|
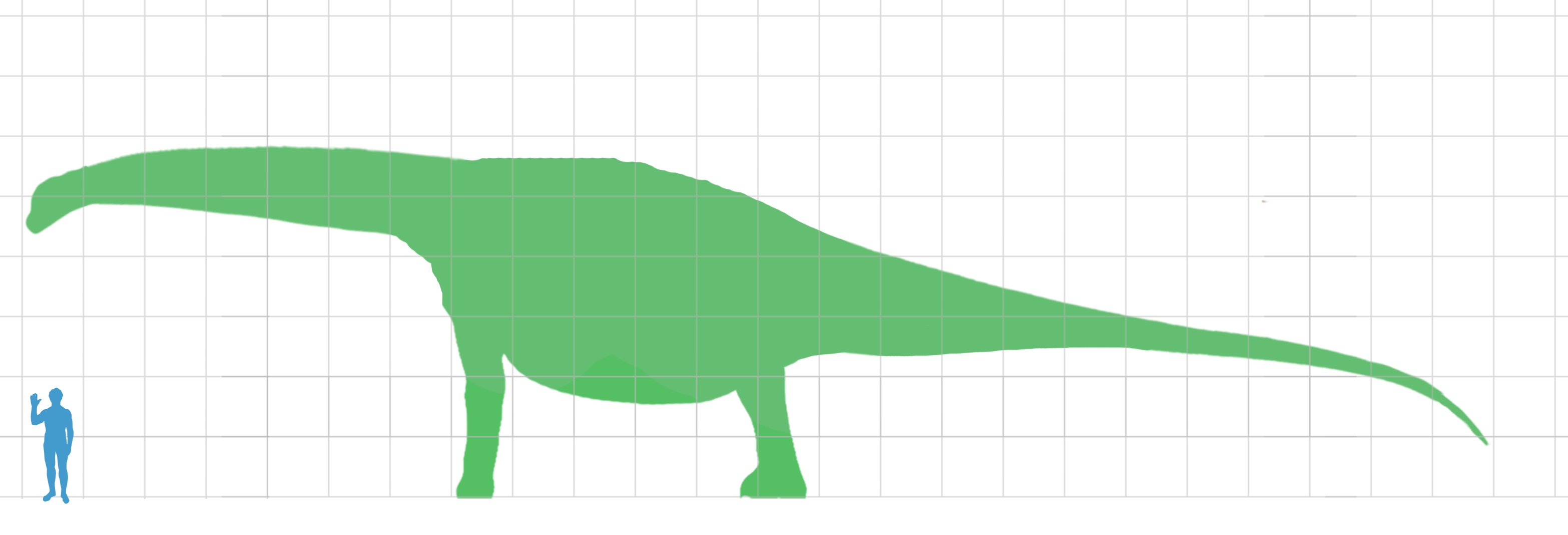
Moabosaurus Utahensis Restoration
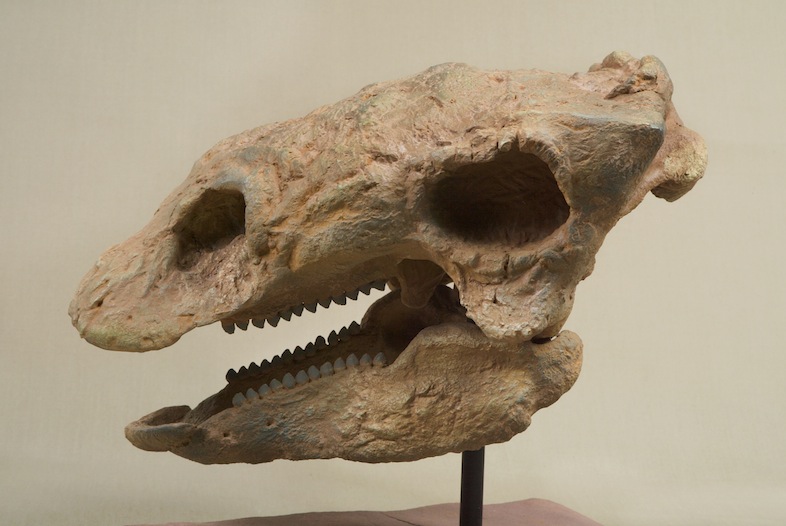
''Moabosaurus'' (meaning " Moab reptile") is a genus of turiasaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Cedar Mountain Formation of Utah, United States. Description ''Moabosaurus'' is characterized by a suite of features including: extremely low neural spines that are thin, transverse ridges in the posterior cervical vertebrae and anterior dorsal vertebrae; strongly procoelous proximal and distal caudal vertebrae; and an ulna with well-developed lateral and medial anteroproximal ridges combined with a large olecranon process. According to the 2017 article which officially named and described ''Moabosaurus'', the animal was said to reach 10 meters (32.8 feet) long. However, the specimens which were examined belonged to juveniles and sub-adults, so it's possible that the creature measured longer when fully-grown. Discovery and naming ''Moabosaurus'' was collected from the Dalton Wells Quarry, which is about 20 km northwest of Moab, Utah. The quarry produced parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kerguelen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turiasaurus
''Turiasaurus'' (meaning " Turia lizard") is a genus of sauropod dinosaurs. It is known from a single fossil specimen representing the species ''Turiasaurus riodevensis'', found in the Kimmeridgian Villar del Arzobispo Formation of Teruel, Spain. Description ''Turiasaurus'' is believed to be the largest dinosaur ever found in Europe, and is among the largest dinosaurs known. It is estimated at in length and with a weight of .Royo-Torres, R., Cobos, A., and Alcalá, L. (2006). "A Giant European Dinosaur and a New Sauropod Clade." ''Science'' 314: 1925-1927.Paul, G.S., 2010, The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs, Princeton University Press. The length of its skull is 70 centimetres, which is not too large. According to the paleontologist Luis Alcalá, this is because a larger head might have caused ''Turiasaurus'' to break its neck. Phylogenetic analysis shows that ''Turiasaurus'' lies outside of the Neosauropoda division and belongs to a new clade, Turiasauria, together wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2017 In Archosaur Paleontology
The year 2017 in archosaur paleontology was eventful. Archosaurs include the only living dinosaur group — birds — and the reptile crocodilians, plus all extinct dinosaurs, extinct crocodilian relatives, and pterosaurs. Archosaur palaeontology is the scientific study of those animals, especially as they existed before the Holocene Epoch began about 11,700 years ago. The year 2017 in paleontology included various significant developments regarding archosaurs. This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that have been described during the year 2017, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that occurred in the year 2017. General research * A study on the evolution of forelimb anatomy, musculature and joint ranges of motion from early archosaurs to sauropodomorph dinosaurs based on data from ''Mussaurus patagonicus'' and extant freshwater crocodile is published by Otero ''et al.'' (2017). Pseudosuchians Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neochoristodera
Neochoristodera is a lineage of specialised crocodile-like fully aquatic choristodere reptiles. Noted for their long jaws and large size, these animals were predominant across the Northern Hemisphere, occurring in freshwater and coastal environments across the Cretaceous and early Cenozoic. Systematics Neochoristoderes form a monophyletic group, however there is no consensus about the relationships of the genera, which have been recovered as a polytomy in recent studies. Neochoristodera contains the named genera ''Champsosaurus'', '' Ikechosaurus'', ''Kosmodraco'', ''Liaoxisaurus'', '' Mengshanosaurus'', ''Simoedosaurus'' and ''Tchoiria''. Various taxa of uncertain affinities within this group are known, including a partial femur of a choristodere, possibly of a neochoristodere from the Cedar Mountain Formation of the United States and an indeterminate partial skeleton from the Kuwajima Formation of Japan. Evolution Neochoristoderes first appear in the Early Cretaceous of Asia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bones develop from ribs that grow sideways and develop into broad flat plates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodilia
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living relatives of birds, as the two groups are the only known survivors of the Archosauria. Members of the order's total group, the clade Pseudosuchia, appeared about 250 million years ago in the Early Triassic period, and diversified during the Mesozoic era. The order Crocodilia includes the true crocodiles (family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term 'crocodiles' is sometimes used to refer to all of these, crocodilians is a less ambiguous vernacular term for members of this group. Large, solidly built, lizard-like reptiles, crocodilians have long flattened snouts, laterally compressed tails, and eyes, ears, and nostrils at the top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight. Their wings were formed by a membrane of skin, muscle, and other tissues stretching from the ankles to a dramatically lengthened fourth finger. There were two major types of pterosaurs. Basal pterosaurs (also called 'non-pterodactyloid pterosaurs' or 'rhamphorhynchoids') were smaller animals with fully toothed jaws and, typically, long tails. Their wide wing membranes probably included and connected the hind legs. On the ground, they would have had an awkward sprawling posture, but the anatomy of their joints and strong claws would have made them effective climbers, and some may have even lived in trees. Basal pterosaurs were insectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastonia (dinosaur)
''Gastonia'' is a genus of herbivorous ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of North America, around 139 to 125 million years ago. It is often considered a nodosaurid closely related to ''Polacanthus''. ''Gastonia'' has a sacral shield and large shoulder spikes. Discovery and species The type specimen of ''Gastonia burgei'' ( CEUM 1307) was discovered in a bonebed from the limestone strata of the lower Cedar Mountain Formation in Yellow Cat Quarry, Grand County, eastern Utah, the type specimen consisting of a single skull. The type specimen was found alongside 4 partial skeletons of ''Gastonia that'' were placed as paratypes, along with the type specimen of ''Utahraptor'' and an Iguanodontid. ''Gastonia'' is among the most common dinosaur fossils in the Cedar Mountain Formation, with many individuals being found across several quarries in the southwest.Kirkland, J.I. (1998). A polacanthine ankylosaur (Ornithischia: Dinosauria) from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iguanodontia
Iguanodontia (the iguanodonts) is a clade of herbivorous dinosaurs that lived from the Middle Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. Some members include ''Camptosaurus'', ''Dryosaurus'', ''Iguanodon'', ''Tenontosaurus'', and the hadrosaurids or "duck-billed dinosaurs". Iguanodontians were one of the first groups of dinosaurs to be found. They are among the best known of the dinosaurs, and were among the most diverse and widespread herbivorous dinosaur groups of the Cretaceous period. Classification Iguanodontia is often listed as an infraorder within a suborder Ornithopoda, though Benton (2004) lists Ornithopoda as an infraorder and does not rank Iguanodontia. Traditionally, iguanodontians were grouped into the superfamily Iguanodontoidea and family Iguanodontidae. However, phylogenetic studies show that the traditional "iguanodontids" are a paraphyletic grade leading up to the hadrosaurs (duck-billed dinosaurs). Groups like Iguanodontoidea are sometimes still used as unranked clades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nedcolbertia
''Nedcolbertia'' is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Period of North America. Discovery and naming Three skeletons of a theropod were discovered in 1993 by Christopher Whittle near Cisco in the basal Yellow Cat Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation of Utah, dating to the Valanginian. These were subsequently studied and reported in 1995 by Kirkland, Britt, Madsen and Burge.J. I. Kirkland, C. H. Whittle, B. B. Britt, S. Madsen and D. Burge. A Small Theropod from the Basal Cedar Mountain Formation (Lower Cretaceous, Barremian) of Eastern Utah. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 15(3), 39A (1995). Though in 1996 it had been announced that the taxon would be named "Nedcolbertia whittlei", in 1998 it was actually described and named by Kirkland, Whittle, Britt, Madsen and Burge as the type species ''Nedcolbertia justinhofmanni''. The generic name honours the American palaeontologist Edwin Harris Colbert, known as "Ned" to his friends. The specific name honou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utahraptor
''Utahraptor'' (meaning "Utah's thief") is a genus of large dromaeosaurid dinosaur that lived in North America during the Early Cretaceous period. It was a heavy-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore. It contains a single species, ''Utahraptor ostrommaysi'', which is one of the largest-known members of the family Dromaeosauridae, measuring long and weighing . Discovery and naming The first specimens of ''Utahraptor'' were found in 1975 by Jim Jensen in the Dalton Wells Quarry in east-central Utah, near the town of Moab, but did not receive much attention. After a find of a large foot-claw by Carl Limone in October 1991, James Kirkland, Robert Gaston, and Donald Burge uncovered further remains of ''Utahraptor'' in 1991 in the Gaston Quarry in Grand County, Utah, within the Yellow Cat and Poison Strip members of the Cedar Mountain Formation. The holotype of ''Utahraptor'', CEUM 184v.86 consists of a second pedal ungual, with potentially assigned elements from other specim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venenosaurus
''Venenosaurus'' ( ) was a sauropod dinosaur. The name literally means "poison lizard", and it was named so after the Poison Strip Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation in Utah, United States, where the fossils were discovered by a Denver Museum of Natural History volunteer Tony DiCroce in 1998. ''Venenosaurus dicrocei'' was first described as a new species in 2001 by Virginia Tidwell, Kenneth Carpenter, and Suzanne Meyer. ''Venenosaurus'' is a relatively small titanosauriform sauropod, measuring long and weighing . It is known from an incomplete skeleton of an adult and a juvenile. The holotype is DMNH 40932 Denver Museum of Natural History. The specimen consisted of tail vertebrae, the left scapula, right radius, left ulna, metacarpals, forefoot phalanges, right pubis, left and right ischia, metatarsals, chevrons, and ribs. Geological and environmental context The ''Venenosaurus'' type specimen was found in the Early Cretaceous (Aptian-Albian) Poison Strip Member of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |