|
Mine Tailings
In mining, tailings are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different to overburden, which is the waste rock or other material that overlies an ore or mineral body and is displaced during mining without being processed. The extraction of minerals from ore can be done two ways: placer mining, which uses water and gravity to concentrate the valuable minerals, or hard rock mining, which pulverizes the rock containing the ore and then relies on chemical reactions to concentrate the sought-after material. In the latter, the extraction of minerals from ore requires comminution, i.e., grinding the ore into fine particles to facilitate extraction of the target element(s). Because of this comminution, tailings consist of a slurry of fine particles, ranging from the size of a grain of sand to a few micrometres. Mine tailings are usually produced from the mill in slurry form, which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broken Hill Town & Line Of Lode Pano, NSW, 08
Broken may refer to: Literature * Broken (Armstrong novel), ''Broken'' (Armstrong novel), a 2006 novel by Kelley Armstrong in the ''Women of the Otherworld'' series * Broken (Slaughter novel), ''Broken'' (Slaughter novel), a 2010 novel by Karin Slaughter Music Albums * ''Broken (And Other Rogue States)'', a 2005 album by Luke Doucet * Broken (MBLAQ EP), ''Broken'' (MBLAQ EP) (2014) * Broken (Nine Inch Nails EP), ''Broken'' (Nine Inch Nails EP), (1992) * Broken (Soulsavers album), ''Broken'' (Soulsavers album) (2009) * Broken (Straight Faced album), ''Broken'' (Straight Faced album) (1996) Songs * Broken (Jake Bugg song), "Broken" (Jake Bugg song) (2013) * Broken (Sam Clark song), "Broken" (Sam Clark song) (2009) * Broken (Coldplay song), "Broken" (Coldplay song) (2019) * Broken (Elisa song), "Broken" (Elisa song) (2003) * Broken (Lifehouse song), "Broken" (Lifehouse song) (2008) * Broken (lovelytheband song), "Broken" (lovelytheband song) (2017) * Broken (Kate Ryan son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(II) Sulfide
Iron(II) sulfide or ferrous sulfide (Br.E. sulphide) is one of a family chemical compounds and minerals with the approximate formula . Iron sulfides are often iron-deficient non-stoichiometric. All are black, water-insoluble solids. Preparation and structure FeS can be obtained by the heating of iron and sulfur: :Fe + S → FeS FeS adopts the nickel arsenide structure, featuring octahedral Fe centers and trigonal prismatic sulfide sites. Reactions Iron sulfide reacts with hydrochloric acid, releasing hydrogen sulfide: :FeS + 2 HCl → FeCl2 + H2S :FeS + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2S In moist air, iron sulfides oxidize to hydrated ferrous sulfate. Biology and biogeochemistry Iron sulfides occur widely in nature in the form of iron–sulfur proteins. As organic matter decays under low-oxygen (or hypoxic) conditions such as in swamps or dead zones of lakes and oceans, sulfate-reducing bacteria reduce various sulfates present in the water, producing hydrogen sulfide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the largest province by area and the second-largest by population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York in the United States. Between 1534 and 1763, Quebec was called ''Canada'' and was the most developed colony in New France. Following the Seven Years' War, Quebec b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Responsible Mining
Responsible mining is commonly defined as mining that involves and respects all stakeholders, minimizes and takes account of its environmental impact, and prioritizes a fair division of economic and financial benefits. There is a strong focus on stakeholder engagement, involving governments and the affected communities. The underlying principles are based on existing international agreements, such as the Rio Declaration and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), involving polluter responsibility, equity, participatory decision making and accountability and transparency. Because the Earth contains a finite amount of minerals – making mining a finite activity – the term responsible mining is preferred over sustainable mining. In practice, responsible mining has different interpretations, referring to advocacy to reform mining activity, as well as to a marketing strategy used by mining companies to promote their operations as environmentally or socially sound. Goals may vary by group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bauxite Tailings
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(OH)), mixed with the two iron oxides goethite (FeO(OH)) and haematite (Fe2O3), the aluminium clay mineral kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) and small amounts of anatase (TiO2) and ilmenite (FeTiO3 or FeO.TiO2). Bauxite appears dull in luster and is reddish-brown, white, or tan. In 1821, the French geologist Pierre Berthier discovered bauxite near the village of Les Baux in Provence, southern France. Formation Numerous classification schemes have been proposed for bauxite but, , there was no consensus. Vadász (1951) distinguished lateritic bauxites (silicate bauxites) from karst bauxite ores (carbonate bauxites): * The carbonate bauxites occur predominantly in Europe, Guyana, Suriname, and Jamaica above carbonate rocks (limestone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
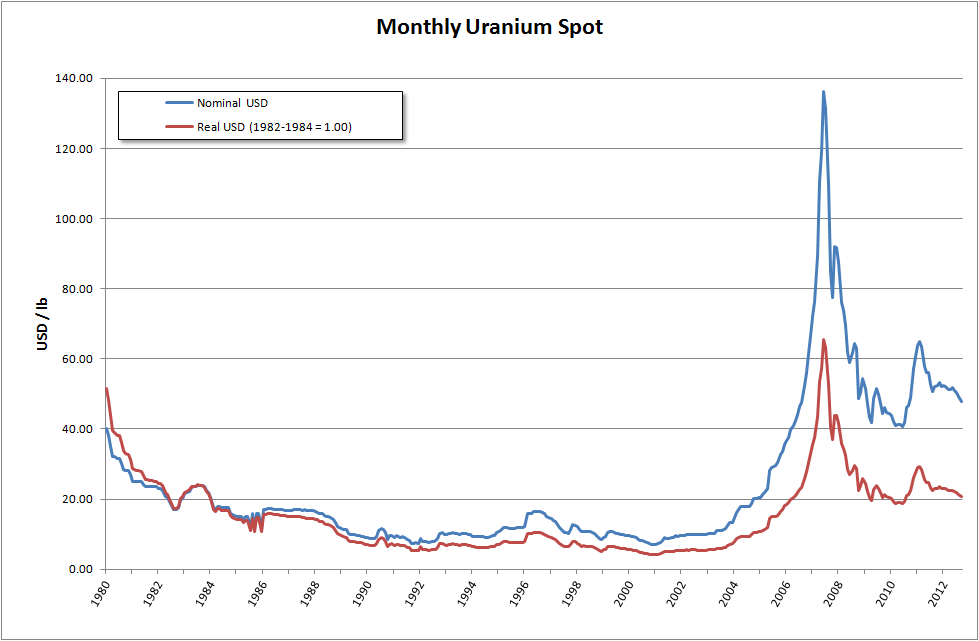
Uranium Market
The uranium market, like all commodity markets, has a history of volatility, moving with the standard forces of supply and demand as well as geopolitical pressures. It has also evolved particularities of its own in response to the unique nature and use of uranium. Historically, uranium has been mined in countries willing to export, including Australia and Canada. However, countries now responsible for more than 50% of the world’s uranium production include Kazakhstan, Namibia, Niger, and Uzbekistan. Uranium from mining is used almost entirely as fuel for nuclear power plants. Following the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, the global uranium market remains depressed, with the uranium price falling more than 50%, declining share values, and reduced profitability of uranium producers since March 2011. As a result, uranium companies worldwide have reduced capacity, closed operations and deferred new production. Before uranium is ready for use as nuclear fuel in reactors, it must und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daughter Isotope
In nuclear physics, a decay product (also known as a daughter product, daughter isotope, radio-daughter, or daughter nuclide) is the remaining nuclide left over from radioactive decay. Radioactive decay often proceeds via a sequence of steps (decay chain). For example, 238U decays to 234Th which decays to 234mPa which decays, and so on, to 206Pb (which is stable): : \ce \overbrace^\ce left, upThe decay chain from lead-212 down to lead-208, showing the intermediate decay products In this example: * 234Th, 234mPa,...,206Pb are the decay products of 238U. * 234Th is the daughter of the parent 238U. * 234mPa (234 metastable) is the granddaughter of 238U. These might also be referred to as the daughter products of 238U. (''Depleted Uranium'' — authors: Naomi H. Harley, Ernest C. Foulkes, Lee H. Hil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high melting point. Thorium is an electropositive actinide whose chemistry is dominated by the +4 oxidation state; it is quite reactive and can ignite in air when finely divided. All known thorium isotopes are unstable. The most stable isotope, 232Th, has a half-life of 14.05 billion years, or about the age of the universe; it decays very slowly via alpha decay, starting a decay chain named the thorium series that ends at stable 208 Pb. On Earth, thorium and uranium are the only significantly radioactive elements that still occur naturally in large quantities as primordial elements. Thorium is estimated to be over three times as abundant as uranium in the Earth's crust, and is chiefly refined from monazite sands as a by-product of extracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly radioactive because all isotopes of uranium are unstable; the half-lives of its naturally occurring isotopes range between 159,200 years and 4.5 billion years. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead, and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals such as uraninite. In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Rock
Phosphorite, phosphate rock or rock phosphate is a non-detrital sedimentary rock that contains high amounts of phosphate minerals. The phosphate content of phosphorite (or grade of phosphate rock) varies greatly, from 4% to 20% phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5). Marketed phosphate rock is enriched ("beneficiated") to at least 28%, often more than 30% P2O5. This occurs through washing, screening, de-liming, magnetic separation or flotation. By comparison, the average phosphorus content of sedimentary rocks is less than 0.2%.Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy, ''Petrology'', Freeman, 1996, 2nd ed. pp. 345–349 The phosphate is present as fluorapatite Ca5(PO4)3F typically in cryptocrystalline masses (grain sizes < 1 μm) referred to as -sedimentary apatite deposits of uncertain origin. It is also present as [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphogypsum
Phosphogypsum (PG) is the calcium sulfate hydrate formed as a by-product of the production of fertilizer from phosphate rock. It is mainly composed of gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O). Although gypsum is a widely used material in the construction industry, phosphogypsum is usually not used, but is stored indefinitely because of its weak radioactivity caused by the presence of naturally occurring uranium (U) and thorium (Th), and their daughter isotopes radium (Ra), radon (Rn) and polonium (Po). The long-range storage of phosphogypsum is controversial.Ayres, R. U., Holmberg, J., Andersson, B., "Materials and the Global environment: Waste Mining in the 21st Century", MRS Bull. 2001, 26, 477. About five tons of phosphogypsum are generated per ton of phosphoric acid production. Annually, the estimated generation of phosphogypsum worldwide is 100 to 280 million metric tons. Production and properties Phosphogypsum is a by-product from the production of phosphoric acid by treating phosphate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |