|
Millepora Platyphylla
''Millepora platyphylla'' is a species of fire coral, a type of hydrocoral, in the family Milleporidae. It is also known by the common names blade fire coral and plate fire coral. It forms a calcium carbonate skeleton and has toxic, defensive polyps that sting. It obtains nutrients by consuming plankton and via symbiosis with photosynthetic algae. The species is found from the Red Sea and East Africa to northern Australia and French Polynesia. It plays an important role in reef-building in the Indo-Pacific region. Depending on its environment, it can have a variety of different forms and structures. Description From class Hydrozoa, ''Millepora platyphylla'' is not a true coral, distinguishing it from the stony corals and soft corals in class Anthozoa. Like other species of fire coral, it can have diverse growth forms, including branches, fans, plates, blades, or encrusting forms. However, they are generally characterized as plate-like or blade-like, which differentiates them fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Hemprich
Wilhelm Friedrich Hemprich (24 June 1796 – 30 June 1825) was a German naturalist and explorer. Hemprich was born in Glatz (Kłodzko), Prussian Silesia, and studied medicine at Breslau and Berlin. It was in Berlin that he became friends with Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, the two men sharing an interest in natural history. Hemprich lectured at Berlin University on comparative physiology, and wrote ''Grundriss der Naturgeschichte'' (Compendium of Natural History) (1820). In his spare time he studied reptiles and amphibians at the zoological museum under Hinrich Lichtenstein. In 1820 Hemprich and Ehrenberg were invited to serve as naturalists on a primarily archeological expedition to Egypt, led by Prussian General von Minutoli. The two naturalists were sponsored by the Berlin Academy. In March 1821 they separated from the main party and travelled up the river Nile to Dongola, the capital of Nubia. They spent the next two years studying the natural history of that part of Egy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. Ehrenberg was an evangelist and was considered to be of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Early collections The son of a judge, Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was born in Delitzsch, near Leipzig. He first studied theology at the University of Leipzig, then medicine and natural sciences in Berlin and became a friend of the famous explorer Alexander von Humboldt. In 1818, he completed his doctoral dissertation on fungi, ''Sylvae mycologicae Berolinenses.'' In 1820–1825, on a scientific expedition to the Middle East with his friend Wilhelm Hemprich, he collected thousands of specimens of plants and animals. He investigated parts of Egypt, the Libyan Desert, the Nile valley and the northern coasts of the Red Sea, where he made a special study of the corals. Subsequently, parts of Syria, Arabia and Abyss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Coral
Fire corals (''Millepora'') are a genus of colonial marine organisms that exhibit physical characteristics similar to that of coral. The name coral is somewhat misleading, as fire corals are not true corals but are instead more closely related to ''Hydra'' and other hydrozoans, making them hydrocorals. They make up the only genus in the monotypic family Milleporidae. Distinguishing characteristics Fire corals have a bright, yellow-green to brown skeletal covering, and are widely distributed in tropical and subtropical waters. They appear in small, brush-like growths on rocks and coral. Divers often mistake fire coral for seaweed, and accidental contact is common. Upon contact, an intense pain can be felt, lasting from two days to two weeks. Occasional relapses of post-treatment inflammation are common. Prominent side effects can include skin irritation, stinging or burning pain, erythema (skin redness), fever, and/or urticarian (hives) lesions. These side effects are due to ven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milleporidae
Fire corals (''Millepora'') are a genus of colonial marine organisms that exhibit physical characteristics similar to that of coral. The name coral is somewhat misleading, as fire corals are not true corals but are instead more closely related to ''Hydra'' and other hydrozoans, making them hydrocorals. They make up the only genus in the monotypic family Milleporidae. Distinguishing characteristics Fire corals have a bright, yellow-green to brown skeletal covering, and are widely distributed in tropical and subtropical waters. They appear in small, brush-like growths on rocks and coral. Divers often mistake fire coral for seaweed, and accidental contact is common. Upon contact, an intense pain can be felt, lasting from two days to two weeks. Occasional relapses of post-treatment inflammation are common. Prominent side effects can include skin irritation, stinging or burning pain, erythema (skin redness), fever, and/or urticarian (hives) lesions. These side effects are due to ven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrozoa
Hydrozoa (hydrozoans; ) are a taxonomic class of individually very small, predatory animals, some solitary and some colonial, most of which inhabit saline water. The colonies of the colonial species can be large, and in some cases the specialized individual animals cannot survive outside the colony. A few genera within this class live in freshwater habitats. Hydrozoans are related to jellyfish and corals and belong to the phylum Cnidaria. Some examples of hydrozoans are the freshwater jelly (''Craspedacusta sowerbyi''), freshwater polyps ('' Hydra''), ''Obelia'', Portuguese man o' war (''Physalia physalis''), chondrophores (Porpitidae), "air fern" (''Sertularia argentea''), and pink-hearted hydroids (''Tubularia''). Anatomy Most hydrozoan species include both a polyp (zoology), polypoid and a medusa (biology), medusoid stage in their lifecycles, although a number of them have only one or the other. For example, ''Hydra'' has no medusoid stage, while ''Liriope tetraphylla, Lir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthozoa
Anthozoa is a subphylum of marine invertebrates which includes the sea anemones, Scleractinia, stony corals and Alcyonacea, soft corals. Adult anthozoans are almost all attached to the seabed, while their larvae can disperse as part of the plankton. The basic unit of the adult is the polyp (zoology), polyp; this consists of a cylindrical column topped by a disc with a central mouth surrounded by tentacles. Sea anemones are mostly solitary, but the majority of corals are Colony (biology), colonial, being formed by the budding of new polyps from an original, founding individual. Colonies are strengthened by calcium carbonate and other materials and take various massive, plate-like, bushy or leafy forms. Anthozoa is included within the phylum Cnidaria, which also includes the jellyfish, Box jellyfish, box jellies and parasitic Myxozoa and Polypodiozoa. The two main subclasses of Anthozoa are the Hexacorallia, members of which have six-fold symmetry in biology, symmetry and includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millepora Dichotoma
''Millepora dichotoma'', the net fire coral, is a species of hydrozoan, consisting of a colony of polyps with a calcareous skeleton. Description ''M. dichotoma'' is a colonial hermatypic coral with a calcareous endoskeleton. They form colonies up to 60 cm wide, but clumps of colonies may be several meters across. They initially build as encrusting coral, adhering themselves to hard substrate. The encrusting formations further develop into other growth forms, such as lace-like, leaf-like blades, and box-work. What growth form an individual develops into is highly dependent on the depth and location of growth as well as on the turbidity of the water in a given location. More fragile structures, such as lace-like, succeed better in deeper, less turbulent waters, whereas box-work forms are able to better succeed in harsher environments. As in other hermatypic corals, part of the metabolism of fire corals relies on zooxanthellae. Symbiotic zooxanthellae give ''M. dichotom''a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millepora Exaesa
Fire corals (''Millepora'') are a genus of colonial marine organisms that exhibit physical characteristics similar to that of coral. The name coral is somewhat misleading, as fire corals are not true corals but are instead more closely related to ''Hydra'' and other hydrozoans, making them hydrocorals. They make up the only genus in the monotypic family Milleporidae. Distinguishing characteristics Fire corals have a bright, yellow-green to brown skeletal covering, and are widely distributed in tropical and subtropical waters. They appear in small, brush-like growths on rocks and coral. Divers often mistake fire coral for seaweed, and accidental contact is common. Upon contact, an intense pain can be felt, lasting from two days to two weeks. Occasional relapses of post-treatment inflammation are common. Prominent side effects can include skin irritation, stinging or burning pain, erythema (skin redness), fever, and/or urticarian (hives) lesions. These side effects are due to ven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidocyte
A cnidocyte (also known as a cnidoblast or nematocyte) is an explosive cell containing one large secretory organelle called a cnidocyst (also known as a cnida () or nematocyst) that can deliver a sting to other organisms. The presence of this cell defines the phylum Cnidaria (corals, sea anemones, hydrae, jellyfish, etc.). Cnidae are used to capture prey and as a defense against predators. A cnidocyte fires a structure that contains a toxin within the cnidocyst; this is responsible for the stings delivered by a cnidarian. Structure and function Each cnidocyte contains an organelle called a cnida, cnidocyst, nematocyst, ptychocyst or spirocyst. This organelle consists of a bulb-shaped capsule containing a coiled hollow tubule structure attached to it. An immature cnidocyte is referred to as a cnidoblast or nematoblast. The externally oriented side of the cell has a hair-like trigger called a cnidocil, which is a mechano- and chemo-receptor. When the trigger is activated, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonophore
A gonophore is a reproductive organ in Hydrozoa that produces gametes. It is a sporosac, a medusa or any intermediate stage. The name is derived from the Greek words (, that which produces seed) and (, -bearing). Gonophores are borne on branching stalks that grow out as a ring from the hydranth (i.e. the hydroid polyp, bearing a mouth, digestive cavity and tentacles) wall. The germ cells are formed from the inner layer of the entocodon. The entocodon is the primordium (i.e. the first cells that give rise to the development of an organ) of the subumbrella (i.e. the concave oral surface of a medusa) in the development of medusae from the gonophore. The gonophores in the order Leptomedusae are borne on much reduced hydranths and are usually protected in a peridermal (i.e. belonging to a hydroid perisarc) gonotheca. Medusae forming on fully developed hydranths are extremely rare; usually the gonophores develop into medusae or into sessile sporosacs. The gonophores in the superfam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millepora Tenera
''Millepora tenera'' is a species of fire coral in the family Milleporidae. It is native to the Red Sea and the western Indo-Pacific region and is a zooxanthellate species with a calcareous skeleton. It was first described in 1949 by the Dutch zoologist Hilbrand Boschma. Distribution and habitat ''Millepora tenera'' is native to the western Indo-Pacific. Its range extends from the Red Sea and the eastern coast of Africa to Japan, Australia, American Samoa and the Mariana Islands. It is found at depths down to about , often in turbid locations where it is tolerant of some degree of siltation. Toxicity Like other fire corals, ''Millepora tenera'' can cause painful rashes when touched by bare skin. Extracts of this coral contain neurotoxins, and can cause convulsions, respiratory failure and death in mice. The extract causes hemolysis, contains a dermonecrotic factor and has antigenic properties. Rabbits immunised with the extract developed neutralising antibodies that were protec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
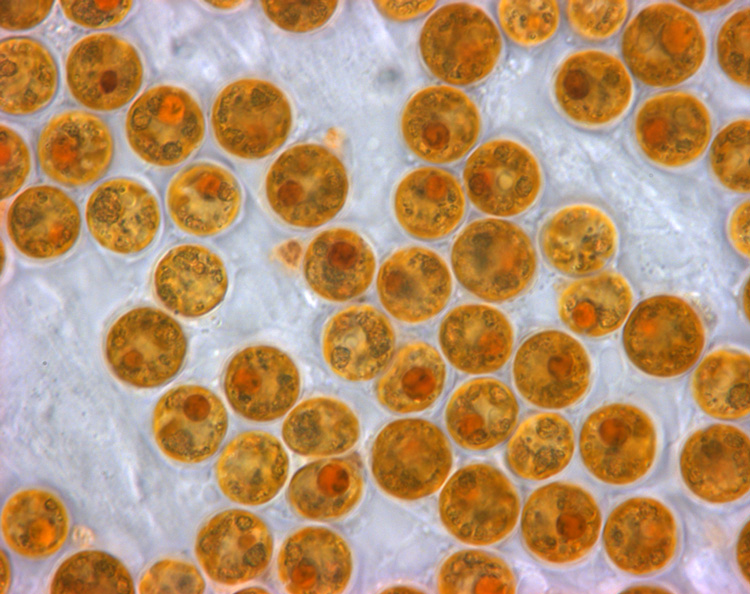
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus '' Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)