|
Mid-Hants Watercress Railway
The Watercress Line is the marketing name of the Mid-Hants Railway, a heritage railway in Hampshire, England, running from New Alresford to Alton where it connects to the National Rail network. The line gained its popular name in the days when it was used to transport locally grown watercress to markets in London. The railway currently operates regular scheduled services, along with dining trains, real ale trains and numerous special events throughout the year. History British Railways ownership In 1861, the Alton, Alresford and Winchester Railway Company was authorised to build a new railway to connect to the existing London & South Western Railway lines at Alton and Winchester. It was opened on 2 October 1865 as the Mid-Hants Railway. Trains were operated by the London & South Western Railway which eventually purchased the Mid-Hants Railway Company in 1884. Stations were initially constructed at Itchen Abbas, Ropley and Alresford. The station at was already in exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
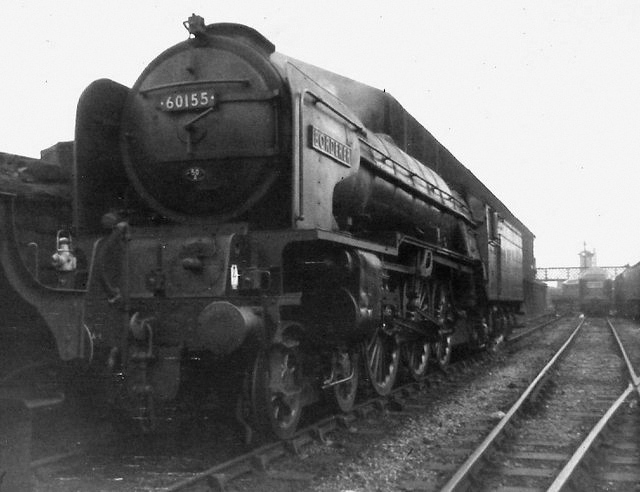
60163 Tornado
LNER Peppercorn Class A1 No. 60163 ''Tornado'' is a 4-6-2 steam locomotive completed in 2008 to an original design by Arthur Peppercorn. It is the first new build British mainline steam locomotive since 1960, and the only Peppercorn Class A1 in existence after the original batch were scrapped. In 2017, ''Tornado'' became the first steam locomotive to officially reach 100 mph on British tracks in over 50 years. After the project was founded by the A1 Steam Locomotive Trust in 1990, construction of ''Tornado'' began in 1994 and mostly took place at Darlington Works, with other components manufactured elsewhere. The project was financed through fundraising initiatives, public donations, sponsorship deals, and hiring out ''Tornado'' itself for special services. The locomotive was granted its mainline certificate in January 2009, having been designed in compliance with modern safety and certification standards''. Tornado'' has worked on heritage and mainline trains across Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Portsmouth and the towns of Havant, Waterlooville, Eastleigh, Fareham and Gosport. A major port, and close to the New Forest, it lies at the northernmost point of Southampton Water, at the confluence of the River Test and Itchen, with the River Hamble joining to the south. Southampton is classified as a Medium-Port City . Southampton was the departure point for the and home to 500 of the people who perished on board. The Spitfire was built in the city and Southampton has a strong association with the ''Mayflower'', being the departure point before the vessel was forced to return to Plymouth. In the past century, the city was one of Europe's main ports for ocean liners and more recently, Southampton is known as the home port of some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
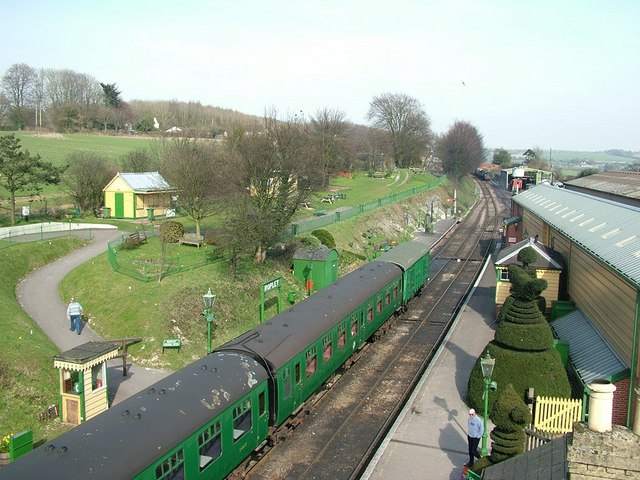
Ropley Railway Station
Ropley railway station is a railway station in Ropley, Hampshire, England, which opened in 1865 and reopened in 1977 after four years' closure, to be served by steam and select diesel trains on the Watercress Line which shares its terminus at Alton railway station along with the more major Alton Line. History The station was opened by the Mid-Hants (Alton Lines) Railway (MHR) on 2 October 1865. The MHR was leased to the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) in August 1880, which fully absorbed the MHR in June 1884. The LSWR amalgamated with other railways to form the Southern Railway on 1 January 1923. The station was destaffed in 1967 and closed by British Rail on 5 February 1973. Preservation Ropley railway station was reopened by the Mid Hants Railway (Watercress Line) on 30 April 1977. It is an intermediate station on the , four-station route which runs from Alton to New Alresford, also in Hampshire. The main locomotive shed and workshops for the Mid Hants Railway ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 205
The British Rail Class 205 ( 3H) diesel-electric multiple units were built by BR at Eastleigh from 1957 to 1962, and in service for 47 years from BR Southern Region to Connex South Central and finally to the Southern franchise. They were eventually replaced by Class 171 Turbostar units. Description This class of unit was built in four different batches for use on different lines. The Southern Region class 201 to 207 DEMUs are nicknamed 'Thumpers' owing to the noise they made while in motion. The first batch of units, numbered 1101–1118, was built in 1957 as two-car units and classified as 2H. They were built for services in Hampshire on the non-electrified routes between , and and between , and . The first units entered service in September 1957. However, owing to increasing passenger numbers, all eighteen units were strengthened to three cars in 1958 and 1969, with the addition of a centre trailer, and therefore were reclassified as 3H units. Upon the introduction of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Axe
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965), written by Richard Beeching and published by the British Railways Board. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and 67,700 British Rail positions, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes for significant investment. The 1963 report also recommended some less well-publicised changes, including a switch to the now-standard practice of containerisation for rail freight, and the replacement of some services wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Region Of British Railways
The Southern Region was a region of British Railways from 1948 until 1992 when railways were re-privatised. The region ceased to be an operating unit in its own right in the 1980s. The region covered south London, southern England and the south coast, including the busy commuter belt areas of Kent, Sussex and Surrey. The region was largely based upon the former Southern Railway area. The Region The Southern Railway was still comparatively profit-making despite World War II, thanks to its extensive third rail DC electrification and the intensive service patterns this allowed for. However, large-scale investment was required in the infrastructure of all of the "Big 4" companies, including the Southern. The Transport Act 1947 provided for the nationalisation of all heavy rail systems in the UK to allow for this investment and, in theory, to improve the rights of railway workers. The railway companies were amalgamated into British Railways, part of the British Transport Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Railway (UK)
The Southern Railway (SR), sometimes shortened to 'Southern', was a British railway company established in the 1923 Grouping. It linked London with the Channel ports, South West England, South coast resorts and Kent. The railway was formed by the amalgamation of several smaller railway companies, the largest of which were the London and South Western Railway (LSWR), the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) and the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR).Bonavia (1987) pp. 26-28 The construction of what was to become the Southern Railway began in 1838 with the opening of the London and Southampton Railway, which was renamed the London & South Western Railway. The railway was noted for its astute use of public relations and a coherent management structure headed by Sir Herbert Walker. At , the Southern Railway was the smallest of the '' Big Four'' railway companies and, unlike the others, the majority of its revenue came from passenger traffic rather than freight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
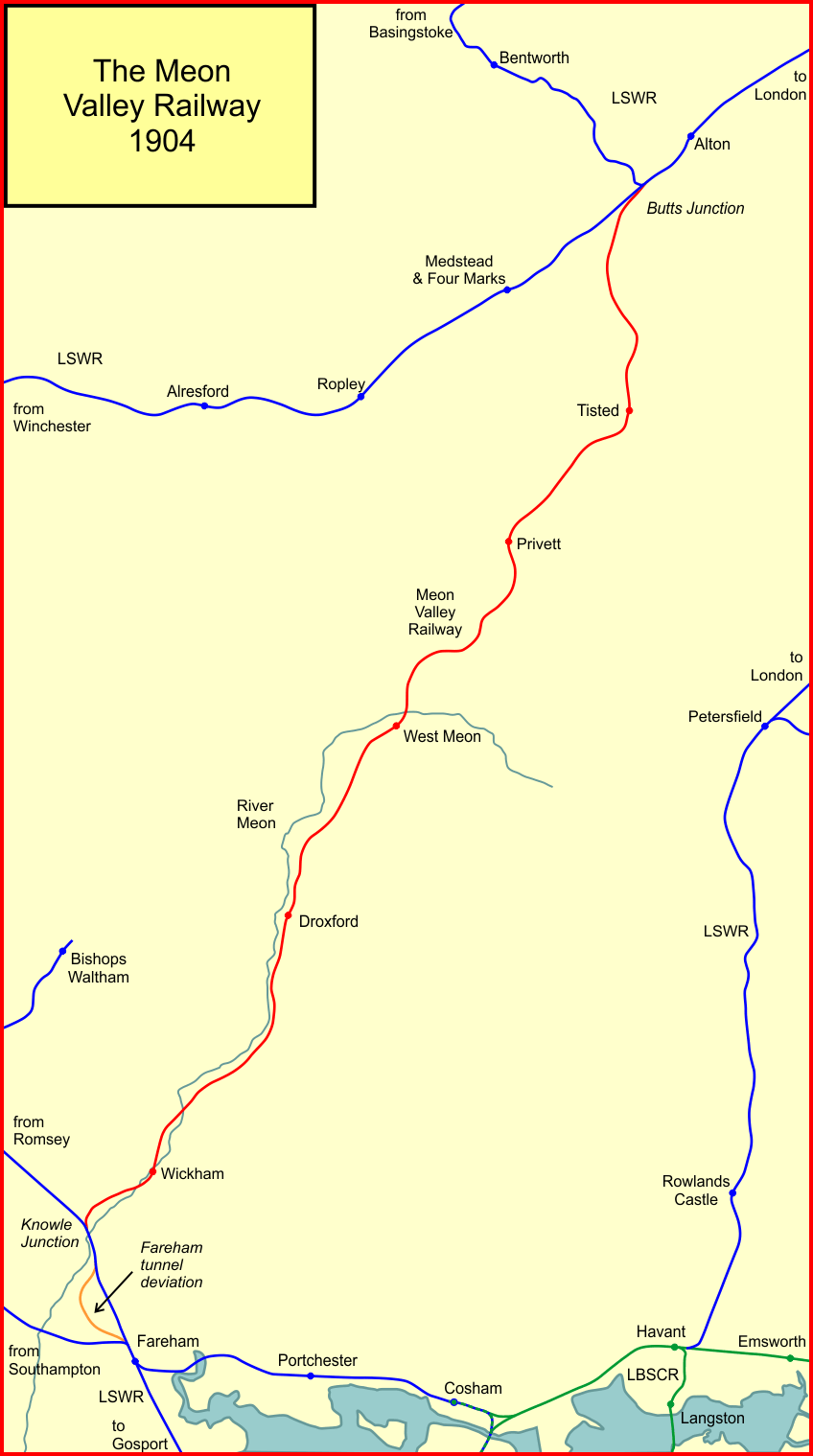
Meon Valley Railway
The Meon Valley Railway was a cross-country railway in Hampshire, England, that ran for 22 miles (36 km) between Alton and Fareham, closely following the course of the River Meon. At its northern (Alton) end, it joined with the Alton Line from London. It was conceived as an additional main line to the area around Gosport, and it was opened in 1903. It never fulfilled its planned potential, and remained a local line through sparsely populated agricultural areas, and it closed to passenger services in 1955; some local goods services continued until total closure in 1968. The name does not refer to an independent company; it was constructed and run by the London and South Western Railway (LSWR). History Background By the last decade of the nineteenth century, the railway map of Great Britain was already mature, and there were few gaps waiting to be filled by speculators. In 1852 the London and South Western Railway had reached Alton, from Brookwood on the London to Southampton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basingstoke And Alton Light Railway
The Basingstoke and Alton Light Railway was opened in 1901, by the London and South Western Railway. It was the first English railway authorised under Light Railway legislation. It ran through unpromising, lightly populated terrain, and was probably built only to exclude competitors from building a line in the area. It had steep gradients and a line speed limit of 20 mph, later raised to 25 mph. It never attracted much business and the hoped-for through traffic never materialised. When the War Office demanded recovered track for laying in France, during the First World War, the LSWR closed the line and lifted the track, in 1917. After the war, local pressure mounted to reinstate the railway; this was resisted by the Southern Railway, which had taken over from the LSWR. The SR had no wish to spend considerable sums to reopen a railway that had lost money and had no positive prospects. A House of Lords Committee effectively forced the SR to resume operation, which it did in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)