Graph transformation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
AGG
the attributed graph grammar system (
GP 2
is a visual rule-based graph programming language designed to facilitate formal reasoning over graph programs. *
GMTE
, the Graph Matching and Transformation Engine for graph matching and transformation. It is an implementation of an extension of Messmer’s algorithm using C++. ** GrGen.NET, the graph rewrite generator, a graph transformation tool emitting C#-code or .NET-assemblies. *
GROOVE
a Java-based tool set for editing graphs and graph transformation rules, exploring the state spaces of graph grammars, and model checking those state spaces; can also be used as a graph transformation engine. *
Verigraph
a software specification and verification system based on graph rewriting ( Haskell). * Tools that solve
eMoflon
an EMF-compliant model-transformation tool with support for Story-Driven Modeling and Triple Graph Grammars. ** a graph rewriting system based on EMF, supporting in-place and model-to-model transformation. *
Fujaba
uses Story driven modelling, a graph rewrite language based on PROGRES. ** Graph databases often support dynamic rewriting of graphs. **
Gremlin
a graph-based programming language (se
Graph Rewriting
. *
Henshin
a graph rewriting system based on EMF, supporting in-place and model-to-model transformation, critical pair analysis, and model checking. *
PROGRES
an integrated environment and very high level language for PROgrammed Graph REwriting Systems. ** VIATRA. * Mechanical engineering tools *
GraphSynth
is an interpreter and UI environment for creating unrestricted graph grammars as well as testing and searching the resultant language variant. It saves graphs and graph grammar rules as
Soley Studio
is an
Functional-structural plant modeling with a graph grammar based language
*
Multicellular development modeling with string-regulated graph grammars
*
Kappa
is a rule-based language for modeling systems of interacting agents, primarily motivated by molecular systems biology. * Artificial Intelligence/Natural Language Processing ** OpenCog provides a basic pattern matcher (on hypergraphs) which is used to implement various AI algorithms. *
RelEx
is an English-language parser that employs graph re-writing to convert a link parse into a dependency parse. * Computer programming language ** The Clean programming language is implemented using graph rewriting.
Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science
148 (1 SPEC. ISS.), pp. 187–198. * König, Barbara (2004). ''Analysis and Verification of Systems with Dynamically Evolving Structure''
Habilitation thesis, Universität Stuttgart
, pp. 65–180. * * * * {{refend
computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
, graph transformation, or graph rewriting, concerns the technique of creating a new graph out of an original graph algorithmically. It has numerous applications, ranging from software engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principl ...
( software construction and also software verification) to layout algorithms and picture generation.
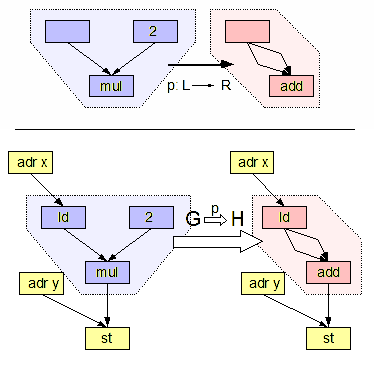
Graph transformations can be used as a computation abstraction. The basic idea is that if the state of a computation can be represented as a graph, further steps in that computation can then be represented as transformation rules on that graph. Such rules consist of an original graph, which is to be matched to a subgraph in the complete state, and a replacing graph, which will replace the matched subgraph.
Formally, a graph rewriting system usually consists of a set of graph rewrite rules of the form , with being called pattern graph (or left-hand side) and being called replacement graph (or right-hand side of the rule). A graph rewrite rule is applied to the host graph by searching for an occurrence of the pattern graph ( pattern matching, thus solving the subgraph isomorphism problem) and by replacing the found occurrence by an instance of the replacement graph. Rewrite rules can be further regulated in the case of labeled graphs, such as in string-regulated graph grammars.
Sometimes graph grammar is used as a synonym for ''graph rewriting system'', especially in the context of formal languages; the different wording is used to emphasize the goal of constructions, like the enumeration of all graphs from some starting graph, i.e. the generation of a graph language – instead of simply transforming a given state (host graph) into a new state.
Graph rewriting approaches

Algebraic approach
The algebraic approach to graph rewriting is based uponcategory theory
Category theory is a general theory of mathematical structures and their relations. It was introduced by Samuel Eilenberg and Saunders Mac Lane in the middle of the 20th century in their foundational work on algebraic topology. Category theory ...
. The algebraic approach is further divided into sub-approaches, the most common of which are the '' double-pushout (DPO) approach'' and the '' single-pushout (SPO) approach''. Other sub-approaches include the ''sesqui-pushout'' and the ''pullback approach''.
From the perspective of the DPO approach a graph rewriting rule is a pair of morphisms in the category of graphs and graph homomorphisms between them: , also written , where is injective. The graph K is called ''invariant'' or sometimes the ''gluing graph''. A '' rewriting step'' or ''application'' of a rule r to a ''host graph'' G is defined by two pushout diagrams both originating in the same morphism , where D is a ''context graph'' (this is where the name ''double''-pushout comes from). Another graph morphism models an occurrence of L in G and is called a '' match''. Practical understanding of this is that is a subgraph that is matched from (see subgraph isomorphism problem), and after a match is found, is replaced with in host graph where serves as an interface, containing the nodes and edges which are preserved when applying the rule. The graph is needed to attach the pattern being matched to its context: if it is empty, the match can only designate a whole connected component of the graph .
In contrast a graph rewriting rule of the SPO approach is a single morphism in the category of labeled multigraphs and ''partial mappings'' that preserve the multigraph structure: . Thus a rewriting step is defined by a single pushout diagram. Practical understanding of this is similar to the DPO approach. The difference is, that there is no interface between the host graph G and the graph G' being the result of the rewriting step.
From the practical perspective, the key distinction between DPO and SPO is how they deal with the deletion of nodes with adjacent edges, in particular, how they avoid that such deletions may leave behind "dangling edges". The DPO approach only deletes a node when the rule specifies the deletion of all adjacent edges as well (this ''dangling condition'' can be checked for a given match), whereas the SPO approach simply disposes the adjacent edges, without requiring an explicit specification.
There is also another algebraic-like approach to graph rewriting, based mainly on Boolean algebra and an algebra of matrices, called ''matrix graph grammars''.
Determinate graph rewriting
Yet another approach to graph rewriting, known as ''determinate'' graph rewriting, came out oflogic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
and database theory. In this approach, graphs are treated as database instances, and rewriting operations as a mechanism for defining queries and views; therefore, all rewriting is required to yield unique results ( up to isomorphism), and this is achieved by applying any rewriting rule concurrently throughout the graph, wherever it applies, in such a way that the result is indeed uniquely defined.
Term graph rewriting
Another approach to graph rewriting is term graph rewriting, which involves the processing or transformation of term graphs (also known as ''abstract semantic graphs'') by a set of syntactic rewrite rules. Term graphs are a prominent topic in programming language research since term graph rewriting rules are capable of formally expressing a compiler's operational semantics. Term graphs are also used as abstract machines capable of modelling chemical and biological computations as well as graphical calculi such as concurrency models. Term graphs can perform automated verification and logical programming since they are well-suited to representing quantified statements in first order logic. Symbolic programming software is another application for term graphs, which are capable of representing and performing computation with abstract algebraic structures such as groups, fields and rings. The TERMGRAPH conference focuses entirely on research into term graph rewriting and its applications.Classes of graph grammar and graph rewriting system
Graph rewriting systems naturally group into classes according to the kind of representation of graphs that are used and how the rewrites are expressed. The term graph grammar, otherwise equivalent to graph rewriting system or graph replacement system, is most often used in classifications. Some common types are: * Attributed graph grammars, typically formalised using either the single-pushout approach or the double-pushout approach to characterising replacements, mentioned in the above section on the algebraic approach to graph rewriting. * Hypergraph grammars, including as more restrictive subclasses port graph grammars, linear graph grammars and interaction nets.Implementations and applications
Graphs are an expressive, visual and mathematically precise formalism for modelling of objects (entities) linked by relations; objects are represented by nodes and relations between them by edges. Nodes and edges are commonly typed and attributed. Computations are described in this model by changes in the relations between the entities or by attribute changes of the graph elements. They are encoded in graph rewrite/graph transformation rules and executed by graph rewrite systems/graph transformation tools. * Tools that are application domain neutral: *AGG
the attributed graph grammar system (
Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
).
*GP 2
is a visual rule-based graph programming language designed to facilitate formal reasoning over graph programs. *
GMTE
, the Graph Matching and Transformation Engine for graph matching and transformation. It is an implementation of an extension of Messmer’s algorithm using C++. ** GrGen.NET, the graph rewrite generator, a graph transformation tool emitting C#-code or .NET-assemblies. *
GROOVE
a Java-based tool set for editing graphs and graph transformation rules, exploring the state spaces of graph grammars, and model checking those state spaces; can also be used as a graph transformation engine. *
Verigraph
a software specification and verification system based on graph rewriting ( Haskell). * Tools that solve
software engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principl ...
tasks (mainly MDA) with graph rewriting:
*eMoflon
an EMF-compliant model-transformation tool with support for Story-Driven Modeling and Triple Graph Grammars. ** a graph rewriting system based on EMF, supporting in-place and model-to-model transformation. *
Fujaba
uses Story driven modelling, a graph rewrite language based on PROGRES. ** Graph databases often support dynamic rewriting of graphs. **
GReAT
Great may refer to:
Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
* Artel Great (bo ...
.
*Gremlin
a graph-based programming language (se
Graph Rewriting
. *
Henshin
a graph rewriting system based on EMF, supporting in-place and model-to-model transformation, critical pair analysis, and model checking. *
PROGRES
an integrated environment and very high level language for PROgrammed Graph REwriting Systems. ** VIATRA. * Mechanical engineering tools *
GraphSynth
is an interpreter and UI environment for creating unrestricted graph grammars as well as testing and searching the resultant language variant. It saves graphs and graph grammar rules as
XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
files and is written in C#.
*Soley Studio
is an
integrated development environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ...
for graph transformation systems. Its main application focus is data analytics in the field of engineering.
* Biology applications
*Functional-structural plant modeling with a graph grammar based language
*
Multicellular development modeling with string-regulated graph grammars
*
Kappa
is a rule-based language for modeling systems of interacting agents, primarily motivated by molecular systems biology. * Artificial Intelligence/Natural Language Processing ** OpenCog provides a basic pattern matcher (on hypergraphs) which is used to implement various AI algorithms. *
RelEx
is an English-language parser that employs graph re-writing to convert a link parse into a dependency parse. * Computer programming language ** The Clean programming language is implemented using graph rewriting.
See also
*Graph theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of ''graph (discrete mathematics), graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of ''Vertex (graph ...
* Shape grammar
*Formal grammar
A formal grammar is a set of Terminal and nonterminal symbols, symbols and the Production (computer science), production rules for rewriting some of them into every possible string of a formal language over an Alphabet (formal languages), alphabe ...
* Abstract rewriting — a generalization of graph rewriting
References
Citations
Sources
* . * . * Heckel, R. (2006). ''Graph transformation in a nutshell''Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science
148 (1 SPEC. ISS.), pp. 187–198. * König, Barbara (2004). ''Analysis and Verification of Systems with Dynamically Evolving Structure''
Habilitation thesis, Universität Stuttgart
, pp. 65–180. * * * * {{refend