|
Mid America Heart Institute
The Mid America Heart Institute (MAHI) is located in Kansas City, Missouri and is one of the first and largest hospitals developed and designed specifically for cardiovascular care. It is a subsidiary of the not-for-profit Saint Luke's Hospital of Kansas City and is a part of Saint Luke's Health System. The Heart Institute is affiliated with the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine and has earned the certification as a Comprehensive Cardiac Center from the Joint Commission. History Cardiovascular care was provided at Saint Luke's Hospital since its inception in 1882. The Mid America Heart Institute was commissioned in 1975. At that time, the vast majority of all heart procedures in the Kansas City area and over 20% of cardiovascular procedures in both Kansas and Missouri were done by providers on staff at Saint Luke's Hospital. The Mid America Heart Institute began construction in 1979 and was dedicated in 1981. An additional five stories were added in 1990. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Luke's Health System
Saint Luke's Health System is a non-profit hospital network in the bi-state Kansas City metro area, located in northeast Kansas and northwest Missouri. It traces its history to its flagship hospital, Saint Luke's Hospital of Kansas City, which was established in 1882. With over 12,000 local employees, Saint Luke's Health System is the third largest private employer in the Kansas City metro. Leadership * Melinda Estes – president and chief executive officer * Bob Bonney – senior vice president, non-acute services and business development * Debe Gash – senior vice president and chief digital officer * Dawn Murphy – senior vice president, human resources * Jan Murray – senior vice president and chief legal counsel * J. Chris Perryman – senior vice president and chief medical officer * Julie Quirin – senior vice president, hospital operations * Chuck Robb – senior vice president, finance & administration and chief financial officer * Richard D. Rolston – senior vice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patient-reported Outcome
A patient-reported outcome (PRO) is a health outcome directly reported by the patient who experienced it. It stands in contrast to an outcome reported by someone else, such as a physician-reported outcome, a nurse-reported outcome, and so on. PRO methods, such as questionnaires, are used in clinical trials or other clinical settings, to help better understand a treatment's efficacy or effectiveness. The use of digitized PROs, or electronic patient-reported outcomes (ePROs), is on the rise in today's health research setting. Terminology PROs should not be confused with PCOs, or '' patient-centered outcomes''. The latter implies the use of a questionnaire covering issues and concerns that are specific to a patient. Instead, ''patient-reported'' outcomes refers to reporting situations in which only the patient provides information related to a specific treatment or condition; this information may or may not be of concern to the patient. Further, PROs should not be confused with PREM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award
The Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award recognizes U.S. organizations in the business, health care, education, and nonprofit sectors for performance excellence. The Baldrige Award is the highest formal recognition of the performance excellence of both public and private U.S. organizations given by the President of the United States. It is administered by the Baldrige Performance Excellence Program, which is based at and managed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce. The Baldrige Performance Excellence Program and the associated award were established by the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Improvement Act of 1987 (Public Law 100–107). The program and award were named for Malcolm Baldrige, who served as United States Secretary of Commerce during the Reagan administration, from 1981 until Baldrige's 1987 death in a rodeo accident. The first award was given November 13, 1988. By 1991, ''The New York Times' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of The United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces. The power of the presidency has grown substantially since the first president, George Washington, took office in 1789. While presidential power has ebbed and flowed over time, the presidency has played an increasingly strong role in American political life since the beginning of the 20th century, with a notable expansion during the presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt. In contemporary times, the president is also looked upon as one of the world's most powerful political figures as the leader of the only remaining global superpower. As the leader of the nation with the largest economy by nominal GDP, the president possesses significant domestic and international hard and soft power. Article II of the Constitution establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) or automated implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD) is a device implantable inside the body, able to perform defibrillation, and depending on the type, cardioversion and pacing of the heart. The ICD is the first-line treatment and prophylactic therapy for patients at risk for sudden cardiac death due to ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. "AICD" was trademarked by the Boston Scientific corporation, so the more generic "ICD" is preferred terminology. Current device batteries last about six to ten years; with advances in technology (batteries with more capacity or potentially rechargeable batteries) it may be possible to increase this well past ten years. The lead (the electrical cable connecting the device to the heart) has a much longer average longevity but can incur various types of malfunction, specifically insulation failure or fracture of the conductor, and require replacement. The process o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
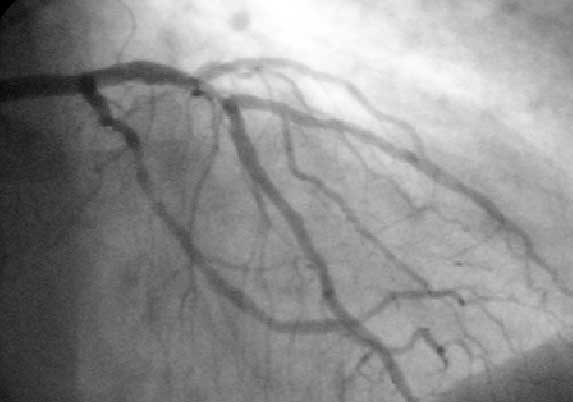
Angioplasty
Angioplasty, is also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis. A deflated balloon attached to a catheter (a balloon catheter) is passed over a guide-wire into the narrowed vessel and then inflated to a fixed size. The balloon forces expansion of the blood vessel and the surrounding muscular wall, allowing an improved blood flow. A stent may be inserted at the time of ballooning to ensure the vessel remains open, and the balloon is then deflated and withdrawn. Angioplasty has come to include all manner of vascular interventions that are typically performed percutaneously. The word is composed of the combining forms of the Greek words ἀνγεῖον ' "vessel" or "cavity" (of the human body) and πλάσσω ' "form" or "mould". Uses and indications Coronary angioplasty A coronary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emitting from within the body rather than radiation that is generated by external sources like X-rays. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on the function. For such reason, it is called a physiological imaging modality. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are the two most common imaging modalities in nuclear medicine. Diagnostic medical imaging Diagnostic In nuclear medicine imaging, radiopharmaceuticals are taken internally, for example, through inhalation, intravenously or orally. Then, external detectors (gamma cameras) capture and form images from the radiation emitted by the radiopharmaceuticals. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City (abbreviated KC or KCMO) is the largest city in Missouri by population and area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 508,090 in 2020, making it the 36th most-populous city in the United States. It is the central city of the Kansas City metropolitan area, which straddles the Missouri–Kansas state line and has a population of 2,392,035. Most of the city lies within Jackson County, with portions spilling into Clay, Cass, and Platte counties. Kansas City was founded in the 1830s as a port on the Missouri River at its confluence with the Kansas River coming in from the west. On June 1, 1850, the town of Kansas was incorporated; shortly after came the establishment of the Kansas Territory. Confusion between the two ensued, and the name Kansas City was assigned to distinguish them soon after. Sitting on Missouri's western boundary with Kansas, with Downtown near the confluence of the Kansas and Missouri Rivers, the city encompasses about , making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnormality in patients with suspected cardiac disease. It is a tool which helps in reaching an ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |