Anti-satellite weapon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Anti-satellite weapons (ASAT) are space weapons designed to incapacitate or destroy
 The specter of bombardment satellites and the reality of ballistic missiles stimulated the Soviet Union to explore defensive space weapons. The Soviet Union first tested the Polyot interceptor in 1963 and successfully tested an orbital anti-satellite (ASAT) weapon in 1968. According to some accounts, Sergei Korolev started some work on the concept in 1956 at his
The specter of bombardment satellites and the reality of ballistic missiles stimulated the Soviet Union to explore defensive space weapons. The Soviet Union first tested the Polyot interceptor in 1963 and successfully tested an orbital anti-satellite (ASAT) weapon in 1968. According to some accounts, Sergei Korolev started some work on the concept in 1956 at his
 On 11 January 2007, the People's Republic of China successfully destroyed a defunct Chinese weather satellite, Fengyun-1C (FY-1C, COSPAR ). The destruction was reportedly carried out by an SC-19 ASAT missile with a kinetic kill
On 11 January 2007, the People's Republic of China successfully destroyed a defunct Chinese weather satellite, Fengyun-1C (FY-1C, COSPAR ). The destruction was reportedly carried out by an SC-19 ASAT missile with a kinetic kill
According to the US government, the primary reason for destroying the satellite was the approximately of toxic hydrazine fuel contained on board, which could pose health risks to persons in the immediate vicinity of the crash site should any significant amount survive the re-entry. On 20 February 2008, it was announced that the launch was carried out successfully and an explosion was observed consistent with the destruction of the hydrazine fuel tank.
 In a statement released after the test,
In a statement released after the test,
– Thediplomat.com, 13 November 2014 The Global Positioning System and communications satellites orbit at higher altitudes of and respectively, putting them out of range of solid-fuelled
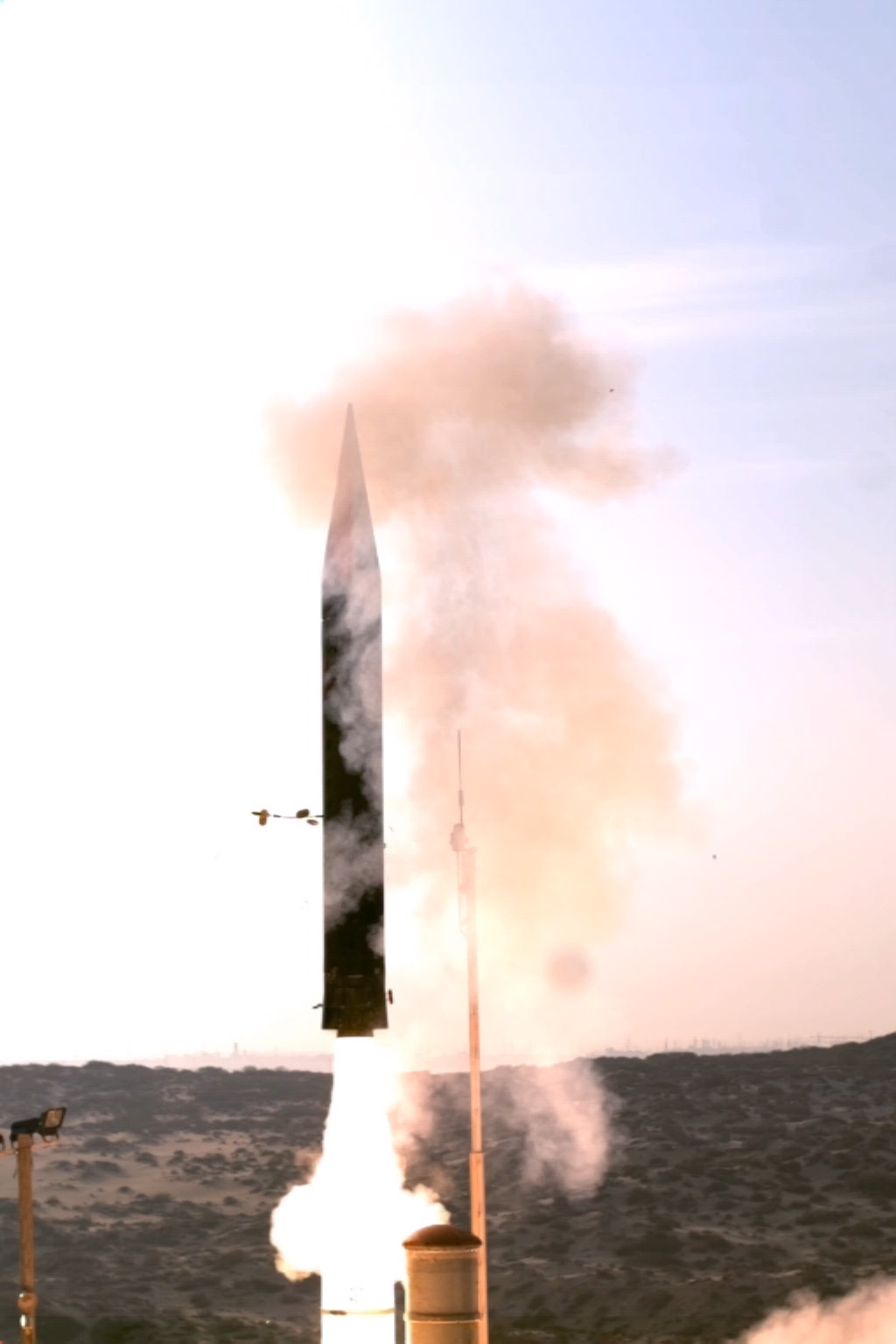 The Arrow 3 or Hetz 3 is an anti-ballistic missile, currently in service. It provides exo-atmospheric interception of ballistic missiles. It is also believed (by experts such as Prof. Yitzhak Ben Yisrael, chairman of the Israel Space Agency), that it will operate as an ASAT. See also full article
The Arrow 3 or Hetz 3 is an anti-ballistic missile, currently in service. It provides exo-atmospheric interception of ballistic missiles. It is also believed (by experts such as Prof. Yitzhak Ben Yisrael, chairman of the Israel Space Agency), that it will operate as an ASAT. See also full article
#1
(4 March 2010).
satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioiso ...
s for strategic or tactical
purposes. Several nations possess operational ASAT systems. Although no ASAT system has been utilised in warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between State (polity), states, governments, Society, societies, or paramilitary groups such as Mercenary, mercenaries, Insurgency, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violenc ...
, a few countries ( China, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
) have successfully shot down their own satellites to demonstrate their ASAT capabilities in a show of force. ASATs have also been used to remove decommissioned satellites.
ASAT roles include: defensive measures against an adversary's space-based and nuclear weapons, a force multiplier
In military science, force multiplication or a force multiplier is a factor or a combination of factors that gives personnel or weapons (or other hardware) the ability to accomplish greater feats than without it. The expected size increase requ ...
for a nuclear first strike First strike most commonly refers to:
* Pre-emptive nuclear strike
* Pre-emptive war
First strike may also refer to:
* ''First Strike'' (1996 film), also known as ''Jackie Chan's First Strike'' or ''Police Story 4: First Strike'', an action movie ...
, a countermeasure against an adversary's anti-ballistic missile defence
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear, chemical, biological, or conventional warheads in a ballistic flight traj ...
(ABM), an asymmetric counter to a technologically superior adversary, and a counter-value weapon.
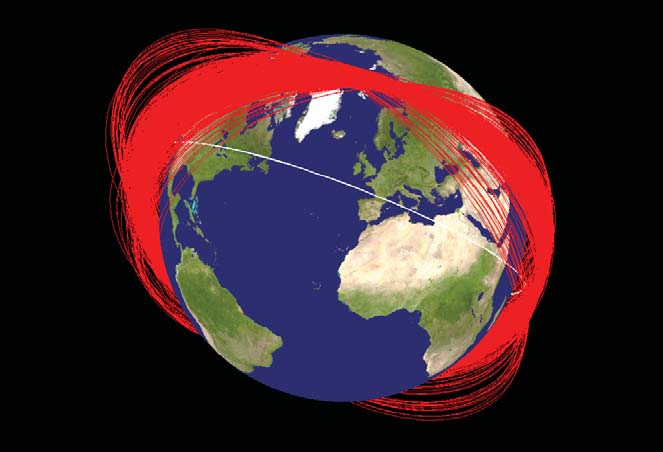
Use of ASATs generates space debris, which can collide with other satellites and generate more space debris. A cascading multiplication of space debris could cause Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
to suffer from Kessler syndrome.
History
The development and design of anti-satellite weapons has followed a number of paths. The initial efforts by the United States and the Soviet Union used ground-launched missiles from the 1950s; many more exotic proposals came afterwards.United States
In the late 1950s, the US Air Force started a series of advanced strategic missile projects under the designation Weapon System WS-199A. One of the projects studied under the 199A umbrella was Martin's '' Bold Orion'' air-launched ballistic missile (ALBM) for theB-47 Stratojet
The Boeing B-47 Stratojet (Boeing company designation Model 450) is a retired American long- range, six-engined, turbojet-powered strategic bomber designed to fly at high subsonic speed and at high altitude to avoid enemy interceptor aircraf ...
, based on the rocket motor from the Sergeant missile. Twelve test launches were carried out between 26 May 1958 and 13 October 1959, but these were generally unsuccessful and further work as an ALBM ended. The system was then modified with the addition of an Altair upper stage to create an anti-satellite weapon with a range. Only one test flight of the anti-satellite mission was carried out, making a mock attack on the Explorer 6 at an altitude of . To record its flight path, the ''Bold Orion'' transmitted telemetry to the ground, ejected flares to aid visual tracking, and was continuously tracked by radar. The missile successfully passed within of the satellite, which would be suitable for use with a nuclear weapon, but useless for conventional warheads.
A similar project carried out under 199A, Lockheed's High Virgo, was initially another ALBM for the B-58 Hustler
The Convair B-58 Hustler, designed and produced by American aircraft manufacturer Convair, was the first operational bomber capable of Mach 2 flight.
The B-58 was developed during the 1950s for the United States Air Force (USAF) Strategic A ...
, likewise based on the Sergeant. It too was adapted for the anti-satellite role, and made an attempted intercept on Explorer 5 on 22 September 1959. However, shortly after launch communications with the missile were lost and the camera packs could not be recovered to see if the test was successful. In any event, work on the WS-199 projects ended with the start of the GAM-87 Skybolt project. Simultaneous US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
projects were also abandoned although smaller projects did continue until the early 1970s.
The use of high-altitude nuclear explosions to destroy satellites was considered after the tests of the first conventional missile systems in the 1960s. During the Hardtack Teak
HARDTACK-Teak was an exoatmospheric high altitude nuclear weapon test performed during Operation Newsreel. It was launched from Johnston Atoll on a Redstone missile.Operation HARDTACK Military Effects Studies Part III: High Altitude Tests' (195 ...
test in 1958 observers noted the damaging effects of the electromagnetic pulse
An electromagnetic pulse (EMP), also a transient electromagnetic disturbance (TED), is a brief burst of electromagnetic energy. Depending upon the source, the origin of an EMP can be natural or artificial, and can occur as an electromagnetic fi ...
(EMP) caused by the explosions on electronic equipment, and during the Starfish Prime test in 1962 the EMP from a warhead detonated over the Pacific damaged three satellites and also disrupted power transmission and communications across the Pacific. Further testing of weapons effects was carried out under the DOMINIC I
Operation Dominic was a series of 31 nuclear test explosions with a total yield conducted in 1962 by the United States in the Pacific. This test series was scheduled quickly, in order to respond in kind to the Soviet resumption of testing af ...
series. An adapted version of the nuclear armed Nike Zeus was used for an ASAT from 1962. Codenamed ''Mudflap'', the missile was designated DM-15S and a single missile was deployed at the Kwajalein atoll until 1966 when the project was ended in favour of the USAF Thor
Thor (; from non, Þórr ) is a prominent god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred groves and trees, strength, the protection of humankind, hallowing ...
-based Program 437 ASAT which was operational until 6 March 1975.
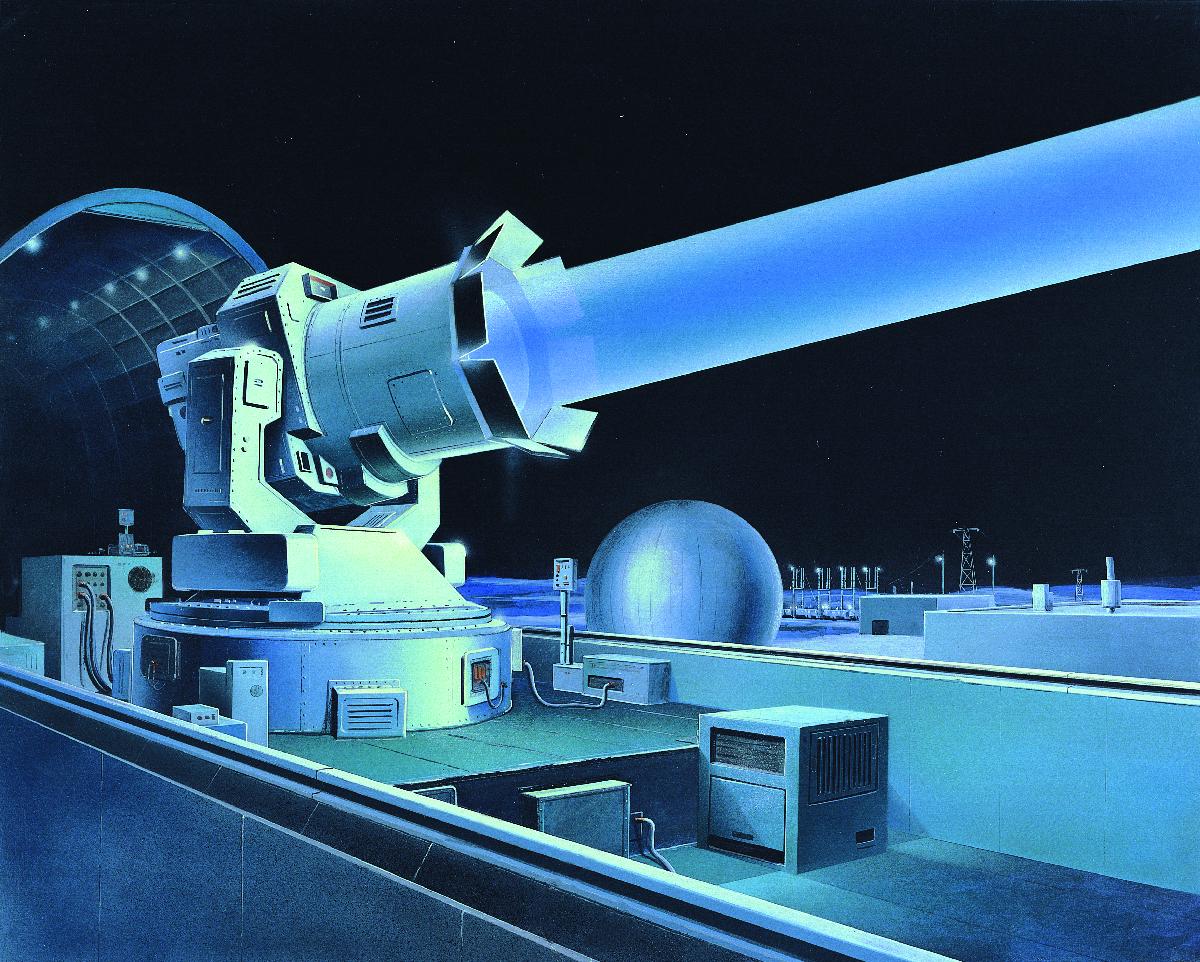
Another area of research was directed-energy weapons, including a nuclear-explosion powered X-ray laser proposal developed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in 1968. Other research was based on more conventional laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
s or masers and developed to include the idea of a satellite with a fixed laser and a deployable mirror for targeting. LLNL continued to consider more edgy technology but their X-ray laser system development was cancelled in 1977 (although research into X-ray lasers was resurrected during the 1980s as part of the SDI).
ASATs were generally given low priority until 1982, when information about a successful USSR program became widely known in the west. A "crash program" followed, which developed into the Vought ASM-135 ASAT, based on the AGM-69 SRAM
The Boeing AGM-69 SRAM (Short-Range Attack Missile) was a nuclear air-to-surface missile. It had a range of up to , and was intended to allow US Air Force strategic bombers to penetrate Soviet airspace by neutralizing surface-to-air missile de ...
with an Altair upper stage. The system was carried on a modified F-15 Eagle that carried the missile directly under the central line of the plane. The F-15's guidance system was modified for the mission and provided new directional cuing through the pilot's head-up display, and allowed for mid-course updates via a data link. The first launch of the new anti-satellite missile took place in January 1984. The first, and only, successful interception was on 13 September 1985. The F-15 took off from Edwards Air Force Base, climbed to and vertically launched the missile at the Solwind P78-1
P78-1 or Solwind was a United States satellite launched aboard an Atlas F rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on February 24, 1979. The satellite's mission was extended by several weeks, so that it operated until it was destroyed ...
, a US gamma ray spectroscopy satellite orbiting at , which was launched in 1979. The last piece of debris from the destruction of Solwind P78-1, catalogued as COSPAR 1979-017GX, SATCAT 16564, deorbited 9 May 2004. Although successful, the program was cancelled in 1988.
On 21 February 2008, the US Navy destroyed the malfunctioning US spy satellite USA-193 using a ship-fired RIM-161 Standard Missile 3 about 247 km (153 mi) above the Pacific Ocean. That test produced 174 pieces of orbital debris large enough to detect that were cataloged by the US military.Data retrieved from the U.S. military's public satellite catalog maintained at While most of the debris re-entered the Earth's atmosphere within a few months, a few pieces lasted slightly longer because they were thrown into higher orbits. The final piece of detectable USA-193 debris re-entered on 28 October 2009.
Soviet Union
 The specter of bombardment satellites and the reality of ballistic missiles stimulated the Soviet Union to explore defensive space weapons. The Soviet Union first tested the Polyot interceptor in 1963 and successfully tested an orbital anti-satellite (ASAT) weapon in 1968. According to some accounts, Sergei Korolev started some work on the concept in 1956 at his
The specter of bombardment satellites and the reality of ballistic missiles stimulated the Soviet Union to explore defensive space weapons. The Soviet Union first tested the Polyot interceptor in 1963 and successfully tested an orbital anti-satellite (ASAT) weapon in 1968. According to some accounts, Sergei Korolev started some work on the concept in 1956 at his OKB-1
PAO S. P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia (russian: Ракетно-космическая корпорация «Энергия» им. С. П. Королёва, Raketno-kosmicheskaya korporatsiya "Energiya" im. S. P. Korolyov ...
, while others attribute the work to Vladimir Chelomei's OKB-52 around 1959. What is certain is that at the beginning of April 1960, Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev ...
held a meeting at his summer residence in Crimea, discussing an array of defence industry issues. Here, Chelomei outlined his rocket and spacecraft program, and received a go-ahead to start development of the UR-200 rocket, one of its many roles being the launcher for his anti-satellite project. The decision to start work on the weapon, as part of the Istrebitel Sputnikov
Istrebitel Sputnikov, or IS (russian: Истребитель спутников, ИС, meaning "destroyer of satellites"Not to be confounded with "sputnik-istrebitel" ("спутник-истребитель"), "fighter satellite".), was a Soviet ...
(IS) (lit. "destroyer of satellites") program, was made in March 1961.
The IS system was "co-orbital", approaching its target over time and then exploding a shrapnel warhead close enough to kill it. The missile was launched when a target satellite's ground track rises above the launch site. Once the satellite is detected, the missile is launched into orbit close to the targeted satellite. It takes 90 to 200 minutes (or one to two orbits) for the missile interceptor to get close enough to its target. The missile is guided by an on-board radar. The interceptor, which weighs , may be effective up to one kilometre from a target.
Delays in the UR-200 missile program prompted Chelomei to request R-7 rockets for prototype testing of the IS. Two such tests were carried out on 1 November 1963 and 12 April 1964. Later in the year Khrushchev cancelled the UR-200 in favour of the R-36, forcing the IS to switch to this launcher, whose space launcher version was developed as the Tsyklon-2. Delays in that program led to the introduction of a simpler version, the 2A, which launched its first IS test on 27 October 1967, and a second on 28 April 1968. Further tests carried out against a special target spacecraft, the DS-P1-M, which recorded hits by the IS warhead's shrapnel. A total of 23 launches have been identified as being part of the IS test series. The system was declared operational in February 1973.
The world's first successful intercept was completed in February 1970. The first successful test (the second overall) achieved 32 hits (each could penetrate 100 mm of armour).
Testing resumed in 1976 as a result of the US work on the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
. Elements within the Soviet space industry convinced Leonid Brezhnev
Leonid Ilyich Brezhnev; uk, links= no, Леонід Ілліч Брежнєв, . (19 December 1906– 10 November 1982) was a Soviet politician who served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union between 1964 and ...
that the Shuttle was a single-orbit weapon that would be launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base Vandenberg may refer to:
* Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name
* USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida
* Vandenberg Sp ...
, manoeuvre to avoid existing anti-ballistic missile sites, bomb Moscow in a first strike, and then land. Although the Soviet military was aware these claims were false, Brezhnev believed them and ordered a resumption of IS testing along with a Shuttle of their own. As part of this work the IS system was expanded to allow attacks at higher altitudes and was declared operational in this new arrangement on 1 July 1979. However, in 1983, Yuri Andropov ended all IS testing and all attempts to resume it failed. Ironically, it was at about this point that the US started its own testing in response to the Soviet program.
In the early 1980s, the Soviet Union also started developing a counterpart to the US air-launched ASAT system, using modified MiG-31D 'Foxhounds' (at least six of which were completed) as the launch platform. The system was called 30P6 "Kontakt", the missile used is 79M6.
The USSR also experimented with Almaz military space stations, arming them with fixed Rikhter R-23 auto-cannons.
Another Soviet design was the 11F19DM Skif-DM/Polyus, an orbital battle station with a megawatt-range laser that failed on launch in 1987.
In 1987, Mikhail Gorbachev visited Baikonur Cosmodrome and was shown an anti-satellite system called "Naryad" (Sentry), also known as 14F11, launched by UR-100N rockets.
ASAT in the era of strategic defence
The era of the Strategic Defense Initiative (proposed in 1983) focused primarily on the development of systems to defend against nuclear warheads, however, some of the technologies developed may be useful also for anti-satellite use. The Strategic Defense Initiative gave the US and Soviet ASAT programs a major boost; ASAT projects were adapted forABM
ABM or Abm may refer to:
Companies
* ABM Industries, a US facility management provider
* ABM Intelligence, a UK software company
* Advantage Business Media, a US digital marketing and information services company
* Associated British Maltsters, ac ...
use and the reverse was also true. The initial US plan was to use the already-developed MHV as the basis for a space based constellation of about 40 platforms deploying up to 1,500 kinetic interceptors. By 1988 the US project had evolved into an extended four-stage development. The initial stage would consist of the Brilliant Pebbles defence system, a satellite constellation of 4,600 kinetic interceptors (KE ASAT) of each in Low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
and their associated tracking systems. The next stage would deploy the larger platforms and the following phases would include the laser and charged particle beam weapons that would be developed by that time from existing projects such as MIRACL. The first stage was intended to be completed by 2000 at a cost of around $125 billion.
Research in the US and the Soviet Union was proving that the requirements, at least for orbital based energy weapon systems, were, with available technology, close to impossible. Nonetheless, the strategic implications of a possible unforeseen breakthrough in technology forced the USSR to initiate massive spending on research in the 12th Five Year Plan, drawing all the various parts of the project together under the control of GUKOS and matching the US proposed deployment date of 2000. Ultimately, the Soviet Union approached the point of experimental implementation of orbital laser platforms with the (failed) launch of Polyus.
Both countries began to reduce expenditure from 1989 and the Russian Federation unilaterally discontinued all SDI research in 1992. Research and Development (both of ASAT systems and other space based/deployed weapons) has, however, reported to have been resumed under the government of Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime m ...
as a counter to renewed US Strategic Defense efforts post Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty. However, the status of these efforts, or indeed how they are being funded through National Reconnaissance Office
The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) is a member of the United States Intelligence Community and an agency of the United States Department of Defense which designs, builds, launches, and operates the reconnaissance satellites of the U.S. ...
projects of record, remains unclear. The US has begun working on a number of programs which could be foundational for a space-based ASAT. These programs include the Experimental Spacecraft System (USA-165
USA-165 or XSS-11 (Experimental Satellite System-11) is a small, washing-machine-sized, low-cost spacecraft developed by the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory's Space Vehicles Directorate to test technology for proximity operations. In particula ...
), the Near Field Infrared Experiment
The Near Field Infrared Experiment (NFIRE) was a satellite that was proposed and developed by the Missile Defense Agency, a division of the United States Department of Defense. It was launched atop a Minotaur rocket, from Wallops Island, at 06:48 ...
(NFIRE), and the space-based interceptor (SBI).
Law
On November 1, 2022, a U.N. working group adopted for the first time a resolution calling on countries to ban destructive anti-satellite missile tests. Although not legally binding, the resolution reflects an increase in international political support for a ban on these weapons. Other countries have noted that the United States has already tested its ASAT destruction capability and, therefore, this U.S.-backed resolution limits the progress of the other countries.Recent ASATs
Chinese ASATs
 On 11 January 2007, the People's Republic of China successfully destroyed a defunct Chinese weather satellite, Fengyun-1C (FY-1C, COSPAR ). The destruction was reportedly carried out by an SC-19 ASAT missile with a kinetic kill
On 11 January 2007, the People's Republic of China successfully destroyed a defunct Chinese weather satellite, Fengyun-1C (FY-1C, COSPAR ). The destruction was reportedly carried out by an SC-19 ASAT missile with a kinetic kill warhead
A warhead is the forward section of a device that contains the explosive agent or toxic (biological, chemical, or nuclear) material that is delivered by a missile, rocket, torpedo, or bomb.
Classification
Types of warheads include:
*Explos ...
similar in concept to the American Exoatmospheric Kill Vehicle. FY-1C was a weather satellite orbiting Earth in polar orbit at an altitude of about , with a mass of about . Launched in 1999, it was the fourth satellite in the Fengyun series.
The missile was launched from a mobile Transporter-Erector-Launcher (TEL) vehicle at Xichang () and the warhead destroyed the satellite in a head-on collision at an extremely high relative velocity. Evidence suggests that the same SC-19 system was also tested in 2005, 2006, 2010, and 2013. In January 2007 China demonstrated a satellite knock out whose detonation alone caused more than 40,000 new chunks of debris with a diameter larger than one centimeter and a sudden increase in the total amount of debris in orbit.
In May 2013, the Chinese government announced the launch of a suborbital rocket carrying a scientific payload to study the upper ionosphere. However, US government sources described it as the first test of a new ground-based ASAT system. An open source analysis, based in part on commercial satellite imagery, found that it may indeed have been a test of a new ASAT system that could potentially threaten US satellites in geostationary Earth orbit. Similarly on 5 February 2018, China tested an exoatmospheric ballistic missile with the potential to be used as an ASAT weapon, the Dong Neng-3, with state media reporting that the test was purely defensive and it achieved its desired objectives.
United States ASATs
USA-193 was an American reconnaissance satellite, which was launched on 14 December 2006 by a Delta II rocket, fromVandenberg Air Force Base Vandenberg may refer to:
* Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name
* USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida
* Vandenberg Sp ...
. It was reported about a month after launch that the satellite had failed. In January 2008, it was noted that the satellite was decaying from orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such a ...
at a rate of per day. On 14 February 2008, it was reported that the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
had been instructed to fire an RIM-161 Standard Missile 3 ABM
ABM or Abm may refer to:
Companies
* ABM Industries, a US facility management provider
* ABM Intelligence, a UK software company
* Advantage Business Media, a US digital marketing and information services company
* Associated British Maltsters, ac ...
weapon at it, to act as an anti-satellite weapon.Associated Press – Broken Satellite Will Be Shot DownAccording to the US government, the primary reason for destroying the satellite was the approximately of toxic hydrazine fuel contained on board, which could pose health risks to persons in the immediate vicinity of the crash site should any significant amount survive the re-entry. On 20 February 2008, it was announced that the launch was carried out successfully and an explosion was observed consistent with the destruction of the hydrazine fuel tank.
Indian ASATs
In April 2012, DRDO's chairman V. K. Saraswat said that India possessed the critical technologies for an ASAT weapon from radars and interceptors developed for Indian Ballistic Missile Defence Programme. In July 2012, Ajay Lele, an Institute for Defence Studies and Analyses fellow, wrote that an ASAT test would bolster India's position if an international regime to control the proliferation of ASATs similar to NPT were to be established. He suggested that a low-orbit test against a purpose-launched satellite would not be seen as irresponsible. The programme was sanctioned in 2017. On 27 March 2019, India successfully conducted an ASAT test called Mission Shakti. The interceptor was able to strike a test satellite at a altitude inlow earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
(LEO), thus successfully testing its ASAT missile. The interceptor was launched at around 05:40 UTC at the Integrated Test Range (ITR) in Chandipur, Odisha and hit its target Microsat-R after 168 seconds. The operation was named ''Mission Shakti''. The missile system was developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)—a research wing of the Indian defence services. With this test, India became the fourth nation with anti-satellite missile capabilities. India stated that this capability is a deterrent and is not directed against any nation.
 In a statement released after the test,
In a statement released after the test, Indian Ministry of External Affairs
The Ministry of External Affairs (abbreviated as MEA; hi, विदेश मंत्रालय, Videśa Mantrālaya, translit-std=ISO) of India is the government agency responsible for implementing Indian foreign policy. The Ministry of Ex ...
said that the test was conducted at low altitude to ensure that the resulting debris would "decay and fall back onto the Earth within weeks". According to Jonathan McDowell, an astrophysicist at Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, some debris might persist for a year, but most should burn up in the atmosphere within several weeks. Brian Weeden of Secure World Foundation agreed, but warned about the possibility of some fragments getting boosted to higher orbits. US Air Force Space Command said that it was tracking 270 pieces of debris from the test.
Following the test, acting United States Secretary of Defense
The United States secretary of defense (SecDef) is the head of the United States Department of Defense, the executive department of the U.S. Armed Forces, and is a high ranking member of the federal cabinet. DoDD 5100.1: Enclosure 2: a The ...
Patrick Shanahan warned about the risks of space debris caused by ASAT tests, but later added that he did not expect debris from the Indian test to last. The United States Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
acknowledged Ministry of External Affairs' statement on space debris and reiterated its intention to pursue shared interests in space including on space security with India. Russia acknowledged India's statement on the test not being targeted against any nation and invited India to join the Russian–Chinese proposal for a treaty against weaponisation of space.
Russian ASATs
The successful flight test of Russia's direct ascent anti-satellite missile, known as PL-19 Nudol, took place on 18 November 2015, according to defence officials familiar with reports of the test. In May 2016, Russia tested the Nudol for the second time. It was launched from the Plesetsk cosmodrome test launch facility, located north of Moscow. Three more launches were reportedly held in December 2016, on 26 March 2018, and on 23 December 2018the latter two from a TEL. A new type of ASAT missile was seen carried by a MiG-31 in September 2018. On 15 April 2020, US officials said Russia conducted a direct ascent anti-satellite missile test that could take out spacecraft or satellites inlow Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
. A new test launch took place on 16 December 2020.
In November 2021, Kosmos 1408 was successfully destroyed by a Russian anti-satellite missile in a test, causing a debris field that affected the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos ( ...
.
Limits of ASATs
While it has been suggested that a country intercepting the satellites of another country in a conflict, namely between China and the United States, could seriously hinder the latter's military operations, the ease of shooting down orbiting satellites and their effects on operations has been questioned. Although satellites have been successfully intercepted at low orbiting altitudes, the tracking of military satellites for a length of time could be complicated by defensive measures like inclination changes. Depending on the level of tracking capabilities, the interceptor would have to pre-determine the point of impact while compensating for the satellite's lateral movement and the time for the interceptor to climb and move. US intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) satellites orbit at about high and move at , so a ChineseIntermediate-range ballistic missile
An intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) is a ballistic missile with a range of 3,000–5,500 km (1,864–3,418 miles), between a medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) and an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Classifying ...
would need to compensate for of movement in the three minutes it takes to boost to that altitude. Even if an ISR satellite is knocked out, the US possesses an extensive array of manned and unmanned ISR aircraft that could perform missions at standoff ranges from Chinese land-based air defences, making them somewhat higher priority targets that would consume fewer resources to better engage.China’s Deceptively Weak Anti-Satellite Capabilities– Thediplomat.com, 13 November 2014 The Global Positioning System and communications satellites orbit at higher altitudes of and respectively, putting them out of range of solid-fuelled
Intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons ...
s. Liquid-fuelled space launch vehicles could reach those altitudes, but they are more time-consuming to launch and could be attacked on the ground before being able to launch in rapid succession. The constellation of 30 GPS satellites provides redundancy where at least four satellites can be received in six orbital planes at any one time, so an attacker would need to disable at least six satellites to disrupt the network.
Even if this is achieved, signal degradation only lasts for 95 minutes, leaving little time to take much decisive action, and backup inertial navigation systems (INS) would still be available for relatively accurate movement as well as laser guidance for weapons targeting. For communications, the Naval Telecommunications System (NTS) used by the US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
uses three elements: tactical communications among a battle group; long-haul communications between shore-based forward Naval Communications Stations (NAVCOMSTAs) and deployed afloat units; and strategic communication connecting NAVCOMSTAs with National Command Authorities (NCA).
The first two elements use line-of-sight () and extended line-of-sight () radios respectively, so only strategic communications are dependent on satellites. China would prefer to cut off deployed units from each other and then negotiate with the NCA to have the battle group withdraw or stand down, but ASATs could only achieve the opposite. Even if somehow a communications satellite were hit, a battle group could still perform its missions in the absence of direct guidance from the NCA.
ASAT development
Israel's developments
 The Arrow 3 or Hetz 3 is an anti-ballistic missile, currently in service. It provides exo-atmospheric interception of ballistic missiles. It is also believed (by experts such as Prof. Yitzhak Ben Yisrael, chairman of the Israel Space Agency), that it will operate as an ASAT. See also full article
The Arrow 3 or Hetz 3 is an anti-ballistic missile, currently in service. It provides exo-atmospheric interception of ballistic missiles. It is also believed (by experts such as Prof. Yitzhak Ben Yisrael, chairman of the Israel Space Agency), that it will operate as an ASAT. See also full article#1
(4 March 2010).
India's developments
In a televised press briefing during the 97th Indian Science Congress held in Thiruvananthapuram, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) Director General Rupesh announced that India was developing the necessary technology that could be combined to produce a weapon to destroy enemy satellites in orbit. On 10 February 2010, DRDO Director-General and Scientific Advisor to the Defence Minister, Dr.Vijay Kumar Saraswat
Vijay Kumar Saraswat is an Indian scientist who formerly served as the Director General of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Chief Scientific Advisor to the Indian Minister of Defence. He retired on 31 May 2003 a ...
stated that India had "all the building blocks necessary" to integrate an anti-satellite weapon to neutralize hostile satellites in low earth and polar orbits.
India is known to have been developing an exo-atmospheric kill vehicle that can be integrated with the missile to engage satellites. On 27 March 2019, India tested its ASAT missile (''Mission Shakti'') destroying a pre-determined target of a live satellite. The DRDO's ballistic missile defence interceptor was used on an Indian satellite for the test. Microsat-R is the suspected target of the Indian ASAT experiment.
Russia's developments
In the early 1980s, the Soviet Union had developed two MiG-31D 'Foxhounds' as a launch platform for a potential Vympel Anti-Satellite weapon system. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, this project was put on hold due to reduced defence expenditures. However, in August 2009, theRussian Air Force
"Air March"
, mascot =
, anniversaries = 12 August
, equipment =
, equipment_label =
, battles =
, decorations =
, batt ...
had announced the resumption of this program. Further reports in May 2010 based on statements from Col. Eduard Sigalov in Russia's air and space defence forces, indicated that Russia was "developing a fundamentally new weapon that can destroy potential targets in space." The Sokol Eshelon
Sokol-Eshelon (russian: Сокол-Эшелон, lit=Falcon-Echelon) is a Soviet/Russian laser weapon–based anti-satellite system. It is an airborne laser based on a Beriev A-60 aircraft. In 2012 it was reported that the project is back under ...
is a prototype laser system based on an A-60 airplane which is reported to be restarting development in 2012.
See also
* Anti-ballistic missile * ''Deep Black'' (1986 book) * High-altitude nuclear explosion * Kessler syndrome * Kill vehicle * Militarisation of space * Multiple Kill Vehicle * Outer Space Treaty * Space debris * Space gun * Space warfareReferences
External link
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Anti-Satellite Weapon Guided missiles by mission Missile types Satellites Space weapons