|
Ministry Of Ceremonies (Han Dynasty)
The Ministry of Ceremonies () was one of the nine ministries of the Chinese Han dynasty. The Minister of Ceremonies (), also known as Grand Master of Ceremonies, was the chief official in charge of religious rites, rituals, prayers, and the maintenance of ancestral temples and altars. The role's title was changed to Upholder of Ceremonies () from 195 to 144 BC before reverting to the original title. Although his main concern was to link the emperor with the supernatural world and Heaven, he was also given the task of setting educational standards for the Imperial University (est. 124 BC) and the academic chairs () who specialized in the Five Classics, the canon of Confucianism. One of the Minister of Ceremonies' many subordinates was the Court Astronomer (; also known as the Prefect Grand Astrologer), who made astronomical observations and drafted the annual lunisolar calendar. The Court Astronomer also upheld a literacy test of 9,000 characters for nominees aspiring to becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Characters
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji''. Chinese characters in South Korea, which are known as ''hanja'', retain significant use in Korean academia to study its documents, history, literature and records. Vietnam once used the '' chữ Hán'' and developed chữ Nôm to write Vietnamese before turning to a romanized alphabet. Chinese characters are the oldest continuously used system of writing in the world. By virtue of their widespread current use throughout East Asia and Southeast Asia, as well as their profound historic use throughout the Sinosphere, Chinese characters are among the most widely adopted writing systems in the world by number of users. The total number of Chinese characters ever to appear in a dictionary is in the tens of thousands, though most are graphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Imperial China
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Administration For Religious Affairs
The State Administration for Religious Affairs (SARA) was an executive agency directly under the State Council of the People's Republic of China which oversaw religious affairs in the country. Originally created in 1951 as the Religious Affairs Bureau, SARA was closely connected with the United Front Work Department of the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party and charged with overseeing the operations of China's five officially sanctioned religious organizations: * Buddhist Association of China * Chinese Taoist Association * Islamic Association of China * Three-Self Patriotic Movement (Protestant) * Catholic Patriotic Association SARA was dissolved in 2018, placing all religious affairs directly under the United Front Work Department. History The State Administration for Religious Affairs was established to exercise control over religious appointments, the selection of clergy, and the interpretation of religious doctrine. SARA was also meant to ensure that the regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and laying the foundations for the much longer lasting Tang dynasty. Founded by Emperor Wen of Sui, the Sui dynasty capital was Chang'an (which was renamed Daxing, modern Xi'an, Shaanxi) from 581–605 and later Luoyang (605–18). Emperors Wen and his successor Yang undertook various centralized reforms, most notably the equal-field system, intended to reduce economic inequality and improve agricultural productivity; the institution of the Five Departments and Six Board (五省六曹 or 五省六部) system, which is a predecessor of Three Departments and Six Ministries system; and the standardization and re-unification of the coinage. They also spread and encouraged Buddhism throughout the empire. By the middle of the dynasty, the newly unifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Rites
The Ministry or Board of Rites was one of the Six Ministries of government in late imperial China. It was part of the imperial Chinese government from the Tang (7th century) until the 1911 Xinhai Revolution. Along with religious rituals and court ceremonial the Ministry of Rites also oversaw the imperial examination and China's foreign relations. A Ministry of Rites also existed in imperial Vietnam. One of its tasks was enforcing the naming taboo. History Under the Han, similar functions were performed by the Ministry of Ceremonies. In early medieval China, its functions were performed by other officials including the Grand Herald. Under the Song (10th-13th centuries), its functions were temporarily transferred to the Zhongshu Sheng. Its administration of China's foreign relations was ended by the establishment of the Zongli Yamen in 1861. Functions *Management of imperial court ceremonies and ritual offerings. *Registration and supervision of Buddhist and Taoist priests with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literacy Test
A literacy test assesses a person's literacy skills: their ability to read and write have been administered by various governments, particularly to immigrants. In the United States, between the 1850s and 1960s, literacy tests were administered to prospective voters, and this had the effect of disenfranchising African Americans and others with diminished access to education. Other countries, notably Australia, as part of its White Australia policy, and South Africa adopted literacy tests either to exclude certain racialized groups from voting or to prevent them from immigrating. Voting From the 1890s to the 1960s, many state governments in the Southern United States administered literacy tests to prospective voters, purportedly to test their literacy in order to vote. The first state to establish literacy tests in the United States was Connecticut. In practice, these tests were intended to disenfranchise racial minorities and others deemed problematic by the ruling party. Souther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestor Worship
The veneration of the dead, including one's ancestors, is based on love and respect for the deceased. In some cultures, it is related to beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of the living. Some groups venerate their direct, familial ancestors. Certain sects and religions, in particular the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church, venerate saints as intercessors with God; the latter also believes in prayer for departed souls in Purgatory. Other religious groups, however, consider veneration of the dead to be idolatry and a sin. In European, Asian, Oceanian, African and Afro-diasporic cultures, the goal of ancestor veneration is to ensure the ancestors' continued well-being and positive disposition towards the living, and sometimes to ask for special favours or assistance. The social or non-religious function of ancestor veneration is to cultivate kinship values, such as filial piety, family loyalty, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
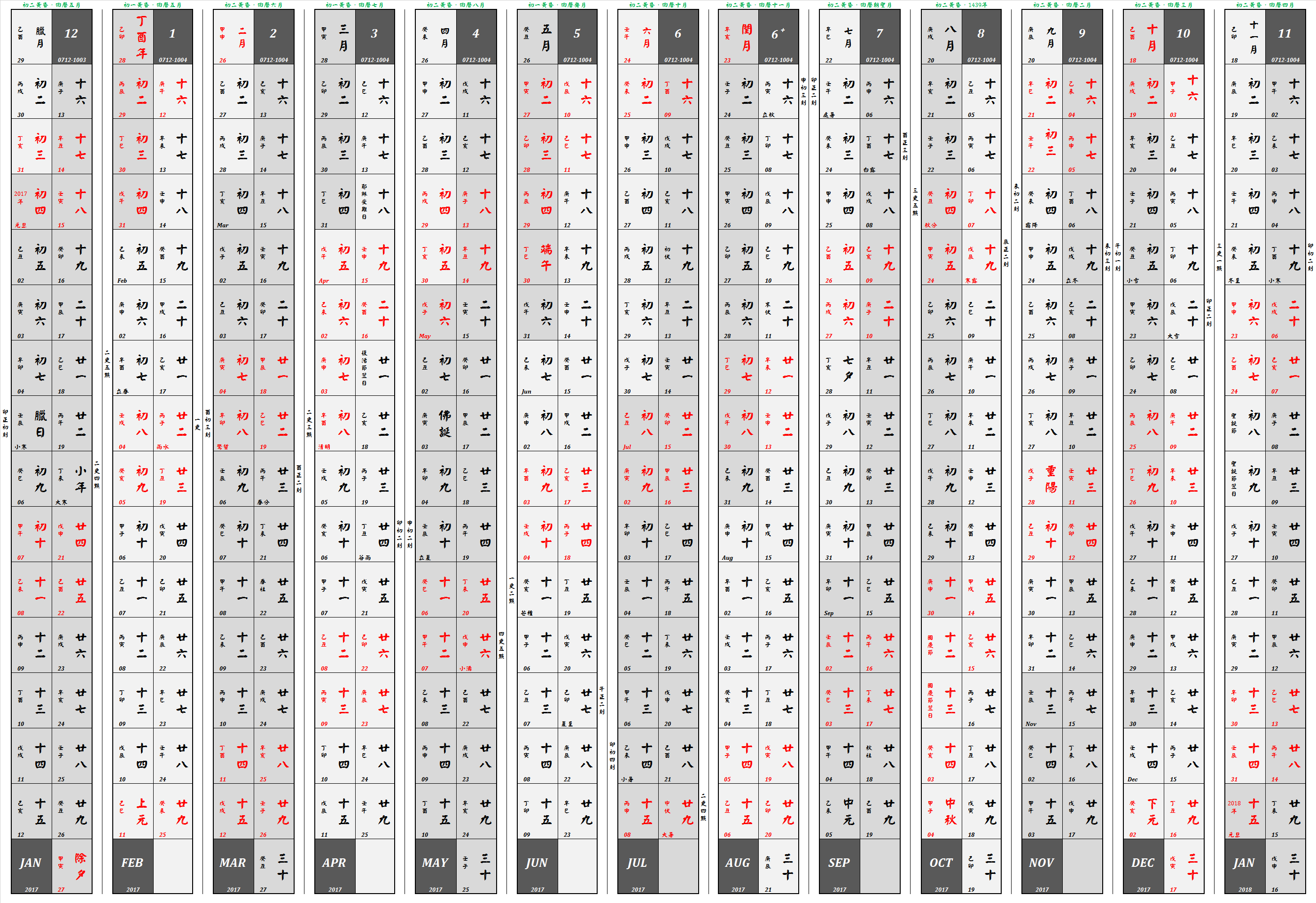
Chinese Calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar (also known as the Agricultural Calendar ��曆; 农历; ''Nónglì''; 'farming calendar' Former Calendar ��曆; 旧历; ''Jiùlì'' Traditional Calendar ��曆; 老历; ''Lǎolì'', is a lunisolar calendar which identifies years, months, and days according to astronomical phenomena. In China, it is defined by the Chinese national standard GB/T 33661–2017, "Calculation and Promulgation of the Chinese Calendar", issued by the Standardization Administration of China on May 12, 2017. Although modern-day China uses the Gregorian calendar, the traditional Chinese calendar governs holidays, such as the Chinese New Year and Lantern Festival, in both China and overseas Chinese communities. It also provides the traditional Chinese nomenclature of dates within a year which people use to select auspicious days for weddings, funerals, moving or starting a business. The evening state-run news program ''Xinwen Lianbo'' in the P.R.C. continues to anno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |