|
Minyichthys
''Minyichthys'' is a circumtropical genus of pipefishes consisting of species from the Indo-Pacific and eastern and western Atlantic regions. The genus is characterized as having a maximum standard length of about 60 mm, with two or three anal fin rays. ''Minyichthys'' species can be differentiated from members of the closely related genus ''Micrognathus'' by their higher frequency of total subdorsal rings (seven to 11 as opposed to three to seven). Like many other pipefishes, male members of this genus carry their young in a brood pouch underneath the tail. These small, secretive fishes live in shallow algae or reef habitats, and in tidal pools and sheltered reef flats. Some species are known to venture into deeper waters. Species The currently recognized species in this genus are: * ''Minyichthys brachyrhinus'' (Herald, 1953) - Indo-Pacific * ''Minyichthys inusitatus'' C. E. Dawson, 1983 - Atlantic Dawson, C. E. 1983. Western Atlantic occurrence of the genus ''Minyic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minyichthys Inusitatus
''Minyichthys inusitatus'', also known as the West Atlantic pipefish is a species of marine fish belonging to the family Syngnathidae. They have been be found off the coast of Panama and Northern Argentina Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ..., though little is known about their full geographic range or preferred habitat in these areas. ''Minyichthys inusitatus'' is thought to live primarily at depths of greater than 30–40 meters. Their diet likely consists of small crustaceans such as copepods, amphipods, and mysid shrimps. Reproduction occurs through ovoviviparity in which the males brood eggs before giving live birth. This small species grows only to lengths of around 2.9 cm on average. References External links ''Minyichthys inusitatus''at FishBase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minyichthys Sentus
''Minyichthys sentus'' is a species of marine fish belonging to the family Syngnathidae. Little is known about this species preferred habitat and their proposed geographic distribution is based on only three specimens, two found in the Atlantic near Southern Spain and one found in the Mediterranean near Gibraltar ) , anthem = " God Save the King" , song = " Gibraltar Anthem" , image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg , map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe , map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green , mapsize = , image_map2 = Gib .... They have been recorded at depths of up to 170 meters. References External links ''Minyichthys sentus''at FishBase Syngnathidae Taxa named by Charles Eric Dawson Fish described in 1982 {{Syngnathiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minyichthys Brachyrhinus
''Minyichthys brachyrhinus'' is a species of marine fish belonging to the family Syngnathidae. Geography They can be found in the coastal waters of Indonesia, Sumatra, the Philippines, Fiji, and Hawaii, though little is known about their preferred habitat in these areas. Diet Their diet likely consists of small crustaceans such as copepods, amphipods, and mysid shrimps. Reproduction Reproduction occurs through ovoviviparity Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop insi ... in which the males brood eggs before giving live birth. References External links ''Minyichthys brachyrhinus''at FishBase Syngnathidae Taxa named by Earl Stannard Herald Fish described in 1953 {{Syngnathiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minyichthys Myersi
''Minyichthys myersi'', also known as Myer's pipefish, is a species of marine fish belonging to the family Syngnathidae. They can be found inhabiting coral in many areas of the Indo-Pacific including Mauritius, Indonesia, the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, and French Polynesia. Their diet likely consists of small crustaceans such as copepods and amphipods. Reproduction occurs through ovoviviparity in which the males brood eggs before giving live birth. Etymology The fish is named in honor of George S. Myers George Sprague Myers (February 2, 1905 – November 4, 1985) was an American ichthyologist who spent most of his career at Stanford University. He served as the editor of ''Stanford Ichthyological Bulletin'' as well as president of the American So ... (1905-1985), from Stanford University. References External links ''Minyichthys myersi''at FishBase Syngnathidae Taxa named by Earl Stannard Herald Taxa named by John Ernest Randall Fish described in 1972 {{S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
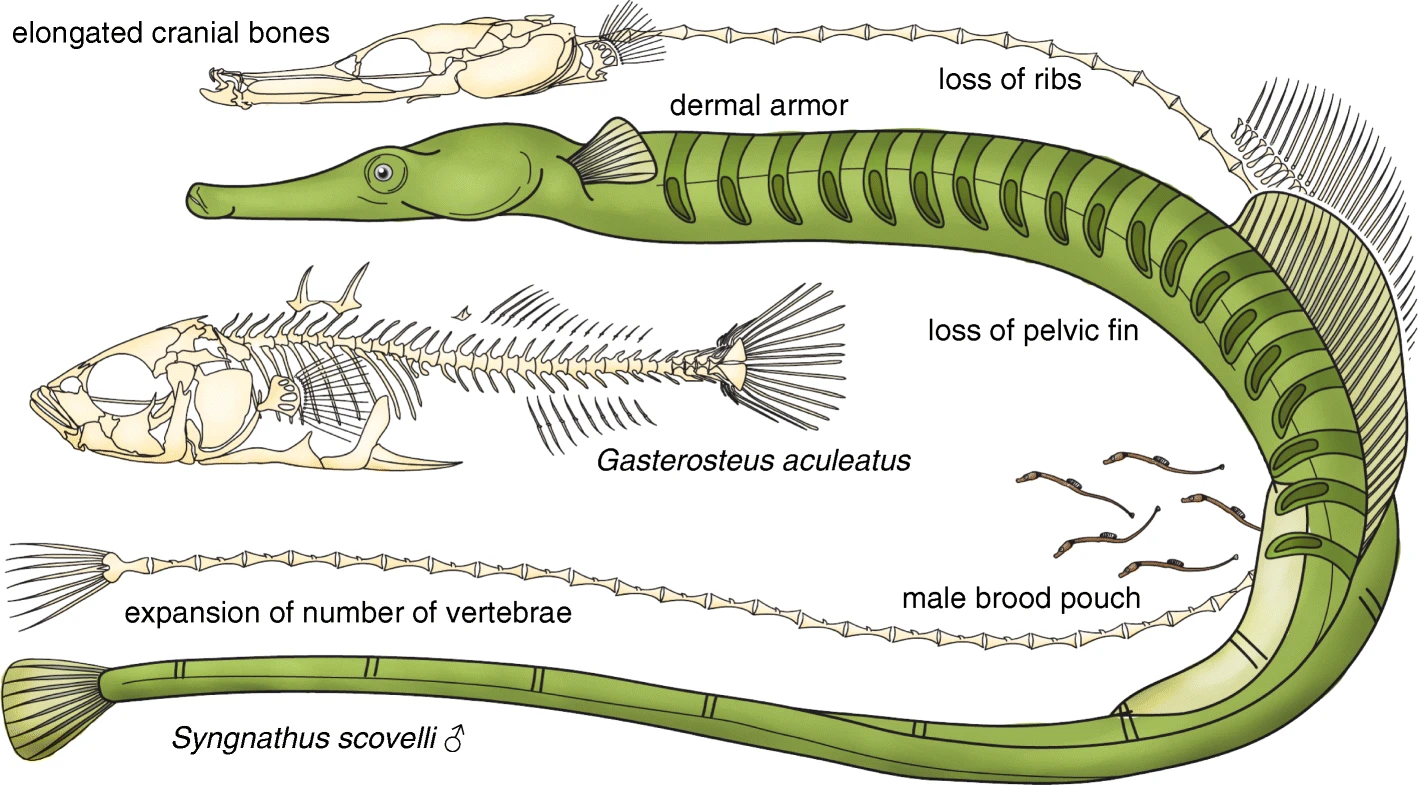
Pipefish
Pipefishes or pipe-fishes (Syngnathinae) are a subfamily of small fishes, which, together with the seahorses and seadragons (''Phycodurus'' and ''Phyllopteryx''), form the family Syngnathidae. Description Pipefish look like straight-bodied seahorses with tiny mouths. The name is derived from the peculiar form of the snout, which is like a long tube, ending in a narrow and small mouth which opens upwards and is toothless. The body and tail are long, thin, and snake-like. They each have a highly modified skeleton formed into armored plating. This dermal skeleton has several longitudinal ridges, so a vertical section through the body looks angular, not round or oval as in the majority of other fishes. A dorsal fin is always present, and is the principal (in some species, the only) organ of locomotion. The ventral fins are consistently absent, and the other fins may or may not be developed. The gill openings are extremely small and placed near the upper posterior angle of the gill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syngnathidae
The Syngnathidae is a family of fish which includes seahorses, pipefishes, and seadragons (''Phycodurus'' and ''Phyllopteryx''). The name is derived from grc, σύν (), meaning "together", and (), meaning "jaw". The fused jaw is one of the traits that the entire family have in common. Description and biology Syngnathids are found in temperate and tropical seas across the world. Most species inhabit shallow, coastal waters, but a few are known from the open ocean, especially in association with sargassum mats. They are characterised by their elongated snouts, fused jaws, the absence of pelvic fins, and by thick plates of bony armour covering their bodies. The armour gives them a rigid body, so they swim by rapidly fanning their fins. As a result, they are relatively slow compared with other fish but are able to control their movements with great precision, including hovering in place for extended periods. Uniquely, after syngnathid females lay their eggs, the male then fertiliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Fish Genera
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean. Marine or marines may refer to: Ocean * Maritime (other) * Marine art * Marine biology * Marine debris * Marine habitats * Marine life * Marine pollution Military * Marines, a naval-based infantry force ** United States Marine Corps ** Royal Marines of the UK ** Brazilian Marine Corps ** Spanish Marine Infantry ** Fusiliers marins (France) ** Indonesian Marine Corps ** Republic of China Marine Corps ** Republic of Korea Marine Corps ** Royal Thai Marine Corps *"Marine" also means "navy" in several languages: ** Austro-Hungarian Navy () ** Belgian Navy (, , ) ** Royal Canadian Navy () *** Provincial Marine (1796–1910), a predecessor to the Royal Canadian Navy ** Navy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo () ** Royal Danish Navy () ** Finnish Navy (, ) ** French Navy () ** Gabonese Navy () ** German Navy () ** Royal Moroccan Navy () ** Royal Netherlands Navy () ** Swedish Navy () Places * Marine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Charles Eric Dawson
Charles Eric "Chuck" Dawson (December 6, 1922 – February 11, 1993) was a Canadian-American ecologist Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ..., ichthyology, ichthyologist, and taxonomy (biology), taxonomist. He held expertise in goby, gobies, flatfishes, and sand stargazers, and was considered "the ultimate authority" on pipefishes in the family Syngnathidae. Life Dawson was born in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, but would eventually spend much of his career at the University of Southern Mississippi's Gulf Coast Research Laboratory in Ocean Springs, Mississippi, where he worked early as an administrator, then researcher, and museum curator. Over his long career Dawson wrote 150 publications, on the majority of which he was the sole author. He recognized 52 Syngnat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Stannard Herald
Earl Stannard Herald (April 10, 1914 - January 16, 1973) was an American zoologist, Ichthyologist and television presenter. He was born in Phoenix, Arizona, and got his PH.D. in 1943. In 1948, he became the director of the Steinhart Aquarium in San Francisco, California, and from 1952 to 1966, he presented the popular science television programme '' Science in Action''. Throughout his life, he studied a variety of aquatic organisms, especially pipefishes, and described many new taxa. He died in Cabo San Lucas, Baja California, in a scuba diving accident. Education and early career Herald graduated as a Bachelor of Arts from the University of California, Los Angeles in 1937, he then completed his Masters at the University of California, Berkeley in 1939 and then his PH.D. at Stanford University in 1943. This selection of institutions allowed Herald to be schooled in zoology by Loye Holmes Miller and Joseph Grinnell, while his training as an ichthyologist was supervised by George S. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ernest Randall
John Ernest "Jack" Randall (May 22, 1924 – April 26, 2020) was an American ichthyologist and a leading authority on coral reef fishes. Randall described over 800 species and authored 11 books and over 900 scientific papers and popular articles. He spent most of his career working in Hawaii. He died in April 2020 at the age of 95. Career John Ernest Randall was born in Los Angeles, California in May 1924, to John and Mildred (McKibben) Randall. In high school he acquired a love of marine fish after a visit to the tide pools of Palos Verdes and, after serving stateside in the Medical Corps of the U.S. Army during the post- D-Day years of WWII,John Randall bio, The Academy of Underwater Arts & Sciences. (http://www.auas-nogi.org/bio_randall_john.html) received his BA degree from the University of California, Los Angeles in 1950. In 1955 he earned his Ph.D in ichthyology from the University of Hawaii. After spending two years as a research associate at the Bishop Museum in Honol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)