|
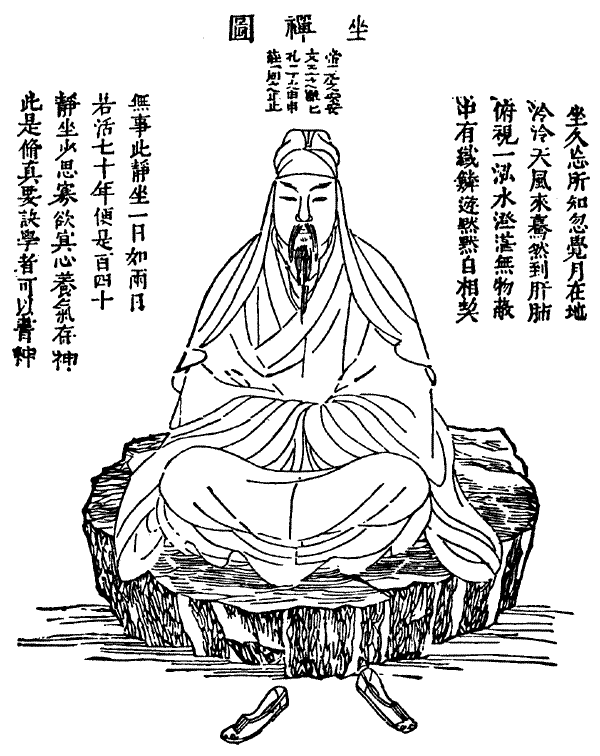
Microcosmic Orbit
The microcosmic orbit (小周天), also known as the Self Winding Wheel of the Law, is a Taoist ''qigong'' energy cultivation technique. It involves deep breathing exercises in conjunction with meditation and concentration techniques which aim to develop the flow of ''qi'' along certain pathways of energy in the human body which may be familiar to those who are studying traditional Chinese medicine, ''qigong'', tai chi, ''Neidan'' and Chinese alchemy. The exercise can be performed usually at first in a sitting position, but it can also be practiced standing as in Zhan zhuang or with movements included as with tai chi. The clear understanding of the microcosmic orbit technique is very important not only because of its historical context in the story of Chinese alchemy but because it is at the heart of many Taoist forms of exercise performed throughout the world by many millions of people today. History The history of the microcosmic orbit dates back to prehistoric times in China, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lü Dongbin
Lü Dongbin is a legendary Chinese scholar and poet who lived during the Tang dynasty whose lifetime supposedly spanned two hundred and twenty years. Elevated to the status of an immortal in the Chinese cultural sphere by Daoists, he is one of the most widely known of the group of deities known as the Eight Immortals. Lü is also a historical figure and mentioned in the official history book ''History of Song''. He is widely considered to be one of the earliest masters of neidan, or internal alchemy. He is also depicted in art dressed as a scholar carrying a sword to dispel evil spirits. Character Lü Dongbin is usually portrayed as a scholarly, clever man with a genuine desire to help people obtain wisdom/enlightenment and to learn the Tao. However, he is often portrayed as having some character "flaws," not an uncommon theme for the colorful Taoist immortals, all of whom in general have various eccentricities: *He is portrayed as having bouts of drunkenness, which was not un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qigong
Qigong ()) is a system of coordinated body-posture and movement, breathing, and meditation said to be useful for the purposes of health, spirituality, and martial arts training. With roots in Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chinese medicine, Chinese philosophy, philosophy, and Chinese martial arts, martial arts, qigong is traditionally viewed by the Chinese and throughout Asia as a practice to cultivate and balance the mystical life-force ''qi''. Qigong practice typically involves moving meditation, coordinating slow-flowing movement, deep rhythmic breathing, and a calm meditative state of mind. People practice qigong throughout China and worldwide for recreation, exercise, relaxation, preventive medicine, self-healing, alternative medicine, meditation, self-cultivation, and training for martial arts. Etymology ''Qigong'' (Pinyin), ''ch'i kung'' (Wade-Giles), and ''chi gung'' (Yale romanization of Mandarin, Yale) are romanizations of two Chinese words "''qì''" and "''gōng''" ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique to train attention and awareness and detach from reflexive, "discursive thinking", achieving a mentally clear and emotionally calm and stable state, while not judging the meditation process itself. Techniques are broadly classified into focused (or concentrative) and open monitoring methods. Focused methods involve attention to specific objects like breath or mantras, while open monitoring includes mindfulness and awareness of mental events. Meditation is practiced in numerous religious traditions, though it is also practised independently from any religious or spiritual influences for its health benefits. The earliest records of meditation ('' dhyana'') are found in the Upanishads, and meditation plays a salient role in the contemplative repertoire of Jainism, Buddhism and Hinduism. Meditation-like techniques are also known in Judaism, Christianity and Islam, in the context of remembrance of and prayer and dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rider (imprint)
Rider is a publishing imprint of Ebury Publishing, a Penguin Random House division, started by William Rider & Son in Britain in 1908 when it took over the occult publisher Phillip Wellby. The editorial director of the new list was Ralph Shirley and under his direction, they began to publish titles as varied as the Rider–Waite tarot deck and Bram Stoker's ''Dracula''. The current Rider motto is "New Ideas for New Ways of Living", and books and authors on the list reflect this. There are still books on the paranormal, with authors like Raymond Moody and Colin Fry; on astral projection with authors Sylvan Muldoon and Hereward Carrington; and spirituality, with books by the Dalai Lama and Jack Kornfield; and books on current and international affairs by authors as diverse as Nobel Prize The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meridian (Chinese Medicine)
The meridian system (, also called channel network) is a pseudoscientific concept from traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) that alleges meridians are paths through which the life-energy known as " qi" (''ch'i'') flows. Meridians are not real anatomical structures: scientists have found no evidence that supports their existence. One historian of medicine in China says that the term is "completely unsuitable and misguided, but nonetheless it has become a standard translation." Major proponents of their existence have not come to any consensus as to how they might work or be tested in a scientific context. History The concept of meridians are first attested in two works recovered from the Mawangdui and Zhangjiashan tombs of the Han-era Changsha Kingdom, the ''Cauterization Canon of the Eleven Foot and Arm Channels'' ''Zúbì Shíyī Mài Jiǔjīng'') and the ''Cauterization Canon of the Eleven Yin and Yang Channels'' ''Yīnyáng Shíyī Mài Jiǔjīng''). In the texts, the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jing (Chinese Medicine)
''Jing'' ( zh, c=精, w=ching1, p=jīng) is the Chinese word for "essence", specifically kidney essence. Along with '' qi'' and '' shen'', it is considered one of the Three Treasures of traditional Chinese medicine. Description According to traditional Chinese medical theory, ''jing'' or ''essence'' can be summarised in two parts: the yin, being congenital or prenatal, and the yang, being postnatal or acquired. Prenatal ''jing'' is acquired at birth from the parents: the father's sperm and the mother's ovum. Postnatal ''jing'' is acquired after birth through food, water, oxygen, as well as environmental and social conditions. The concept is expounded in the Bagua and within the '' I Ching''. The yin and yang ''jing'' transform to create and replenish each other. The yang ''jing'' circulates through the eight extraordinary vessels and transforms to become and replenish yin; in turn the marrow becomes blood, body fluid and semen. ''Jing'' should not be confused with the related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagua
The ''bagua'' ( zh, c=八卦, p=bāguà, l=eight trigrams) is a set of symbols from China intended to illustrate the nature of reality as being composed of mutually opposing forces reinforcing one another. ''Bagua'' is a group of trigrams—composed of three lines, each either "broken" or "unbroken", which represent yin and yang, respectively. Each line having two possible states allows for a total of 23 = 8 trigrams, whose early enumeration and characterization in China has had an effect on the history of Chinese philosophy and cosmology. The trigrams are related to the divination practice as described within the ''I Ching'' and practiced as part of the Shang and Zhou state religion, as well as with the concepts of '' taiji'' and the five elements within traditional Chinese metaphysics. The trigrams have correspondences in astronomy, divination, meditation, astrology, geography, geomancy (feng shui), anatomy, decorative arts, the family, martial arts (particularly tai chi an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dantian
Dantian is a concept in traditional Chinese medicine loosely translated as "elixir field", "sea of '' qi''", or simply "energy center." Dantian are the "''qi'' focus flow centers," important focal points for meditative and exercise techniques such as qigong, martial arts such as tai chi, and in traditional Chinese medicine. Dantian is also now commonly understood to refer to the diaphragm in various Qigong practices and breath control techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing for singing and speaking. Along with '' jing'' and '' shen'', it is considered one of the Three Treasures of traditional Chinese medicine. Overview Historically the first detailed description of the lower Dantian is in the '' Laozi zhongjing'' from the 3rd century CE, which refers to the elixir-of-life field where "essence" and "spirit" are stored; it is related to regeneration and sexual energy, menstruation and semen.Laozi zhongjing (Central Scripture of Laozi), sec. 17. Translation published in Fabri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Da Qiao
The Two Qiaos of Jiangdong () were two sisters of the Qiao family who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. In the novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', the two Qiaos were sisters of exceptional beauty who were the pivot to the Battle of Chibi, one of the most impactful battles of the pre-Three Kingdoms period. Cao Cao, Chancellor of the Eastern Han dynasty, was depicted in the novel to be interested in having the two sisters, to the point that his intentions were evident in his son's poem "Ode to the Bronze Sparrow Platform" (銅雀臺賦); consequently leading Zhou Yu of Jiangdong to go to war with Cao Cao. In historical records The Qiao sisters' names were not recorded in history, so in later times they are simply referred to as Da Qiao (literally "older Qiao") and Xiao Qiao (literally "younger Qiao"). They were from Wan County (皖縣), Lujiang Commandery (廬江郡), which is in present-day Anqing, Anhui. Da Qiao married the warlord Sun Ce, who establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosopher's Stone
The philosopher's stone is a mythic alchemical substance capable of turning base metals such as mercury into gold or silver; it was also known as "the tincture" and "the powder". Alchemists additionally believed that it could be used to make an elixir of life which made possible rejuvenation and immortality. For many centuries, it was the most sought-after goal in alchemy. The philosopher's stone was the central symbol of the mystical terminology of alchemy, symbolizing perfection at its finest, divine illumination, and heavenly bliss. Efforts to discover the philosopher's stone were known as the Magnum Opus ("Great Work"). Antiquity The earliest known written mention of the philosopher's stone is in the ''Cheirokmeta'' by Zosimos of Panopolis (). Alchemical writers assign a longer history. Elias Ashmole and the anonymous author of ''Gloria Mundi'' (1620) claim that its history goes back to Adam, who acquired the knowledge of the stone directly from God. This knowledge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |