Upper Siang District on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Upper Siang (Pron:/ˈsjæŋ or ˈsɪæŋ/) is an administrative district in the state of
here
an
here
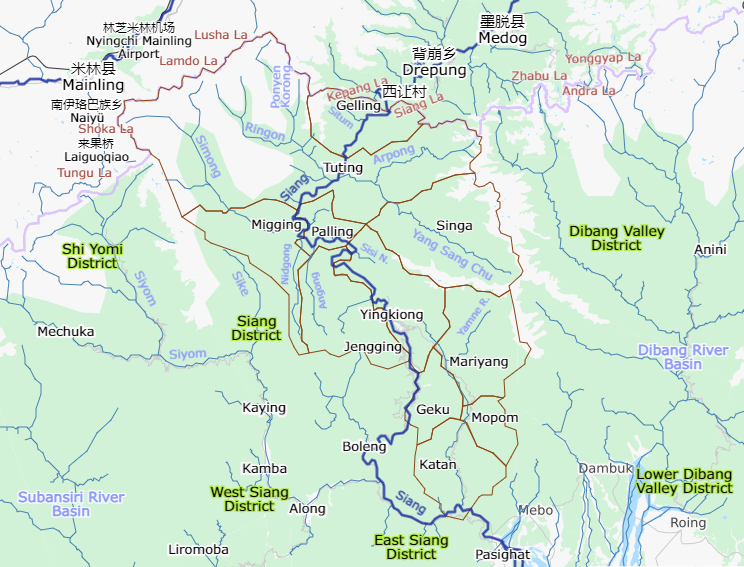 Administrative circles include Yingkiong, Jengging, Mariyang, Geku, Katan, Mopom, Tuting, Gelling, Singa, Palling, Migging.
Administrative circles include Yingkiong, Jengging, Mariyang, Geku, Katan, Mopom, Tuting, Gelling, Singa, Palling, Migging.
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares int ...
in India. It is the fourth least populous district in the country (out of 640).
History
The majority of the people are of the Adi tribe while the Memba, Khamba tribe also exists there. Part of the area was controlled by the TibetanKingdom of Powo
The Kingdom of Powo or sPo bo () was a kingdom located in present-day Bomê County, Tibet. The ruler of Powo used the title Kanam Gyelpo (''kaH gnam rgyal po'') or Kanam Depa (''kaH gnam sde pa'').
It was said that the monarchs of Powo were desc ...
when streams of Tibetan pilgrims searching for one of the 'hidden lands' or beyul
According to the beliefs of the Nyingma school of Tibetan Buddhism, Beyul () are hidden valleys often encompassing hundreds of square kilometers, which Padmasambhava blessed as refuges. Tertöns may reveal them from terma at specific and appro ...
( bo, sbas-yul) referred to in the prophecies of Guru Rinpoche
Padmasambhava ("Born from a Lotus"), also known as Guru Rinpoche (Precious Guru) and the Lotus from Oḍḍiyāna, was a tantric Buddhist Vajra master from India who may have taught Vajrayana in Tibet (circa 8th – 9th centuries)... According ...
in the East Himalayas from the mid-seventeenth century came south over the Doshong La pass, to seek the particular location of one of these earthly paradises called Padma bkod (written variously Pema köd, Pemakö and Pemako), literally 'Lotus Array' in the region. The region became administered by British India with the Simla Accord of 1914 and the demarcation of the McMahon Line
The McMahon Line is the boundary between Tibet and British India as agreed in the maps and notes exchanged by the respective plenipotentiaries on 24–25 March 1914 at Delhi, as part of the 1914 Simla Convention.
The line delimited the resp ...
, though China considers it part of South Tibet
South Tibet is a claimed area by China with the literal translation of the Chinese term '' (), which may refer to different geographic areas:
* The southern part of Tibet, covering the middle reaches of the Yarlung Tsangpo River Valley between ...
.
The district was formed in 1999 when it was split from East Siang district.
Geography
The district headquarters are located atYingkiong
Yingkiong is a town in and the administrative headquarters of Upper Siang district in the Northeast Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. It is located north of Itanagar, the capital of the state, and east of the River Siang. According to the ...
. Upper Siang district occupies an area of ,
The district is the location of the massive Upper Siang Hydroelectric Project.
Transport
The proposed Mago-Thingbu
Thingbu is a settlement in Tawang district in the north-eastern state of Arunachal Pradesh, India.
Location
It is located on the proposed Mago-Thingbu to Vijaynagar Arunachal Pradesh Frontier Highway along the McMahon Line, alignment map ...
to Vijaynagar Arunachal Pradesh Frontier Highway along the McMahon Line
The McMahon Line is the boundary between Tibet and British India as agreed in the maps and notes exchanged by the respective plenipotentiaries on 24–25 March 1914 at Delhi, as part of the 1914 Simla Convention.
The line delimited the resp ...
, (will intersect with the proposed East-West Industrial Corridor Highway) and will pass through this district, alignment map of which can be seehere
an
here
Divisions
There are twoArunachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly
The Arunachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly is the unicameral state legislature of Arunachal Pradesh state in north-eastern India. The seat of the Legislative Assembly is at Itanagar, the capital of the state. The Legislative Assembly comprise ...
constituencies in this district: Tuting-Yingkiong and Mariyang-Geku. Both are part of Arunachal East Lok Sabha constituency. Administrative circles include Yingkiong, Jengging, Mariyang, Geku, Katan, Mopom, Tuting, Gelling, Singa, Palling, Migging.
Administrative circles include Yingkiong, Jengging, Mariyang, Geku, Katan, Mopom, Tuting, Gelling, Singa, Palling, Migging.
Demographics
According to the 2011 census Upper Siang district has apopulation
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
of 35,320, roughly equal to the nation of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarchy ...
. This gives it a ranking of 637th in India (out of a total of 640). The district has a population density of . Its population growth rate
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
over the decade 2001–2011 was 5.77%. Upper Siang has a sex ratio
The sex ratio (or gender ratio) is usually defined as the ratio of males to females in a population. As explained by Fisher's principle, for evolutionary reasons this is typically about 1:1 in species which reproduce sexually. Many species devia ...
of 891 females
Female (symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females a ...
for every 1000 males, and a literacy rate
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, huma ...
of 59.94%. Scheduled Tribes make up 80.60% of the population.
Various tribal groups of the Adi people Adi or ADI may refer to:
Names and titles
* Adi (mythology), an Asura in Hindu faith who appears in the Matsya Purāṇa
* Adi (name), a given name in Hebrew and a nickname in other languages
* Adi (title), a Fijian title used by females of chie ...
and the Memba
The Memba are a people of Arunachal Pradesh. The Memba population is currently around four to five thousand. They mainly live in the districts of Shi Yomi, West Siang and Upper Siang. Some also in nearby Tibet. The religious life of the Memba ...
tribe live in the district. The Adi tribe generally follows Donyi-Polo
Donyi-Polo (also Donyi-Poloism) is the designation given to the indigenous religion, of animistic and shamanic type, of the Tani and other Tibeto-Burman peoples of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in Northeast India. The name "Donyi-Polo" means "Su ...
, and the Memba are followers of Tibetan Buddhism.
Languages
Languages spoken includeAdi Adi or ADI may refer to:
Names and titles
* Adi (mythology), an Asura in Hindu faith who appears in the Matsya Purāṇa
* Adi (name), a given name in Hebrew and a nickname in other languages
* Adi (title), a Fijian title used by females of chie ...
, a Sino-Tibetan
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
tongue with approximately 140 000 speakers, and Tshangla
Tshangla is a Sino-Tibetan language of the Bodish branch closely related to the Tibetic languages. Tshangla is primarily spoken in Eastern Bhutan and acts as a lingua franca in the region; it is also spoken in the adjoining Tawang tract in the I ...
and Khampa Tibetan languages both belonging to the Bodish group, these languages are written in both the Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dial ...
and Latin script
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern Italy ...
s.
At the time of the 2011 census, 72.01% of the population spoke Adi Adi or ADI may refer to:
Names and titles
* Adi (mythology), an Asura in Hindu faith who appears in the Matsya Purāṇa
* Adi (name), a given name in Hebrew and a nickname in other languages
* Adi (title), a Fijian title used by females of chie ...
, 6.54% Bhotia, 4.44% Nepali, 3.93% Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been de ...
, 1.91% Odia
Odia, also spelled Oriya or Odiya, may refer to:
* Odia people in Odisha, India
* Odia language, an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family
* Odia alphabet, a writing system used for the Odia languag ...
, 1.78% Assamese, 1.42% Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
and 1.25% as their first language.
Flora and fauna
In 1986 Upper Siang district became home to Mouling National Park, which has an area of . A new mammal to science, Mebo giant flying squirrel (''Petaurista siangensis'') has been reported from this district.Banking facilities in Upper Siang
List of banks functioning in Upper Siang. *State Bank Of India
State Bank of India (SBI) is an Indian multinational public sector bank and financial services statutory body headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. SBI is the 49th largest bank in the world by total assets and ranked 221st in the ''Fortune ...
, Tuting
*State Bank Of India
State Bank of India (SBI) is an Indian multinational public sector bank and financial services statutory body headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. SBI is the 49th largest bank in the world by total assets and ranked 221st in the ''Fortune ...
, Yingkiong
References
External links
* {{Arunachal Pradesh Districts of Arunachal Pradesh 1999 establishments in Arunachal Pradesh