|
Milang Tribe
The Milang tribe (alternately Millang, Malaa, or Holon) are a tribe of the Adi people of Arunachal Pradesh and nearby Jonai, in Assam, India. Etymology The term ''Milang'' is an exonym, used by non-members of the tribe to refer to the tribe. Members of the tribe prefer the name ''Malaa''. Language Malaa people use a language unintelligible to most of the other Adi tribes. There have been several theories regarding this language; most Malaa maintain that they adopted their language from a people called Soi-sotem, who inhabited their lands long before Malaa settled there. The Malaa remember the Soi-sotem in their ballads as: : ''Soi belu kettunge, Sotem belu kettunge''. Soi sotem were believed to come from Kalang Ade(dite), the highest peak in the land of the Milang beyond which is the land of Idu Mishmi tribe, Idu Mishmi people. Religion The Malaa are adherents of indigenous Donyi-Poloism, the practice of praying to the almighty Sun goddess and The Moon God. The priests, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adi People
Adi or ADI may refer to: Names and titles * Adi (mythology), an Asura in Hindu faith who appears in the Matsya Purāṇa * Adi (name), a given name in Hebrew and a nickname in other languages * Adi (title), a Fijian title used by females of chiefly rank Places * Adi (Khanapur), Belgaum District, Karnataka, India * Adi (Chikodi), Belgaum District, Karnataka, India * Ahmedabad Junction railway station, Ahmedabad, India (code ADI) * Adi, Israel, a community settlement in northern Israel * Adi Island, an island in West Papua, Indonesia * Arandis Airport, Arandis, Namibia (IATA: ADI) Organizations * Aerodynamics Inc., a small airline in the US * Aircraft Designs Inc, an aircraft design firm in Monterey, California * Alfred Deakin Institute, at Deakin University, in Geelong, Australia * American Documentation Institute, former name of the Association for Information Science and Technology * Analog Devices, Inc, producer of semiconductors (ADI is their symbol on the New York Stock E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed border with China in the north at the McMahon Line. Itanagar is the state capital of Arunachal Pradesh. Arunachal Pradesh is the largest of the Seven Sister States of Northeast India by area. Arunachal Pradesh shares a 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region. As of the 2011 Census of India, Arunachal Pradesh has a population of 1,382,611 and an area of . It is an ethnically diverse state, with predominantly Monpa people in the west, Tani people in the centre, Mishmi and Tai people in the east, and Naga people in the southeast of the state. About 26 major tribes and 100 sub-tribes live in the state. The main tribes of the state are Adi, Nyshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonai
Jonai ( as, জোনাই) is a Sub-Division of Dhemaji District in the state of Assam in India. Etymology The name ''Jonai'' is derived from the name of a Chutia princess named ''Jona'' who was married off to a Kachari prince named ''Kansan''. As per folklore, the Kachari prince had entered the Chutia kingdom along with 900 men as he had left his kingdom due to some personal issues. The Chutia princess having heard about this encroachment ordered her soldiers to make the prince and his followers captive and to bring them to the royal court in Sadiya. Later, as events turned out, the princess fell in love with the prince, and she was married off to him and they settled in Jonai. The other followers too married local women. The Sonowal Kacharis are thought to be descendants of this group of people and recall the queen as ''Jonadoi Ai''. Demographics Jonai is the easternmost sub-division of Dhemaji District, about 554 km from the state capital, Guwahati. It is located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a wide strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese and Boro are the official languages of Assam, while Bengali is an additional official language in the Barak Valley. Assam is known for Assam tea and Assam silk. The state was the first site for oil drilling in Asia. Assam is home to the one-horned Indian rhinoceros, along with the wild water buffalo, pygmy hog, tiger and various species of Asiatic birds, and provides one of the last wild habitats for the Asian elephant. The Assamese economy is aided by wildlife tourism to Kaziranga National Park and Manas National Park, which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, or linguistic community in question; it is their self-designated name for themselves, their homeland, or their language. An exonym (from Greek: , 'outer' + , 'name'; also known as xenonym) is an established, ''non-native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used only outside that particular place, group, or linguistic community. Exonyms exist not only for historico-geographical reasons but also in consideration of difficulties when pronouncing foreign words. For instance, is the endonym for the country that is also known by the exonym ''Germany'' in English, in Spanish and in French. Naming and etymology The terms ''autonym'', ''endonym'', ''exonym'' and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
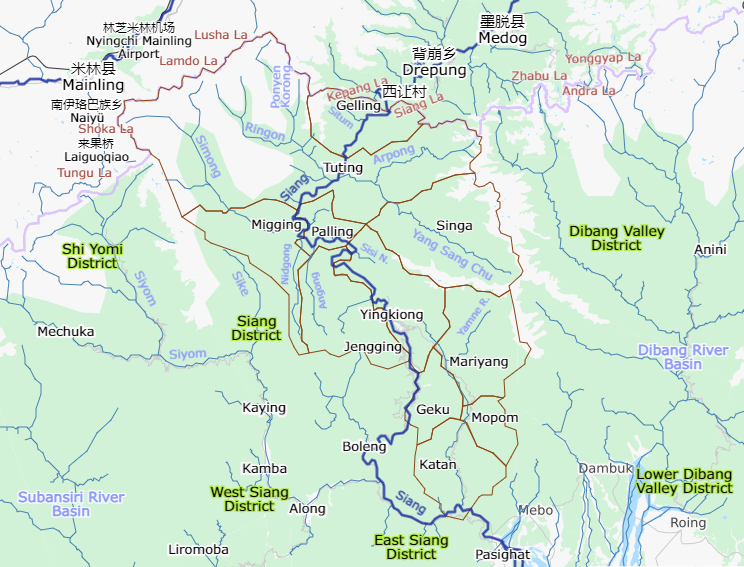
Upper Siang District
Upper Siang (Pron:/ˈsjæŋ or ˈsɪæŋ/) is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India. It is the fourth least populous district in the country (out of 640). History The majority of the people are of the Adi tribe while the Memba, Khamba tribe also exists there. Part of the area was controlled by the Tibetan Kingdom of Powo when streams of Tibetan pilgrims searching for one of the 'hidden lands' or beyul ( bo, sbas-yul) referred to in the prophecies of Guru Rinpoche in the East Himalayas from the mid-seventeenth century came south over the Doshong La pass, to seek the particular location of one of these earthly paradises called Padma bkod (written variously Pema köd, Pemakö and Pemako), literally 'Lotus Array' in the region. The region became administered by British India with the Simla Accord of 1914 and the demarcation of the McMahon Line, though China considers it part of South Tibet. The district was formed in 1999 when it was split from Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padam Tribe
Padam is a sub-tribe of the Adi tribe of Abotani clan which speaks one of the Sino-Tibetan languages. Padam makes up 30–35% of the Adis and are the strongest sub-tribe of the Adis. They were a nomadic warrior race and used to had a reputation as fierce warrior by pre colonial period, they are believed to have migrated to present Arunachal Pradesh from Tibet. They were also known by the name Bor Abors in the past by their Assam counterparts and the British government. They inhabits in the region of upper siang, east siang, lower Dibang valley and parts of Lohit and Namsai district of Arunachal Pradesh Location Although it is almost from Pasighat, their land resides in the Upper Siang district, throughout the Lower Dibang Valley The Lower Dibang Valley district (Pron:/dɪˈbæŋ/) is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in northeastern India. It is the tenth least populous district in the country. History In June 1980, the Dibang Valley district .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aconitum
''Aconitum'' (), also known as aconite, monkshood, wolf's-bane, leopard's bane, mousebane, women's bane, devil's helmet, queen of poisons, or blue rocket, is a genus of over 250 species of flowering plants belonging to the family Ranunculaceae. These herbaceous perennial plants are chiefly native to the mountainous parts of the Northern Hemisphere in North America, Europe, and Asia; growing in the moisture-retentive but well-draining soils of mountain meadows. Most ''Aconitum'' species are extremely poisonous and must be handled very carefully. Several ''Aconitum'' hybrids, such as the Arendsii form of ''Aconitum carmichaelii'', have won gardening awards—such as the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. Some are used by florists. Etymology The name ''aconitum'' comes from the Greek word , which may derive from the Greek ''akon'' for dart or javelin, the tips of which were poisoned with the substance, or from ''akonae'', because of the rocky ground on which th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aconitine
Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus '' Aconitum'' (family Ranunculaceae), known also commonly by the names wolfsbane and monkshood. Monkshood is notorious for its toxic properties. Aconitine is also present in Yunnan Baiyao, a proprietary traditional Chinese medicine. Uses Aconitine was previously used as an antipyretic and analgesic and still has some limited application in herbal medicine, although the narrow therapeutic index makes calculating appropriate dosage difficult. Structure and reactivity Biologically active isolates from '' Aconitum'' and ''Delphinium'' plants are classified as norditerpenoid alkaloids, which are further subdivided based on the presence or absence of the C18 carbon. Aconitine is a C19-norditerpenoid, based on its presence of this C18 carbon. It is barely soluble in water, but very soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform or diethyl ether. Aconitine is also soluble in mixtures of alcohol an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)