|
Mingyi Swe
Mingyi Swe ( my, မင်းကြီးဆွေ, ; officially styled as Minye Thihathu (မင်းရဲ သီဟသူ, ); and as Minye Theinkhathu (မင်းရဲ သိင်္ခသူ), ; 1490s – 1549) was viceroy of Toungoo (Taungoo) from 1540 to 1549 during the reign of his son-in-law King Tabinshwehti of Toungoo dynasty. He was also the father of King Bayinnaung, as well as key viceroys in Bayinnaung's administration. He rose to the position of viceroy of the ancestral home of the dynasty, after having started out as a royal household servant of Tabinshwehti. All the Toungoo kings from Bayinnaung to Mahadhammaraza Dipadi descended from him. Background The genealogy of Mingyi Swe and his first wife Shin Myo Myat (ရှင်မျိုးမြတ်), the parents of King Bayinnaung, is unclear. Though there are no extant contemporary records regarding Bayinnaung's ancestry or childhood, different traditions about the king's genealogy have persisted.Thaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Toungoo
This is a list of rulers of Taungoo, the predecessor principality of the Taungoo Dynasty of what is now Myanmar. The principality of Taungoo, at the edge of the realm of Upper Burma-based kingdoms, was a rebellion-prone vassal state. The region was ruled by hereditary viceroys as well as appointed governors, depending on the power of the high king at Pinya, and later Inwa (Ava). Many of the rulers of Taungoo were assassinated while in office, and a few others died in action, showing the frontier nature of the region. The high kings at Ava at times had only nominal control or no control in many stretches.Sein Lwin Lay 2006: 10–13 After 1612, the office of viceroy at Taungoo became a mere appointed governorship as the Restored Taungoo kings abolished then existing hereditary viceroyships throughout the entire Irrawaddy valley.Lieberman 2003: 161–162 Origins The first recorded administration of the Taungoo region came in 1191 when King Sithu II appointed Ananda Thuriya, a son-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahadhammaraza Dipadi
Maha Dhammaraza Dipati ( my, မဟာ ဓမ္မရာဇာ ဓိပတိ, ; pi, Mahādhammarājadhipati; 1714–1754), was the last king of Toungoo dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1733 to 1752. The young king inherited a kingdom already in severe decline, and his inexperience only made the decline faster, finally resulting in the end of House of Toungoo and the collapse of the kingdom over his 18-year reign.Htin Aung 1967: 152–156 Early life The future king was born to Prince Taninganway and his chief queen Thiri Maha Mingala Dewi. He was the fifth child and fourth son of the couple. He was given Singu in fief in his youth. He became the heir presumptive because all three elder brothers died young. He was made the heir apparent on 6 May 1727 (1st waning of Kason 1089 ME).Hmannan Vol. 3 2003: 362 Reign Five years into his reign, the armies of Manipur invaded and plundered the northern Burmese provinces. The Burmese were unable to suppress them. Since the move of capita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rule In Burma
( Burmese) , conventional_long_name = Colony of Burma , common_name = Burma , era = Colonial era , event_start = First Anglo-Burmese War , year_start = 1824 , date_start = 5 March , event_end = Independence declared , year_end = 1948 , date_end = 4 January , life_span = 1824–1948 , event1 = Anglo-Burmese Wars , date_event1 = 1824–1826, 1852–1853, 1885 , event2 = Separation from British India , date_event2 = 1937 ( Government of Burma Act) , event3 = Japanese and Thai occupation , date_event3 = 1942–1945 , p1 = British Raj , flag_p1 = British_Raj_Red_Ensign.svg , p2 = Konbaung Dynasty , flag_p2 = Flag of Konbaung Dynasty (Nonrectangular).svg , p3 = State of Burma , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borassus Flabellifer
''Borassus flabellifer'', commonly known as doub palm, palmyra palm, tala or tal palm, toddy palm, wine palm or ice apple, is native to South Asia (especially in Bangladesh & South India) and Southeast Asia. It is reportedly naturalized in Socotra and parts of China. Description ''Borassus flabellifer'' is a robust tree and can reach a height of . The trunk is grey, robust and ringed with leaf scars; old leaves remain attached to the trunk for several years before falling cleanly. The leaves are fan-shaped and long, with robust black teeth on the petiole margins. Like all ''Borassus'' species, ''B. flabellifer'' is dioecious with male and female flowers on separate plants. The male flowers are less than long and form semi-circular clusters, which are hidden beneath scale-like bracts within the catkin-like inflorescences. In contrast, the female flowers are golfball-sized and solitary, sitting upon the surface of the inflorescence axis. After pollination, these blooms develop i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taungoo District
Taungoo District (Taungngu, Toungoo, my, တောင်ငူခရိုင်) is a district of the Bago Division in central Burma (Myanmar). The capital lies at Taungoo. History Taungoo District was created by the Pagan Dynasty in the 1280s, and was much larger. It was ruled by appointed governors through succeeding dynasties. In 1510, Taungoo District briefly became the small, independent kingdom of Taunggyi. But within twenty years that kingdom soon controlled most of Burma, the capital was moved to Pegu, and Taungoo became a district again. By the mid-19th century, Taungoo was governed by a local governor appointed by the Konbaung kings. The Taungoo District consisted of 52 wards, including today's Pyinmana and Naypyidaw regions. The Taungoo District was cut in half after the Second Anglo-Burmese War. The British annexed the southern half, including the city of Taungoo while the northern portion, including Pyinmana and Ela, remained Burmese. Townships The district contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
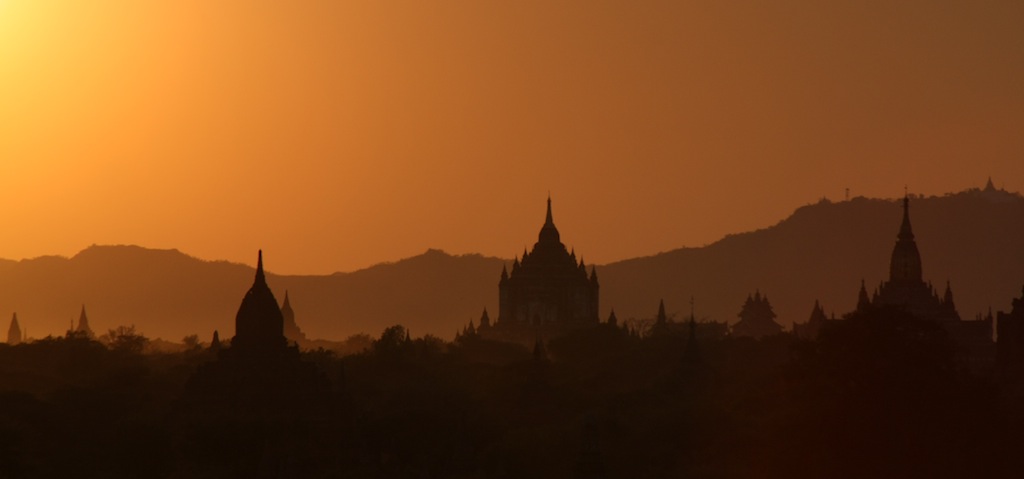
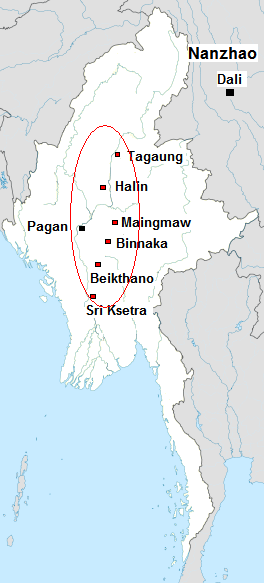
Bagan
Bagan (, ; formerly Pagan) is an ancient city and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the Mandalay Region of Myanmar. From the 9th to 13th centuries, the city was the capital of the Bagan Kingdom, the first kingdom that unified the regions that would later constitute Myanmar. During the kingdom's height between the 11th and 13th centuries, more than 10,000 Buddhist temples, pagodas and monasteries were constructed in the Bagan plains alone, of which the remains of over 2200 temples and pagodas survive. The Bagan Archaeological Zone is a main attraction for the country's nascent tourism industry. Etymology Bagan is the present-day standard Burmese pronunciation of the Burmese word ''Pugan'' ( my-Mymr, ပုဂံ), derived from Old Burmese ''Pukam'' ( my-Mymr, ပုကမ်). Its classical Pali name is ''Arimaddanapura'' ( my-Mymr, အရိမဒ္ဒနာပူရ, lit. "the City that Tramples on Enemies"). Its other names in Pali are in reference to its extreme dry zone cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagan Dynasty
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying under one polity the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. By t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mi Saw U
, image = , caption = , reign = 7 February 1313 – February 1325 , coronation = , succession = Chief queen consort of Pinya , predecessor = new office , successor = Atula Maha Dhamma Dewi , suc-type = Successor , reign1 = 17 December 1297 – 7 February 1313 , coronation1 = 20 October 1309 , succession1 = Chief queen consort of Pinle , predecessor1 = ''new office'' , successor1 = ''disestablished'' , reign2 = 1290s – 17 December 1297 , coronation2 = , succession2 = Queen of the Central Palace of Pagan , predecessor2 = ''vacant'' , successor2 = ''disestablished'' , spouse = Kyawswa (1289–1297) Thihathu (1297–1325) , issue = Uzana I Kyawswa I Nawrahta , issue-link = , full name = , house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinya Kingdom
The Kingdom of Pinya ( my, ပင်းယခေတ်, ), also known as the Vijaia State (၀ိဇယတိုင်း), was the kingdom that ruled Central Myanmar (Burma) from 1313 to 1365. It was the successor state of Myinsaing, the polity that controlled much of Upper Burma between 1297 and 1313. Founded as the de jure successor state of the Pagan Empire by Thihathu, Pinya faced internal divisions from the start. The northern province of Sagaing led by Thihathu's eldest son Saw Yun successfully fought for autonomy in 1315−17, and formally seceded in 1325 after Thihathu's death. The rump Pinya Kingdom was left embroiled in an intense rivalry between Thihathu's other sons Uzana I and Kyawswa I until 1344. Pinya had little control over its vassals; its southernmost vassals Toungoo (Taungoo) and Prome (Pyay) were practically independent. Central authority briefly returned during Kyawswa I's reign (1344−50) but broke down right after his death. In the 1350s, Kyawswa II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thihathu
Thihathu ( my, သီဟသူ, ; 1265–1325) was a co-founder of the Myinsaing Kingdom, and the founder of the Pinya Kingdom in today's central Burma (Myanmar).Coedès 1968: 209 Thihathu was the youngest and most ambitious of the three brothers that successfully defended central Burma from Mongol invasions in 1287 and in 1300–01. He and his brothers toppled the regime at Pagan in 1297, and co-ruled central Burma. After his eldest brother Athinkhaya's death in 1310, Thihathu pushed aside the middle brother Yazathingyan, and took over as the sole ruler of central Burma. His decision to designate his adopted son Uzana I heir-apparent caused his eldest biological son, Saw Yun to set up a rival power center in Sagaing in 1315. Although Saw Yun nominally remained loyal to his father, after Thihathu's death in 1325, the two houses of Myinsaing officially became rival kingdoms in central Burma. Early life Thihathu was born in 1265 to a prominent family in Myinsaing in Central Burm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minkhaung I Of Toungoo
Minkhaung I of Toungoo ( my, တောင်ငူ မင်းခေါင်ငယ် ) was viceroy of Toungoo from 1446 to 1451. Having accidentally inherited the Toungoo throne after his father's sudden death, Minkhaung proved an ineffectual ruler of this perpetually unruly frontier vassal state of Ava Kingdom. He was assassinated in early 1452 by a servant of his cousin Minye Kyawhtin, who went on to seize Toungoo in his rebellion against King Narapati I of Ava.Sein Lwin Lay 2006: 32–33 All royal chronicles starting with the ''Maha Yazawin'' chronicle, identify Minkhaung I of Toungoo as an ancestor (paternal great-great grandfather) of King Bayinnaung of Toungoo Dynasty.Thaw Kaung 2010: 118–119 He may also be the historical basis for the Taungoo Mingaung ''nat'' of the Thirty Seven Nats, the official pantheon of traditional Burmese spirits. Note that at least one writer, Hla Thamein, has identified Minkhaung II of Toungoo Minkhaung II of Toungoo ( my, တောင� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarabya Of Toungoo
Tarabya of Toungoo ( my, တောင်ငူ တရဖျား, ) was viceroy of Toungoo from 1440 to 1446. Prior to Toungoo, he had held governorships at Amyint and Yanaung. Brief He was a son of Gov. Tarabya I of Pakhan, and younger brother of Queen Saw Min Hla.Hmannan Vol. 2 2003: 70 He was appointed governor of Amyint with the title of Tarabya in early 1434 by King Mohnyin Thado.(Hmannan Vol. 2 2003: 69–70): The king made the appointment after a series of failed campaigns to Pinle, Yamethin and Taungdwin; the campaigns began in the dry season of 1433–34, and took 3 months. It means the appointment was made February 1434. In 1439, King Minye Kyawswa I succeeded the Ava throne, and appointed Tarabya governor of the strategic town of Yanaung in the Prome region as a step to regain Toungoo which had been in revolt since 1426.Sein Lwin Lay 2006: 30 In 1440,(Sein Lwin Lay 2006: 30): Toungoo surrendered in 802 ME (30 March 1440 to 29 March 1441), after which Tarabya was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_fruit.jpg)

.png)