|
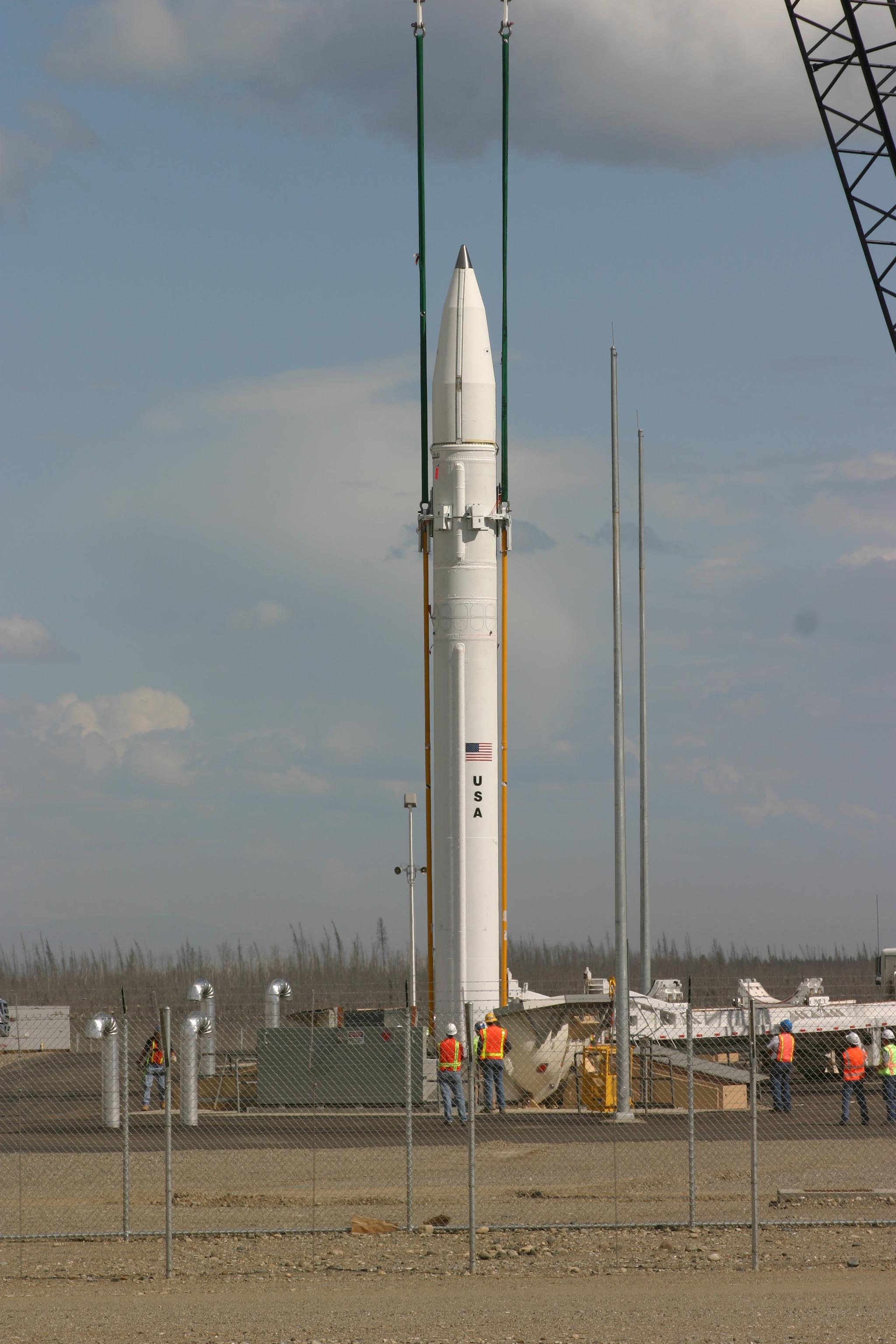
Missile Ballistics
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocket is made guided). Missiles have five system components: targeting, guidance system, flight system, engine and warhead. Missiles come in types adapted for different purposes: surface-to-surface and air-to-surface missiles ( ballistic, cruise, anti-ship, anti-submarine, anti-tank, etc.), surface-to-air missiles (and anti-ballistic), air-to-air missiles, and anti-satellite weapons. Airborne explosive devices without propulsion are referred to as shells if fired by an artillery piece and bombs if dropped by an aircraft. Unguided jet- or rocket-propelled weapons are usually described as rocket artillery. Historically, the word ''missile'' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this usage is still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FGM-148 Javelin
The FGM-148 Javelin, or Advanced Anti-Tank Weapon System-Medium (AAWS-M), is an American-made portable anti-tank missile system in service since 1996, and continuously upgraded. It replaced the M47 Dragon anti-tank missile in US service. Its fire-and-forget design uses automatic infrared guidance that allows the user to seek cover immediately after launch, in contrast to wire-guided systems, like the system used by the Dragon, which require a user to guide the weapon throughout the engagement. The Javelin's high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead can defeat modern tanks by top attack, hitting them from above, where their armor is thinnest, and is also useful against fortifications in a direct attack flight. , the Javelin had been used in around 5,000 successful engagements. Overview Javelin is a fire-and-forget missile with lock-on before launch and automatic self-guidance. The system takes a top attack flight profile against armored vehicles, attacking the usually thinner top arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warhead
A warhead is the forward section of a device that contains the explosive agent or toxic (biological, chemical, or nuclear) material that is delivered by a missile, rocket, torpedo, or bomb. Classification Types of warheads include: * Explosive: An explosive charge is used to disintegrate the target, and damage surrounding areas with a blast wave. ** Conventional: Chemicals such as gunpowder and high explosives store significant energy within their molecular bonds. This energy can be released quickly by a trigger, such as an electric spark. Thermobaric weapons enhance the blast effect by utilizing the surrounding atmosphere in their explosive reactions. ***Blast: A strong shock wave is provided by the detonation of the explosive. *** Fragmentation: Metal fragments are projected at high velocity to cause damage or injury. *** Continuous rod: Metal bars welded on their ends form a compact cylinder of interconnected rods, which is violently expanded into a contiguous zig-zag-shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomb
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the Exothermic process, exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechanical stress (mechanics), stress, the impact and penetration of pressure-driven projectiles, pressure damage, and explosion-generated effects. Bombs have been utilized since the 11th century starting in East Asia. The term bomb is not usually applied to explosive devices used for civilian purposes such as construction or mining, although the people using the devices may sometimes refer to them as a "bomb". The military use of the term "bomb", or more specifically aerial bomb action, typically refers to airdropped, unpowered explosive weapons most commonly used by air forces and naval aviation. Other military explosive weapons not classified as "bombs" include shell (projectile), shells, depth charges (used in water), or lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery Piece
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armor. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannons, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to shell-firing guns, howitzers, and mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artillery'', ''gun artillery'', or - a layman term - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell (projectile)
A shell, in a military context, is a projectile whose payload contains an explosive, incendiary, or other chemical filling. Originally it was called a bombshell, but "shell" has come to be unambiguous in a military context. Modern usage sometimes includes large solid kinetic projectiles that is properly termed shot. Solid shot may contain a pyrotechnic compound if a tracer or spotting charge is used. All explosive- and incendiary-filled projectiles, particularly for mortars, were originally called ''grenades'', derived from the French word for pomegranate, so called because of the similarity of shape and that the multi-seeded fruit resembles the powder-filled, fragmentizing bomb. Words cognate with ''grenade'' are still used for an artillery or mortar projectile in some European languages. Shells are usually large-caliber projectiles fired by artillery, armored fighting vehicles (e.g. tanks, assault guns, and mortar carriers), warships, and autocannons. The shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive Device
An explosive device is a device that relies on the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide a violent release of energy. Applications of explosive devices include: *Building implosion (demolition) * Excavation *Explosive forming *Explosive welding *Mining *Murder **Assassination *Riot control *Terrorism *War Types of explosive devices include: *Explosive weapon **Anti-personnel mine **Artillery shells **Bomb **Grenade **Improvised explosive device **Land mine **Nuclear explosive device ** Unexploded ordnance *Car bomb *Letter bomb *Stun grenade *Some pyrotechnics **Fireworks *Explosively pumped flux compression generator *Explosive-driven ferroelectric generator An explosive-driven ferroelectric generator (EDFEG, explosively pumped ferroelectric generator, EPFEG, or FEG) is a compact pulsed power generator, a device used for generation of short high-voltage high-current pulse. The energies available are fai ... Demolition hu:Robbanóeszköz {{Explosive-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-satellite Weapon
Anti-satellite weapons (ASAT) are space weapons designed to incapacitate or destroy satellites for strategic or tactical purposes. Several nations possess operational ASAT systems. Although no ASAT system has been utilised in warfare, a few countries (China, India, Russia, United Kingdom and the United States) have successfully shot down their own satellites to demonstrate their ASAT capabilities in a show of force. ASATs have also been used to remove decommissioned satellites. ASAT roles include: defensive measures against an adversary's space-based and nuclear weapons, a force multiplier for a nuclear first strike, a countermeasure against an adversary's anti-ballistic missile defence (ABM), an asymmetric counter to a technologically superior adversary, and a counter-value weapon. Use of ASATs generates space debris, which can collide with other satellites and generate more space debris. A cascading multiplication of space debris could cause Earth to suffer from Ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-to-air Missile
The newest and the oldest member of Rafael's Python family of AAM for comparisons, Python-5 (displayed lower-front) and Shafrir-1 (upper-back) An air-to-air missile (AAM) is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying another aircraft. AAMs are typically powered by one or more rocket motors, usually solid fueled but sometimes liquid fueled. Ramjet engines, as used on the Meteor, are emerging as propulsion that will enable future medium-range missiles to maintain higher average speed across their engagement envelope. Air-to-air missiles are broadly put in two groups. Those designed to engage opposing aircraft at ranges of less than 16 km are known as short-range or "within visual range" missiles (SRAAMs or WVRAAMs) and are sometimes called "dogfight" missiles because they are designed to optimize their agility rather than range. Most use infrared guidance and are called heat-seeking missiles. In contrast, medium- or long-range missiles (MRAAMs or L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-ballistic Missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear weapon, nuclear, Chemical weapon, chemical, Bioagent, biological, or conventional weapon, conventional warheads in a ballistics, ballistic flight trajectory. The term "anti-ballistic missile" is a generic term conveying a system designed to intercept and destroy any type of ballistic threat; however, it is commonly used for systems specifically designed to counter intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Current counter-ICBM systems There are a limited number of systems worldwide that can intercept intercontinental ballistic missiles: * The Russian A-135 anti-ballistic missile system (renamed in 2017 to A-235) is used for the defense of Moscow. It became operational in 1995 and was preceded by the A-35 anti-ballistic missile system. The system uses ABM-4 Gorgon, Gorgon and Gazelle (missile), Gazelle missiles pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-tank Missile
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a Missile guidance, guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy Armoured fighting vehicle, heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder-launched weapons, which can be transported by a single soldier, to larger tripod-mounted weapons, which require a squad or team to transport and fire, to vehicle and aircraft mounted missile systems. Earlier man-portable anti-tank weapons like anti-tank rifles and magnetic anti-tank mines, generally had very short range, sometimes on the order of metres or tens of metres. Rocket-propelled high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) systems appeared in World War II and extended range to the order of hundreds of metres, but accuracy was low and hitting targets at these ranges was largely a matter of luck. It was the combination of rocket propulsion and remote wire guidance that made the ATGM much more effective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-submarine Missile
An anti-submarine missile is a standoff anti-submarine weapon. Often a variant of anti-ship missile designs, an anti-submarine systems typically use a jet or rocket engine, to deliver an explosive warhead aimed directly at a submarine, a depth charge, or a homing torpedo that is carried from a launch ship, or other platform, to the vicinity of a target. History Depth charges were the earliest weapons designed for use by ships against submerged submarines. These explosives were initially dropped as the ship moved over the presumed location of a submarine. Before World War II, shipboard sonar was unable to maintain contact with a submarine at close range. Various mortar-type projectors, including Hedgehog and Squid, were devised during World War II to allow a ship to maintain sonar contact while lobbing explosive charges toward the submarine. During the Cold War, missiles were developed to provide greater range with reduced recoil. Some missiles and rockets, such as Hong San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
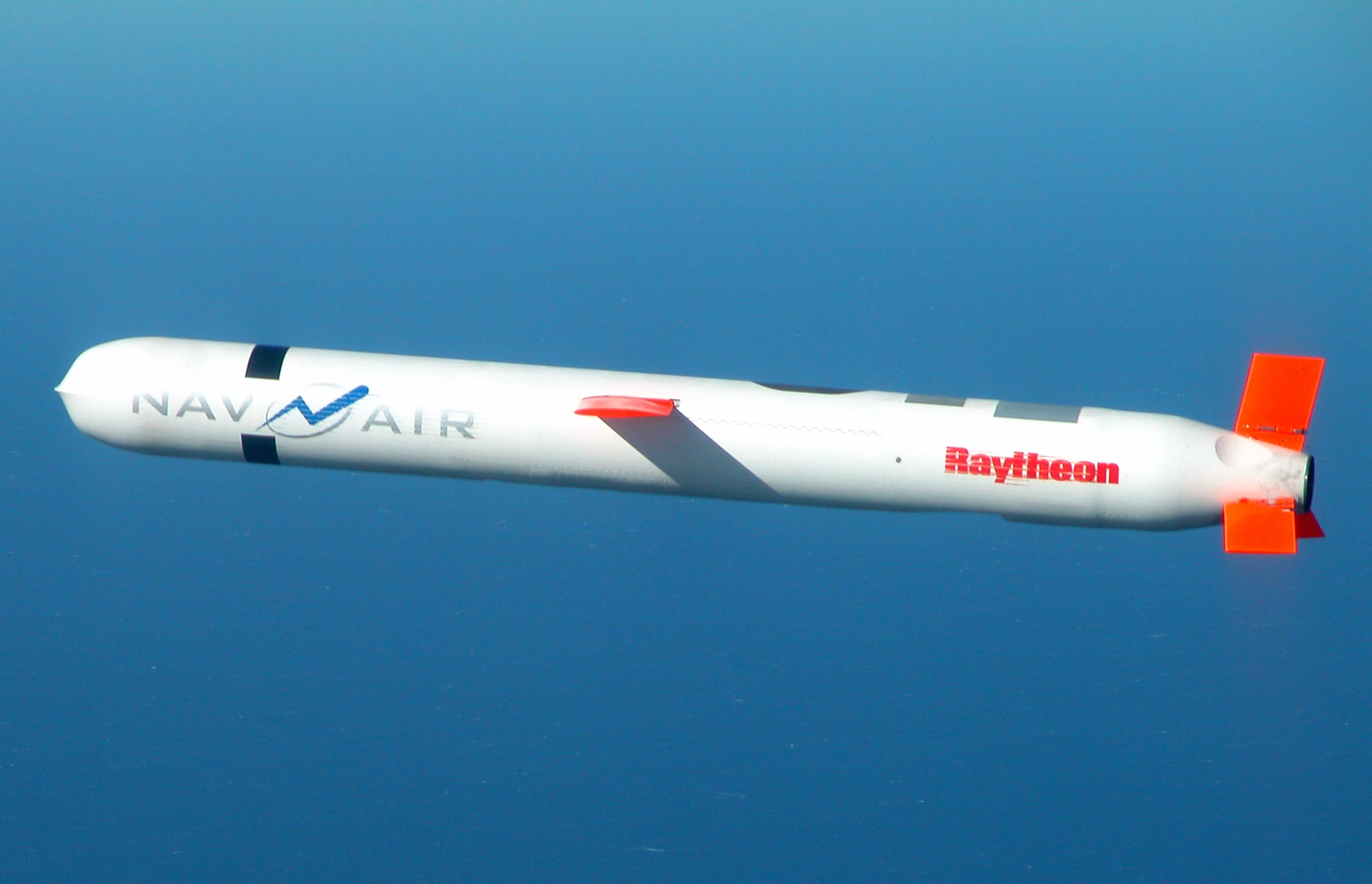
Cruise Missile
A cruise missile is a guided missile used against terrestrial or naval targets that remains in the atmosphere and flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision. Modern cruise missiles are capable of travelling at high subsonic, supersonic, or hypersonic speeds, are self-navigating, and are able to fly on a non-ballistic, extremely low-altitude trajectory. History The idea of an "aerial torpedo" was shown in the British 1909 film ''The Airship Destroyer'' in which flying torpedoes controlled wirelessly are used to bring down airships bombing London. In 1916, the American aviator Lawrence Sperry built and patented an "aerial torpedo", the Hewitt-Sperry Automatic Airplane, a small biplane carrying a TNT charge, a Sperry autopilot and a barometric altitude control. Inspired by the experiments, the United States Army developed a similar flying bomb cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)


