|
Model Transformation
A model transformation, in model-driven engineering, is an automated way of modifying and creating platform-specific model from platform-independent ones. An example use of model transformation is ensuring that a family of models is consistent, in a precise sense which the software engineer can define. The aim of using a model transformation is to save effort and reduce errors by automating the building and modification of models where possible. Overview Model transformations can be thought of as programs that take models as input. There is a wide variety of kinds of model transformation and uses of them, which differ in their inputs and outputs and also in the way they are expressed. A model transformation usually specifies which models are acceptable as input, and if appropriate what models it may produce as output, by specifying the metamodel to which a model must conform. Classification of model transformations Model transformations and languages for them have been clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model-driven Engineering
Model-driven engineering (MDE) is a software development methodology that focuses on creating and exploiting domain models, which are conceptual model (computer science), conceptual models of all the topics related to a specific problem. Hence, it highlights and aims at representation (mathematics), abstract representations of the Knowledge representation and reasoning, knowledge and activities that govern a particular domain (software engineering), application domain, rather than the computing (i.e. algorithmic) concepts. MDE is a subfield of a software design approach referred as round-trip engineering. The scope of the MDE is much wider than that of the model-driven architecture, Model-Driven Architecture. Overview The MDE approach is meant to increase productivity by maximizing compatibility between systems (via reuse of standardized models), simplifying the process of design (via models of recurring design patterns in the application domain), and promoting communication betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Soley
Richard Mark Soley (born c. 1960, in Baltimore, Maryland, died 8 Nov., 2023, in Lexington, Massachusetts) was an American computer scientist and businessman, and chairman and CEO of the Object Management Group, Inc. (OMG). He was also the executive director of the Cloud Standards Customer Council, and executive director of the Industrial Internet Consortium, managed by the OMG. Life and work Soley studied Computer Science and Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he obtained his S.B. in 1982, his S.M. in 1985 and his Ph.D. in 1989. He began his professional life at Honeywell, working on the Multics operating system. Soley joined OMG as Technical Director in 1989, leading the development of OMG's standardization process and the original CORBA specification. In 1996, he led the effort to move into vertical market standards (starting with healthcare, finance, telecommunications and manufacturing) and modeling. Those efforts made OMG a major early adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Publishing
Springer Publishing Company is an American publishing company of academic journals and books, focusing on the fields of nursing, gerontology, psychology, social work, counseling, public health, and rehabilitation (neuropsychology). It was established in 1951 by Bernhard Springer, a great-grandson of Julius Springer, and is based in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. History Springer Publishing Company was founded in 1950 by Bernhard Springer, the Berlin-born great-grandson of Julius Springer, who founded Springer Science+Business Media, Springer-Verlag (now Springer Science+Business Media). Springer Publishing's first landmark publications included ''Livestock Health Encyclopedia'' by R. Seiden and the 1952 ''Handbook of Cardiology for Nurses''. The company's books soon branched into other fields, including medicine and psychology. Nursing publications grew rapidly in number, as Modell's ''Drugs in Current Use'', a small annual paperback, sold over 150,000 copies over several edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
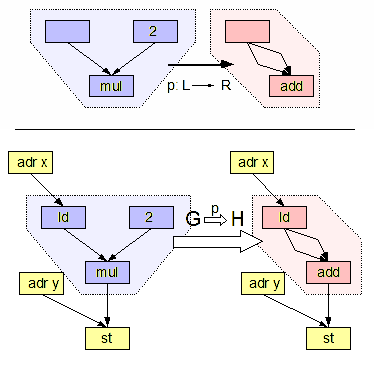
Graph Transformation
In computer science, graph transformation, or graph rewriting, concerns the technique of creating a new graph out of an original graph algorithmically. It has numerous applications, ranging from software engineering ( software construction and also software verification) to layout algorithms and picture generation. Graph transformations can be used as a computation abstraction. The basic idea is that if the state of a computation can be represented as a graph, further steps in that computation can then be represented as transformation rules on that graph. Such rules consist of an original graph, which is to be matched to a subgraph in the complete state, and a replacing graph, which will replace the matched subgraph. Formally, a graph rewriting system usually consists of a set of graph rewrite rules of the form L \rightarrow R, with L being called pattern graph (or left-hand side) and R being called replacement graph (or right-hand side of the rule). A graph rewrite rule is app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Transformation
In computing, data transformation is the process of converting data from one format or structure into another format or structure. It is a fundamental aspect of most data integrationCIO.com. Agile Comes to Data Integration. Retrieved from: https://www.cio.com/article/2378615/data-management/agile-comes-to-data-integration.html and data management tasks such as data wrangling, data warehousing, data integration and application integration. Data transformation can be simple or complex based on the required changes to the data between the source (initial) data and the target (final) data. Data transformation is typically performed via a mixture of manual and automated steps.DataXFormer. Morcos, Abedjan, Ilyas, Ouzzani, Papotti, Stonebraker. An interactive data transformation tool. Retrieved from: http://livinglab.mit.edu/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/DataXFormer-An-Interactive-Data-Transformation-Tool.pdf Tools and technologies used for data transformation can vary widely based on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Program Transformation
A program transformation is any operation that takes a computer program and generates another program. In many cases the transformed program is required to be semantically equivalent to the original, relative to a particular Formal semantics of programming languages, formal semantics and in fewer cases the transformations result in programs that semantically differ from the original in predictable ways. While the transformations can be performed manually, it is often more practical to use a List of Program Transformation Systems, program transformation system that applies specifications of the required transformations. Program transformations may be specified as automated procedures that modify compiler data structures (e.g. abstract syntax trees) representing the program text, or may be specified more conveniently using patterns or templates representing parameterized source code fragments. A practical requirement for source code transformation systems is that they be able to ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation (other)
Transformation may refer to: Science and mathematics In biology and medicine * Metamorphosis, the biological process of changing physical form after birth or hatching * Malignant transformation, the process of cells becoming cancerous * Transformation (genetics), genetic alteration of a cell by DNA uptake In mathematics * Transformation (function), concerning functions from sets to themselves. For functions in the broader sense, see function (mathematics). **Affine transformation, in geometry **Linear transformation between modules in linear algebra. Also called a linear map. ***Transformation matrix which represent linear maps in linear algebra. *Integral transform, between a function in one domain to a function in another * Natural transformation between functors in category theory. * Unitary transformation, between two Hilbert spaces * Geometric transformation, between sets of points in geometry **Infinitesimal transformation, a limiting case of a geometrical transformatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Program Refinement
Refinement is a generic term of computer science that encompasses various approaches for producing correct computer programs and simplifying existing programs to enable their formal verification. Program refinement In formal methods, program refinement is the verifiable transformation of an ''abstract'' (high-level) formal specification into a ''concrete'' (low-level) executable program. '' Stepwise refinement'' allows this process to be done in stages. Logically, refinement normally involves implication, but there can be additional complications. The progressive just-in-time preparation of the product backlog (requirements list) in agile software development approaches, such as Scrum, is also commonly described as refinement. Data refinement Data refinement is used to convert an abstract data model (in terms of sets for example) into implementable data structures (such as arrays). Operation refinement converts a specification of an operation on a system into an implementab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain-specific Language
A domain-specific language (DSL) is a computer language specialized to a particular application domain. This is in contrast to a general-purpose language (GPL), which is broadly applicable across domains. There are a wide variety of DSLs, ranging from widely used languages for common domains, such as HTML for web pages, down to languages used by only one or a few pieces of software, such as MUSH soft code. DSLs can be further subdivided by the kind of language, and include domain-specific ''markup'' languages, domain-specific ''modeling'' languages (more generally, specification languages), and domain-specific ''programming'' languages. Special-purpose computer languages have always existed in the computer age, but the term "domain-specific language" has become more popular due to the rise of domain-specific modeling. Simpler DSLs, particularly ones used by a single application, are sometimes informally called mini-languages. The line between general-purpose languages and doma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platform-specific Model
A platform-specific model is a model of a software or business system that is linked to a specific technological platform (e.g. a specific programming language, operating system, document file format or database). Platform-specific models are indispensable for the actual implementation of a system. For example, if a business needs to implement an online shop, then their software system will need to store different kinds of information: available goods, user info such as credit cards, etc. The designer might decide to use for this purpose an Oracle database. For this to work, the designer will need to express concepts (e.g. the concept of a user) in a relational model using the Oracle's SQL dialect. This Oracle's specific relational model is an example of a ''Platform-specific model''. In Model-driven architecture, a platform-specific model is where the design of the model is constructed with the intended execution-platform driving design choices. Related Concepts * ATLAS Tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model-driven Architecture
Model-driven architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001."OMG pursues new strategic direction to build on success of past efforts" Overview Model Driven Architecture® (MDA®) "provides an approach for deriving value from models and architecture in support of the full life cycle of physical, organizational and I.T. systems". A model is a (representation of) an abstraction of a system. MDA® provides value by producing models ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |