|
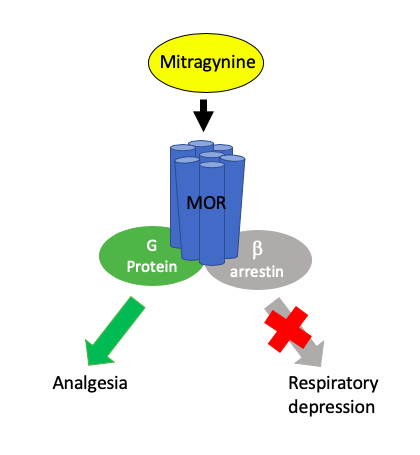
Mitragynine Biased Agonism
Mitragynine is an indole-based alkaloid and the most abundant active alkaloid in the Southeast Asian plant ''Mitragyna speciosa'', commonly known as ''kratom.'' The total alkaloid concentration in dried leaves ranges from 0.5 to 1.5%. In Thai varieties, mitragynine is the most abundant component (up to 66% of total alkaloids) while 7-hydroxymitragynine is a minor constituent (up to 2% of total alkaloid content). In Malaysian kratom varieties, mitragynine is present at lower concentration (12% of total alkaloids). Such preparations are orally consumed and typically involve dried kratom leaves which are brewed into tea or ground and placed into capsules. Mitragynine consumption for medicinal and recreation purposes dates back centuries, although early use was primarily limited to Southeast Asian countries such as Indonesia and Thailand where the plant grows indigenously. Recently, mitragynine use has spread throughout Europe and the Americas as both a recreational and medicinal drug. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C8 H7 N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indole is widely distributed in the natural environment and can be produced by a variety of bacteria. As an intercellular signal molecule, indole regulates various aspects of bacterial physiology, including spore formation, plasmid stability, resistance to drugs, biofilm formation, and virulence. The amino acid tryptophan is an indole derivative and the precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin. General properties and occurrence Indole is a solid at room temperature. It occurs naturally in human feces and has an intense fecal odor. At very low concentrations, however, it has a flowery smell, and is a constituent of many perfumes. It also occurs in coal tar. The corresponding substituent is called indolyl. Indole undergoes electrophilic substitution, mainly at position 3 (see diagra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which is processed chemically to produce heroin and other synthetic opioids for medicinal use and for the illegal drug trade. The latex also contains the closely related opiates codeine and thebaine, and non-analgesic alkaloids such as papaverine and noscapine. The traditional, labor-intensive method of obtaining the latex is to scratch ("score") the immature seed pods (fruits) by hand; the latex leaks out and dries to a sticky yellowish residue that is later scraped off and dehydrated. The word '' meconium'' (derived from the Greek for "opium-like", but now used to refer to newborn stools) historically referred to related, weaker preparations made from other parts of the opium poppy or different species of poppies. The production methods have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitragynine Biased Agonism
Mitragynine is an indole-based alkaloid and the most abundant active alkaloid in the Southeast Asian plant ''Mitragyna speciosa'', commonly known as ''kratom.'' The total alkaloid concentration in dried leaves ranges from 0.5 to 1.5%. In Thai varieties, mitragynine is the most abundant component (up to 66% of total alkaloids) while 7-hydroxymitragynine is a minor constituent (up to 2% of total alkaloid content). In Malaysian kratom varieties, mitragynine is present at lower concentration (12% of total alkaloids). Such preparations are orally consumed and typically involve dried kratom leaves which are brewed into tea or ground and placed into capsules. Mitragynine consumption for medicinal and recreation purposes dates back centuries, although early use was primarily limited to Southeast Asian countries such as Indonesia and Thailand where the plant grows indigenously. Recently, mitragynine use has spread throughout Europe and the Americas as both a recreational and medicinal drug. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
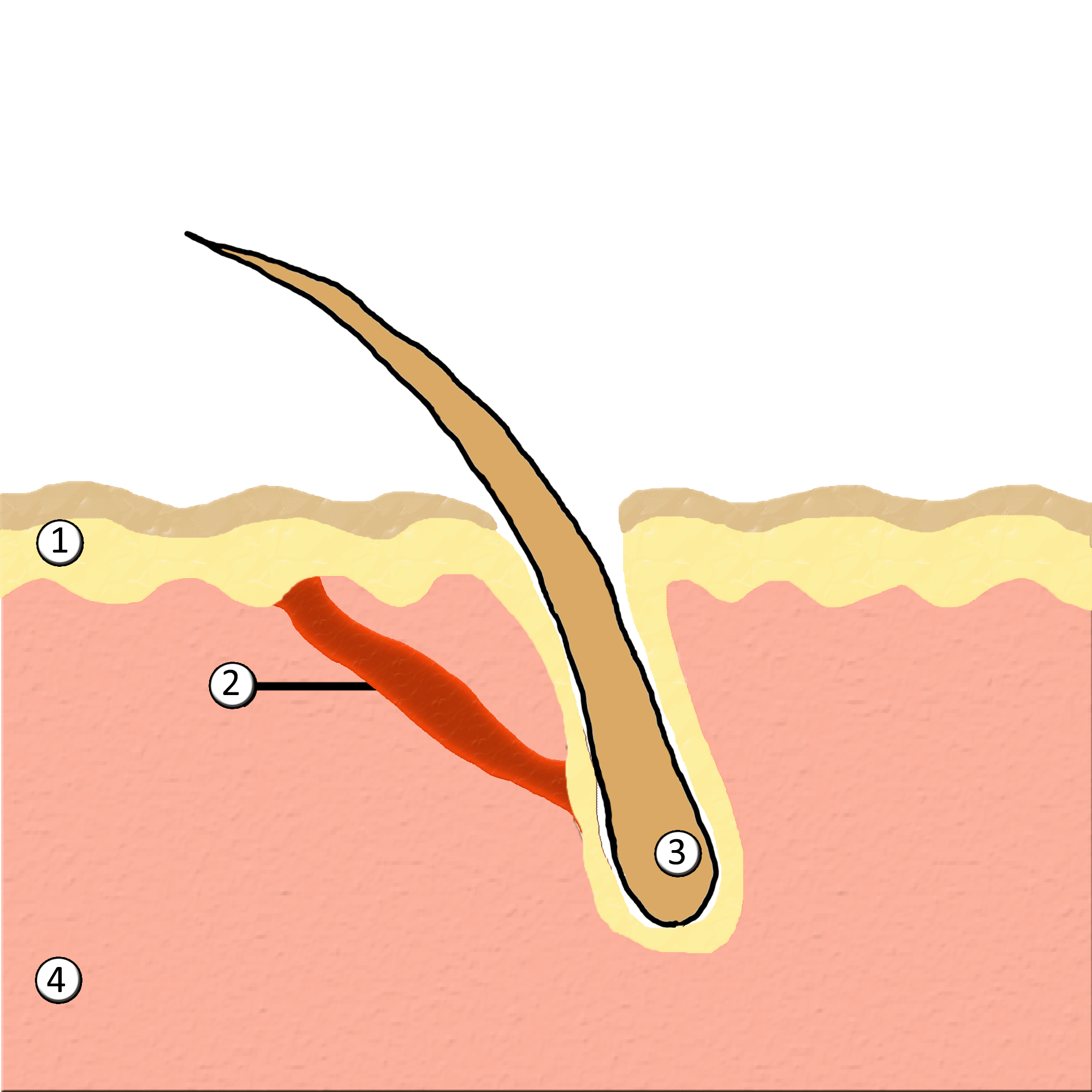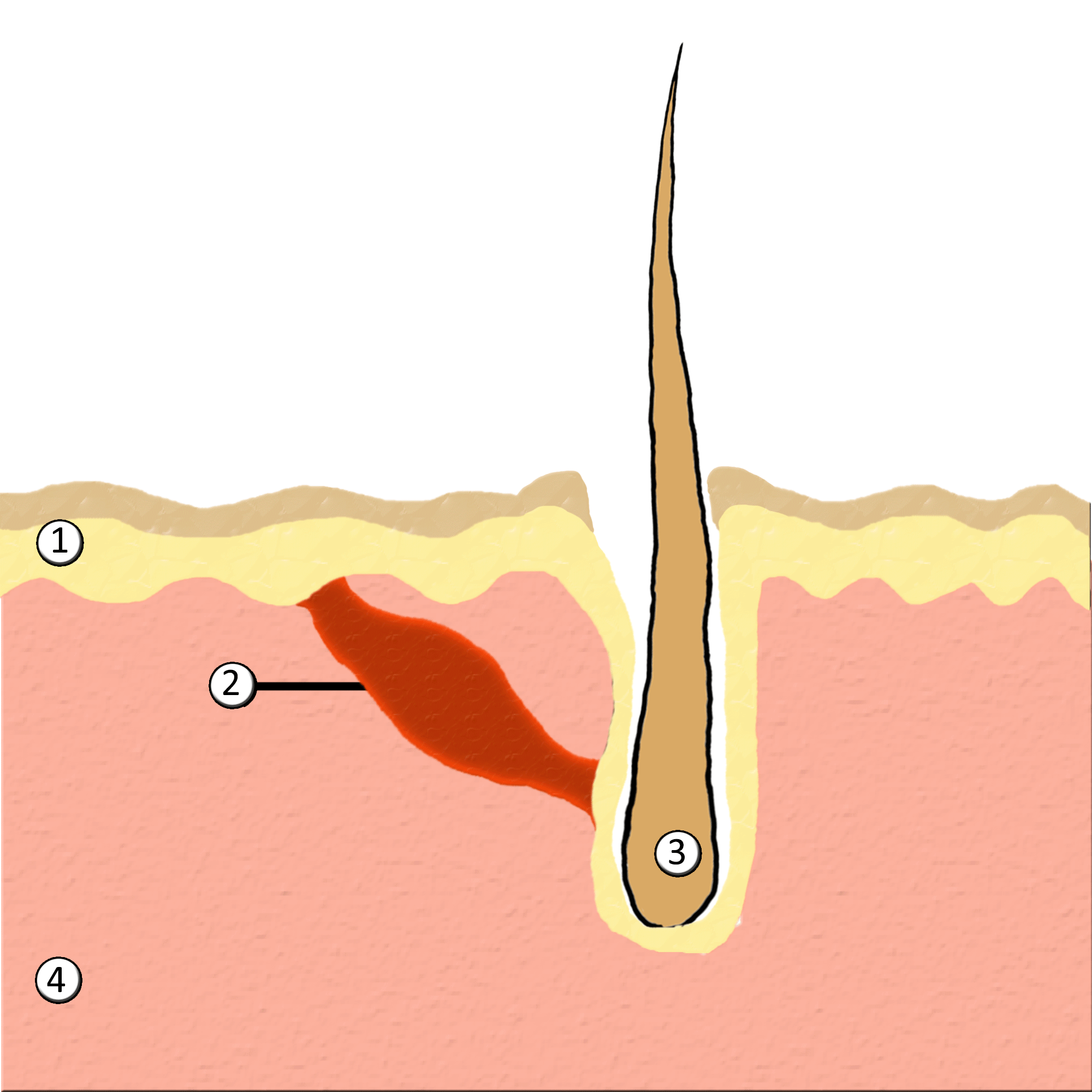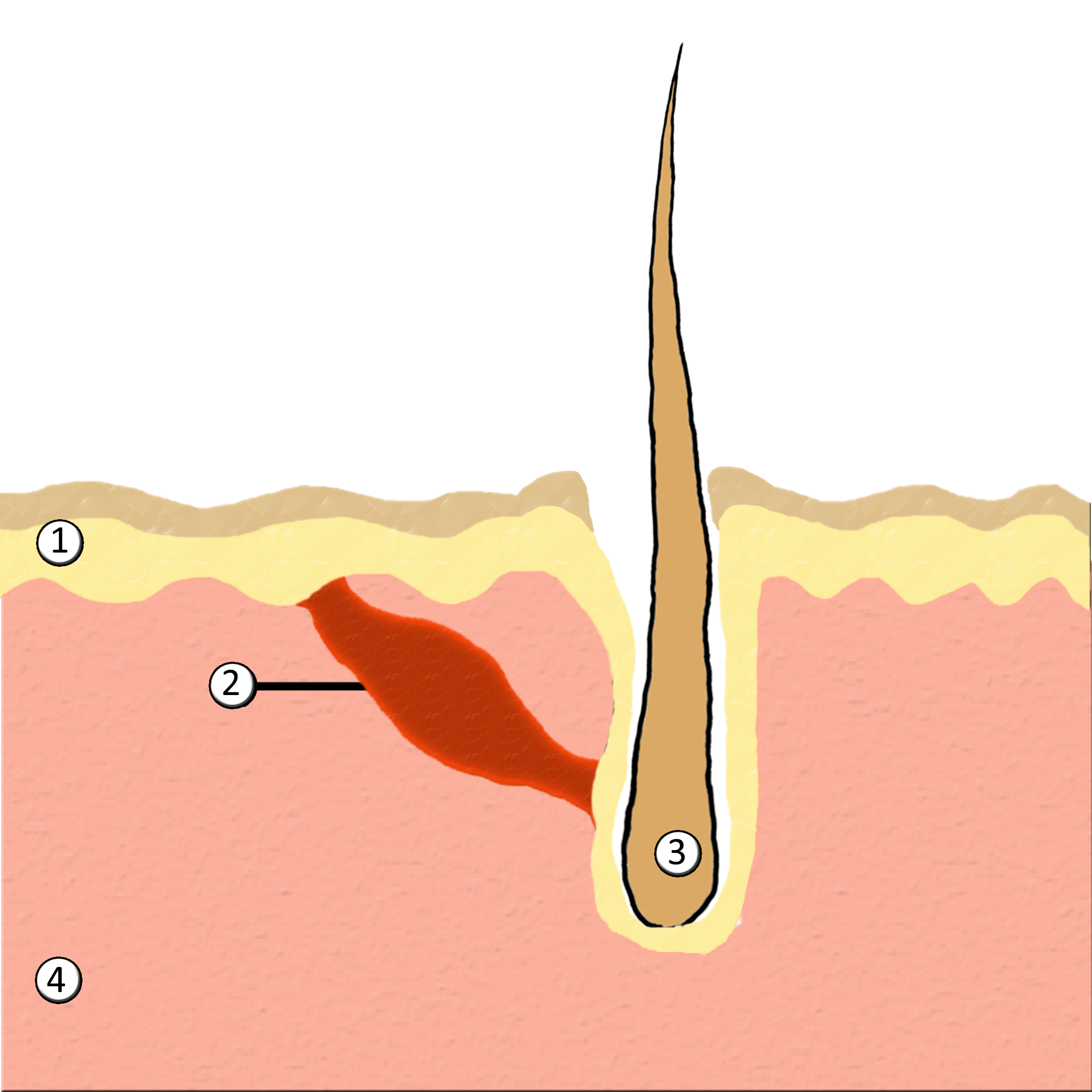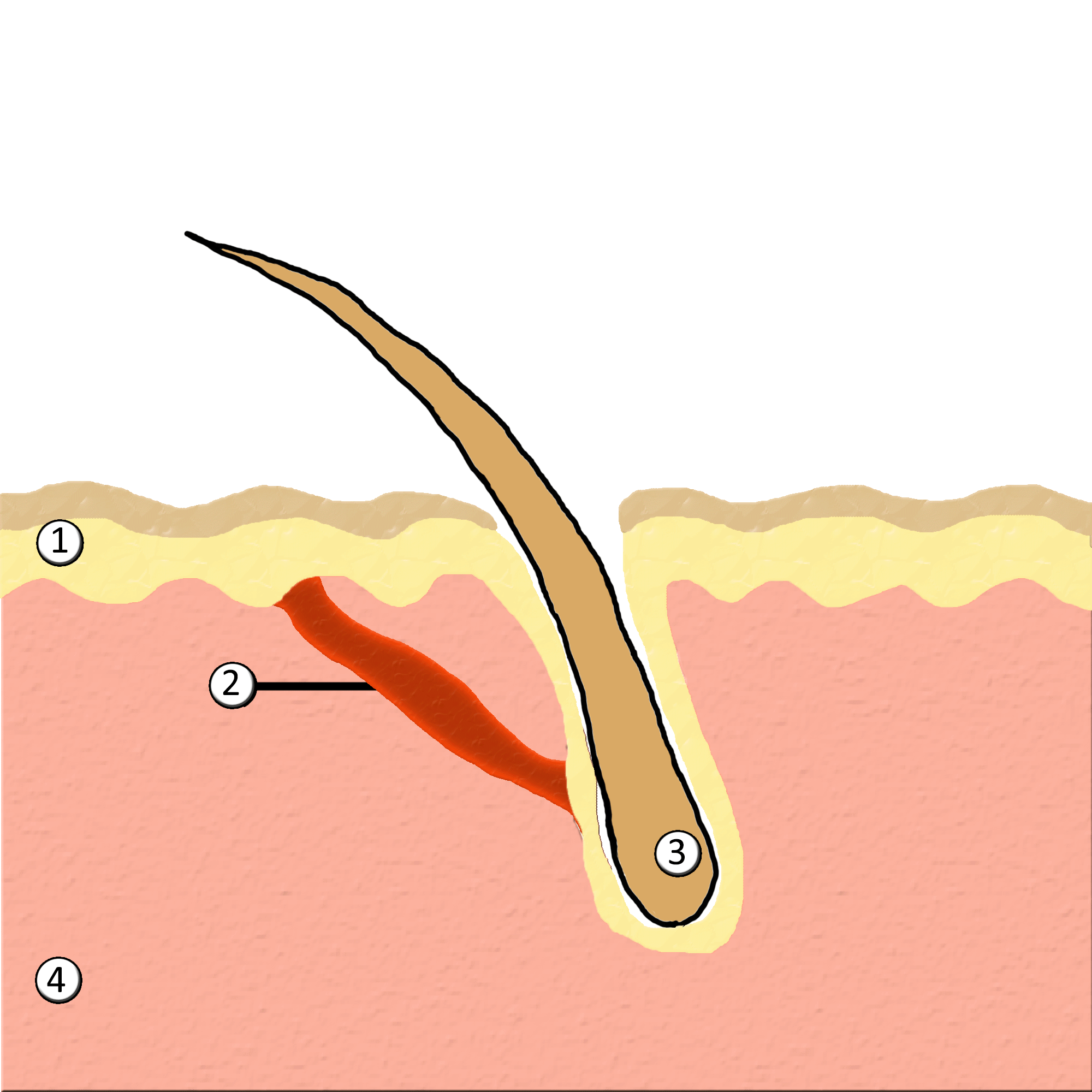
Goose Bumps
Goose bumps, goosebumps or goose-pimples are the bumps on a person's skin at the base of body hairs which may involuntarily develop when a person is tickled, cold or experiencing strong emotions such as fear, euphoria or sexual arousal. The formation of goose bumps in humans under stress is considered to be a vestigial reflex. Its function in other apes is to raise the body's hair, and would have made human ancestors appear larger to scare off predators or to increase the amount of air trapped in the fur to make it more insulating. The reflex of producing goose bumps is known as piloerection or the pilomotor reflex, or, more traditionally, horripilation. It occurs in many mammals; a prominent example is porcupines, which raise their quills when threatened, or sea otters when they encounter sharks or other predators. Anatomy and biology Goose bumps are created when tiny muscles at the base of each hair, known as ''arrector pili muscles'', contract and pull the hair straight u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955 and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, who soon followed with diazepam (Valium) in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic ( sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. High doses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan (DXM) is a medication most often used as a cough suppressant in over-the-counter cold and cough medicines. It is sold in syrup, tablet, spray, and lozenge forms. In 2022, the FDA approved a formulation of it combined with bupropion named Auvelity to serve as a rapid acting antidepressant in patients with major depressive disorder. It is in the morphinan class of medications with sedative, dissociative, and stimulant properties (at lower doses). Dextromethorphan does not have a significant affinity for the mu-opioid receptor activity typical of morphinan compounds and exerts its therapeutic effects through several other receptors. In its pure form, dextromethorphan occurs as a white powder. Dextromethorphan is also used recreationally. When exceeding approved dosages, dextromethorphan acts as a dissociative hallucinogen. It has multiple mechanisms of action, including actions as a nonselective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and a sigma-1 receptor agonis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime Malaysia–Thailand border, border with Thailand and Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia, and a maritime border with the Philippines and Vietnam. Kuala Lumpur is the national capital, the country's largest city, and the seat of the Parliament of Malaysia, legislative branch of the Government of Malaysia, federal government. The nearby Planned community#Planned capitals, planned capital of Putrajaya is the administrative capital, which represents the seat of both the Government of Malaysia#Executive, executive branch (the Cabine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditioned Place Preference
Conditioned place preference (CPP) is a form of Pavlovian conditioning used to measure the motivational effects of objects or experiences. This motivation comes from the pleasurable aspect of the experience, so that the brain can be reminded of the context that surrounded the "encounter". By measuring the amount of time an animal spends in an area that has been associated with a stimulus, researchers can infer the animal's liking for the stimulus. This paradigm can also be used to measure conditioned place aversion with an identical procedure involving aversive stimuli instead. Both procedures usually involve mice or rats as subjects. This procedure can be used to measure extinction and reinstatement of the conditioned stimulus. Certain drugs are used in this paradigm to measure their reinforcing properties. Two different methods are used to choose the compartments to be conditioned, and these are biased vs. unbiased. The biased method allows the animal to explore the apparatus, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cough Medicine
Cold medicines are a group of medications taken individually or in combination as a treatment for the symptoms of the common cold and similar conditions of the upper respiratory tract. The term encompasses a broad array of drugs, including analgesics, antihistamines and decongestants, among many others. It also includes drugs which are marketed as cough suppressants or antitussives, but their effectiveness in reducing cough symptoms is unclear or minimal. While they have been used by 10% of American children in any given week, they are not recommended in Canada or the United States in children six years or younger because of lack of evidence showing effect and concerns of harm. In 2020, one version containing codeine and guaifenesin was the 377th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States with more than 400thousand prescriptions. Types There are a number of different cough and cold medications, which may be used for various coughing symptoms. The commercially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7-hydroxymitragynine
7-Hydroxymitragynine is a terpenoid indole alkaloid from the plant ''Mitragyna speciosa'', commonly known as Kratom. It is often referred to as ‘7-OH’. It was first described in 1994 and is a natural product derived from the mitragynine present in the Kratom leaf. It is considered an oxidized derivative and active metabolite of mitragynine. 7-OH binds to opioid receptors like mitragynine, but research suggests that 7-OH binds with greater potency and contributes heavily to the analgesic activity of mitragynine as a metabolite. Metabolism After a kratom study, it was revealed that 7-OH converts into Mitragynine pseudoindoxyl. Pharmacology 7-Hydroxymitragynine, like mitragynine, appears to be a mixed opioid receptor agonist/ antagonist, acting as a partial agonist at µ-opioid receptors and as a competitive antagonist at the δ- and κ-opioid receptors. Evidence suggests that 7-OH is more potent than both mitragynine and morphine. 7-OH does not activate the β-ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |