model should not be confused with a theory: while a model seeks only to represent reality with the purpose of better understanding or predicting the world, a theory is more ambitious in that it claims to be an explanation of reality. Types of model ''Model'' in specific contexts As a noun, ''model'' has specific meanings in certain fields, derived from its original meaning of "structural design or layout": * Model (art), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model (CGI)
In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical coordinate-based Computer representation of surfaces, representation of a surface of an object (inanimate or living) in Three-dimensional space, three dimensions via 3D computer graphics software, specialized software by manipulating edges, vertices, and polygons in a simulated 3D space. Three-dimensional (3D) models represent a physical body using a collection of points in 3D space, connected by various geometric entities such as triangles, lines, curved surfaces, etc. Being a collection of data (Point (geometry), points and other information), 3D models can be created manually, algorithmically (procedural modeling), or by 3D scanning, scanning. Their surfaces may be further defined with texture mapping. Outline The product is called a 3D model, while someone who works with 3D models may be referred to as a 3D artist or a 3D modeler. A 3D model can also be displayed as a two-dimensional image t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory (mathematical Logic)
In mathematical logic, a theory (also called a formal theory) is a set of sentences in a formal language. In most scenarios a deductive system is first understood from context, giving rise to a formal system that combines the language with deduction rules. An element \phi\in T of a deductively closed theory T is then called a theorem of the theory. In many deductive systems there is usually a subset \Sigma \subseteq T that is called "the set of axioms" of the theory T, in which case the deductive system is also called an " axiomatic system". By definition, every axiom is automatically a theorem. A first-order theory is a set of first-order sentences (theorems) recursively obtained by the inference rules of the system applied to the set of axioms. General theories (as expressed in formal language) When defining theories for foundational purposes, additional care must be taken, as normal set-theoretic language may not be appropriate. The construction of a theory begins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axiom
An axiom, postulate, or assumption is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The word comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'that which is thought worthy or fit' or 'that which commends itself as evident'. The precise definition varies across fields of study. In classic philosophy, an axiom is a statement that is so evident or well-established, that it is accepted without controversy or question. In modern logic, an axiom is a premise or starting point for reasoning. In mathematics, an ''axiom'' may be a " logical axiom" or a " non-logical axiom". Logical axioms are taken to be true within the system of logic they define and are often shown in symbolic form (e.g., (''A'' and ''B'') implies ''A''), while non-logical axioms are substantive assertions about the elements of the domain of a specific mathematical theory, for example ''a'' + 0 = ''a'' in integer arithmetic. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model (logic)
In universal algebra and in model theory, a structure consists of a set along with a collection of finitary operations and relations that are defined on it. Universal algebra studies structures that generalize the algebraic structures such as groups, rings, fields and vector spaces. The term universal algebra is used for structures of first-order theories with no relation symbols. Model theory has a different scope that encompasses more arbitrary first-order theories, including foundational structures such as models of set theory. From the model-theoretic point of view, structures are the objects used to define the semantics of first-order logic, cf. also Tarski's theory of truth or Tarskian semantics. For a given theory in model theory, a structure is called a model if it satisfies the defining axioms of that theory, although it is sometimes disambiguated as a '' semantic model'' when one discusses the notion in the more general setting of mathematical models. Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model (mimicry)
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. In the simplest case, as in Batesian mimicry, a mimic resembles a model, so as to deceive a dupe, all three being of different species. A Batesian mimic, such as a hoverfly, is harmless, while its model, such as a wasp, is harmful, and is avoided by the dupe, such as an insect-eating bird. Birds hunt by sight, so the mimicry in that case is visual, but in other cases mimicry may make use of any of the senses. Most types of mimicry, including Batesian, are deceptive, as the mimics are not harmful, but Müllerian mimicry, where different harmful species resemble each other, is honest, as when species of wasps and of bees all have genuinely aposematic warning coloration. More complex types may be bipolar, involving only two species, such as when the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
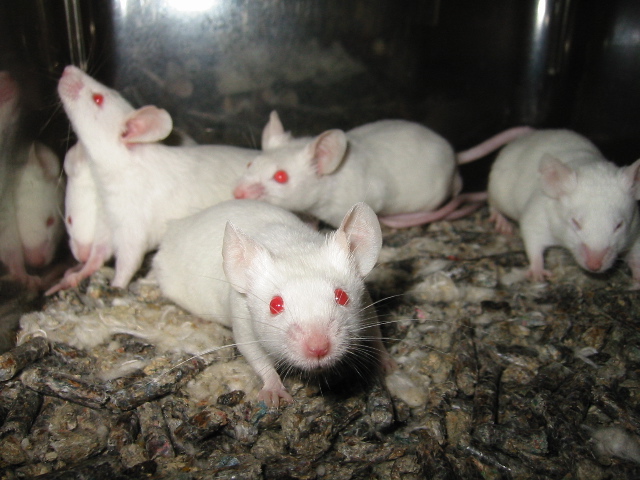
Model Organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Research using animal models has been central to most of the achievements of modern medicine. It has contributed most of the basic knowledge in fields such as human physiology and biochemistry, and has played significant roles in fields such as neuroscience and infectious disease. The results have included the near- eradication of polio and the development of organ transplantation, and have benefited both humans and animals. From 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
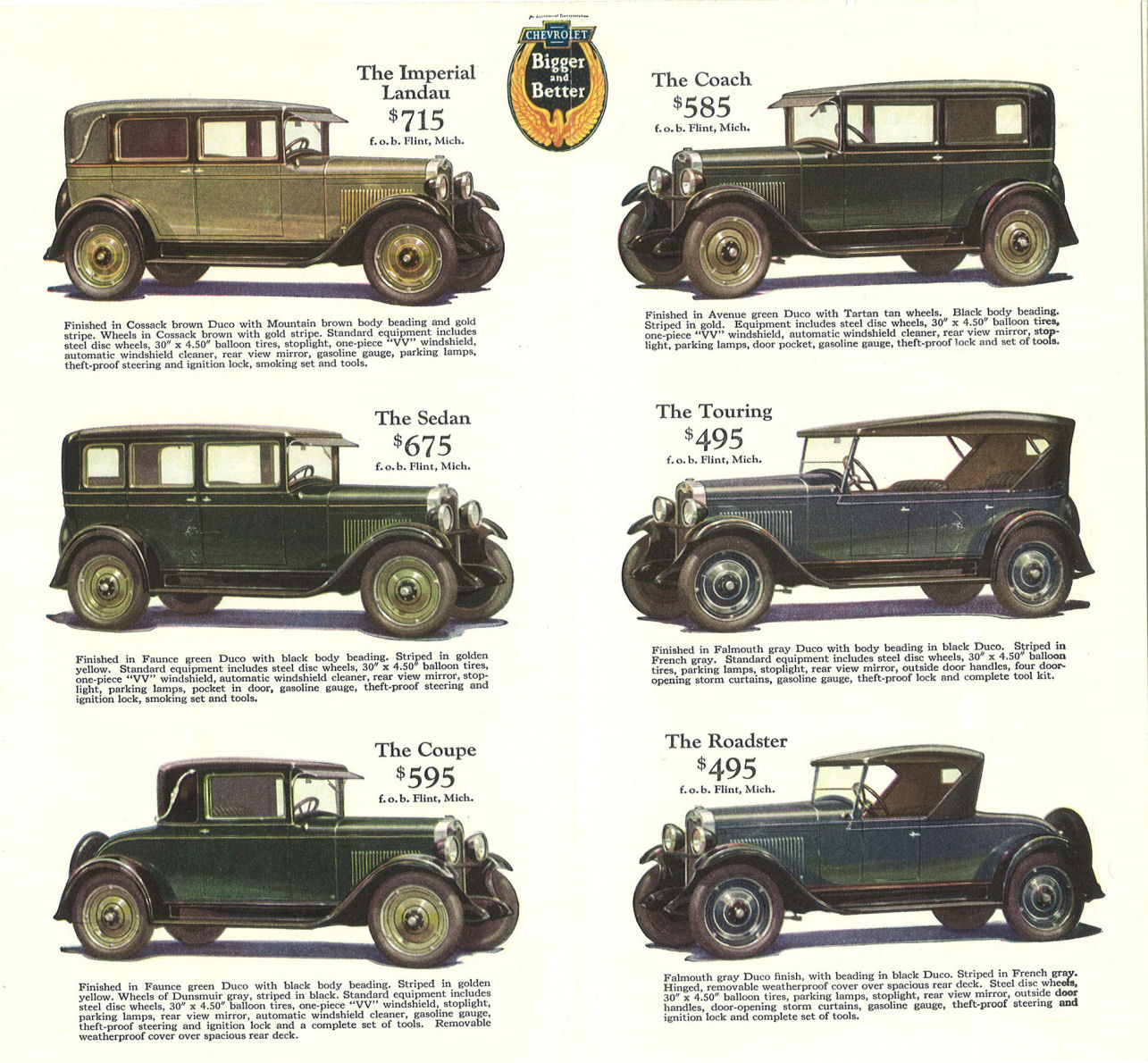
Car Model
The model of a car is its design, in the context of the manufacturer's range or series of cars. Different models, variants are distinguishable by technology, components, underpinnings, and/or style and appearance. The methods used to categorise cars into models differ significantly between manufacturers. Frequently, several different body variants are offered, depending on market demand; and when completing their 'production lifespan', sufficiently successful models are usually followed by a new 'generation' of that model. The name of a model (range or series) is almost always trademarked, so that competing manufacturers cannot also use it (unless the owner permits it, for an agreed licence fee). A popular model can have a significantly valuable brand, brand name, and manufacturers often take great care in fostering and maintaining the brand image of the models bearing the name, both in terms of key model characteristics, as well as the targeted market, and the expected or desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |