|
Mittelhochdeutsch
Middle High German (MHG; german: Mittelhochdeutsch (Mhd.)) is the term for the form of German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High German and into Early New High German. High German is defined as those varieties of German which were affected by the Second Sound Shift; the Middle Low German and Middle Dutch languages spoken to the North and North West, which did not participate in this sound change, are not part of MHG. While there is no ''standard'' MHG, the prestige of the Hohenstaufen court gave rise in the late 12th century to a supra-regional literary language (') based on Swabian, an Alemannic dialect. This historical interpretation is complicated by the tendency of modern editions of MHG texts to use ''normalised'' spellings based on this variety (usually called "Classical MHG"), which make the written language appear more consistent than it actually is in the manuscripts. Scholars are uncertain as to w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High German Consonant Shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development (sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probably began between the third and fifth centuries and was almost complete before the earliest written records in High German were produced in the eighth century. From Proto-Germanic, the resulting language, Old High German, can be neatly contrasted with the other continental West Germanic languages, which for the most part did not experience the shift, and with Old English, which remained completely unaffected. General description The High German consonant shift altered a number of consonants in the southern German dialects – which includes Standard German, Yiddish, and Luxembourgish – and so explains why many German words have different consonants from the related words in English, Dutch and the Scandinavian languages. The term is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
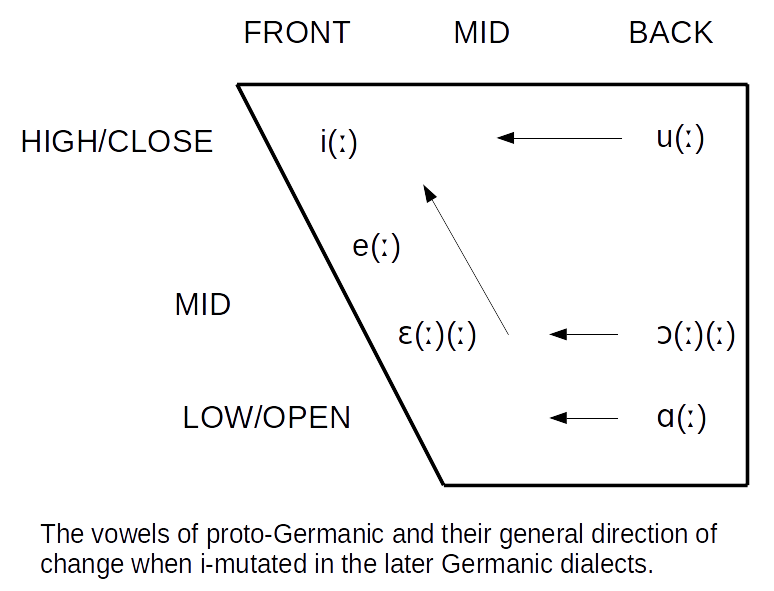
Germanic Umlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel ( fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to (raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around AD 450 or 500 and affected all of the early languages except Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong verbs such as ''sing/sang/sung''. While Germanic umlaut has had important consequences for all modern Germanic languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. " Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented in writing since about 1225/34 (''Sachsenspiegel''). During the Hanseatic period (from about 1300 to about 1600), Middle Low German was the leading written language in the north of Central Europe and served as a lingua franca in the northern half of Europe. It was used parallel to medieval Latin also for purposes of diplomacy and for deeds. Terminology While ''Middle Low German'' (MLG) is a scholarly term developed in hindsight, speakers in their time referred to the language mainly as (Saxon) or (the Saxon language). This terminology was also still known in Luther's time in the adjacent Central German-speaking areas. Its Latin equivalent was also used as meaning 'Low German' (among other meanings). Some languages whose first contacts w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050. There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High German is an umbrella term for the group of continental West Germanic dialects which underwent the set of consonantal changes called the Second Sound Shift. At the start of this period, the main dialect areas belonged to largely independent tribal kingdoms, but by 788 the conquests of Charlemagne had brought all OHG dialect areas into a single polity. The period also saw the development of a stable linguistic border between German and Gallo-Romance, later French. The surviving OHG texts were all written in monastic scriptoria and, as a result, the overwhelming majority of them are religious in nature or, when secular, belong to the Latinate literary culture of Christianity. The earliest written texts in Old High German, glosses and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Central German
East Central German or East Middle German (german: Ostmitteldeutsch) is the eastern non-Franconian languages, Franconian Central German language and is part of High German languages, High German. Present-day Standard German as a High German languages, High German variant, has actually developed from a compromise of East Central (especially Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon that was promoted by Johann Christoph Gottsched) and East Franconian German. East Central German dialects are mainly spoken in Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany and parts of Brandenburg, and were formerly also spoken in Silesia and Bohemia. Dialects East Central German is spoken in large parts of what is today known as the cultural area of Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany (''Mitteldeutschland''). It comprises according to Glottolog: * Central East Middle German ** High Prussian dialect, High Prussian (''Hochpreußisch'') (nearly extinct) ** Thuringian dialect, Thuringian (''Thür ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew (notably Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish is primarily written in the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, its worldwide peak was 11 million, with the number of speakers in the United States and Canada then totaling 150,000. Eighty-five percent of the approximately six million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hambu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Ostsiedlung
(, literally "East-settling") is the term for the Early Medieval and High Medieval migration-period when ethnic Germans moved into the territories in the eastern part of Francia, East Francia, and the Holy Roman Empire (that Germans had already conquered) and beyond; and the consequences for settlement development and social structures in the areas of immigration. Generally sparsely and only relatively recently populated by Slavic, Baltic and Finnic peoples, the area of colonization, also known as , encompassed (with relation to modern-day countries) Germany east of the Saale and Elbe rivers, the states of Lower Austria and Styria in Austria, the Baltics, Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Hungary, and Transylvania in Romania. Since the 1980s, historians have interpreted the as a part of a civil and social development, termed the ''High Middle Age Land Consolidation'' ( de , Hochmittelalterlicher Landesausbau). In a pan-European intensification process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Final-obstruent Devoicing
Final-obstruent devoicing or terminal devoicing is a systematic phonological process occurring in languages such as Catalan, German, Dutch, Breton, Russian, Polish, Lithuanian, Turkish, and Wolof. In such languages, voiced obstruents in final position (at the end of a word) become voiceless before voiceless consonants and in pausa. The process can be written as *Cvoice/sub> → Cvoice/sub>/__#. Languages with final-obstruent devoicing Germanic languages Most modern continental West Germanic languages developed final devoicing, the earliest evidence appearing in Old Dutch around the 9th or 10th century. * Afrikaans * Dutch, also Old and Middle Dutch * (High) German, also Middle High German * Gothic (for fricatives) * Limburgish * Low German, also Middle Low German * Luxembourgish (only when not resyllabified) * Old English (for fricatives, inconsistently for ) * West Frisian. In contrast, North Frisian (and some Low German dialects in North Frisia that have a Frisian subst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to noun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, northwest of Hamburg. Its total length is . The Elbe's major tributaries include the rivers Vltava, Saale, Havel, Mulde, Schwarze Elster, and Ohře. The Elbe river basin, comprising the Elbe and its tributaries, has a catchment area of , the twelfth largest in Europe. The basin spans four countries, however it lies almost entirely just in two of them, Germany (65.5%) and the Czech Republic (33.7%, covering about two thirds of the state's territory). Marginally, the basin stretches also to Austria (0.6%) and Poland (0.2%). The Elbe catchment area is inhabited by 24.4 million people, the biggest cities within are Berlin, Hamburg, Prague, Dresden and Leipzig. Etymology Firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


