|
Micipsa
Micipsa (Numidian: MKWSN; , ; died BC) was the eldest legitimate son of Masinissa, the King of Numidia, a Berber kingdom in North Africa. Micipsa became the King of Numidia in 148 BC. Early life In 151 BC, Masinissa sent Micipsa and his brother Gulussa to Carthage to demand that exiled pro-Numidian politicians be allowed to return, but they were refused entry at the city gates. As the royal party turned to depart, Hamilcar the Samnite and a group of his supporters attacked Micipsa's convoy, killing some of his attendants. This incident led to a retaliatory strike on the Carthaginian town of Oroscopa that heralded the start of the Carthaginian–Numidian War and eventually precipitated the Third Punic War. Succession to the throne In the spring of 148 BC Masinissa died and the tripartite division of the kingdom among the elderly king's three sons, Micipsa, Gulussa, and Mastanabal, took place by Publius Cornelius Scipio Aemilianus, to whom Masinissa had given the authority to admi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugurtha
Jugurtha or Jugurthen (Libyco-Berber ''Yugurten'' or '' Yugarten'', c. 160 – 104 BC) was a king of Numidia. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Jugurtha and his two adoptive brothers, Hiempsal and Adherbal, succeeded him. Jugurtha arranged to have Hiempsal killed and, after a civil war, defeated and killed Adherbal in 112 BC. The death of Adherbal, which was against the wishes of Rome, along with the growing popular anger in Rome at Jugurtha's success in bribing Roman senators and thus avoiding retribution for his crimes, led to the Jugurthine War between Rome and Numidia. After a number of battles in Numidia between Roman and Numidian forces, Jugurtha was captured in 105 BC and paraded through Rome as part of Gaius Marius' Roman triumph. He was thrown into the Tullianum prison, where he was executed by strangulation in 104 BC. Jugurtha was survived by his son Oxyntas. Etymology The Numidian name Jugurtha matches the ancient naming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulussa
Gulussa was the second legitimate son of Masinissa. Gulussa became the King of Numidia along with his two brothers around 148 BC and reigned as part of a triumvirate for about three years. Biography In 148 BC, Masinissa, feeling that he was near death, consulted with Scipio Aemilianus regarding the settlement of his state. Resuscitating, perhaps, a Libyan custom which shared the authority between three persons, Scipio Aemilianus established the three legitimate surviving sons as kings: Micipsa, Gulussa and Mastanabal. The royal power was divided among the three princes. Micipsa, the eldest, was in charge of the administration; it was to him that Masinissa had given his ring which, judging from the stelae of the Abizar style, was a sign of power. Gulussa was given the command of the armies. As for Mastanabal, who was said to have been instructed in Greek, he was charged with justice, and relations with vassal tribal leaders. War with Carthaginians Gulussa already had a soli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masinissa
Masinissa ( nxm, , ''MSNSN''; ''c.'' 238 BC – 148 BC), also spelled Massinissa, Massena and Massan, was an ancient Numidian king best known for leading a federation of Massylii Berber tribes during the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), ultimately uniting them into a kingdom that became a major regional power in North Africa. Much of what is known about Masinissa comes from the Livy's ''History of Rome,'' and to a lesser extent Cicero's Scipio's Dream. As the son of a Numidian chieftain allied to Carthage, he fought against the Romans in the Second Punic War, but later switched sides upon concluding that Rome would prevail. With the support of his erstwhile enemy, he united the eastern and western Numidian tribes and founded the Kingdom of Numidia. As a Roman ally, Masinissa took part in the decisive Battle of Zama in 202 BC that effectively ended the war in Carthage's defeat; he also allowed his wife Sophonisba, a famed Carthaginian noblewoman who had influenced Numidian af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia, Libya, and some parts of Morocco. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii in the east and the Masaesyli in the west. During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into one kingdom. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state. Numidia, at its largest extent, was bordered by Mauretania to the west, at the Moulouya River, Africa Proconsularis to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Sahara to the south. It was one of the first major states in the history of Algeria and the Berbers. History Independence The Greek historians referred to these peoples as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg , caption = The Berber ethnic flag , population = 36 million , region1 = Morocco , pop1 = 14 million to 18 million , region2 = Algeria , pop2 = 9 million to ~13 million , region3 = Mauritania , pop3 = 2.9 million , region4 = Niger , pop4 = 2.6 million, Niger: 11% of 23.6 million , region5 = France , pop5 = 2 million , region6 = Mali , pop6 = 850,000 , region7 = Libya , pop7 = 600,000 , region8 = Belgium , pop8 = 500,000 (including descendants) , region9 = Netherlands , pop9 = 467,455 (including descendants) , region10 = Burkina Faso , pop10 = 406,271, Burkina Faso: 1.9% of 21.4 million , region11 = Egypt , pop11 = 23,000 or 1,826,580 , region12 = Tunisia , pop12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
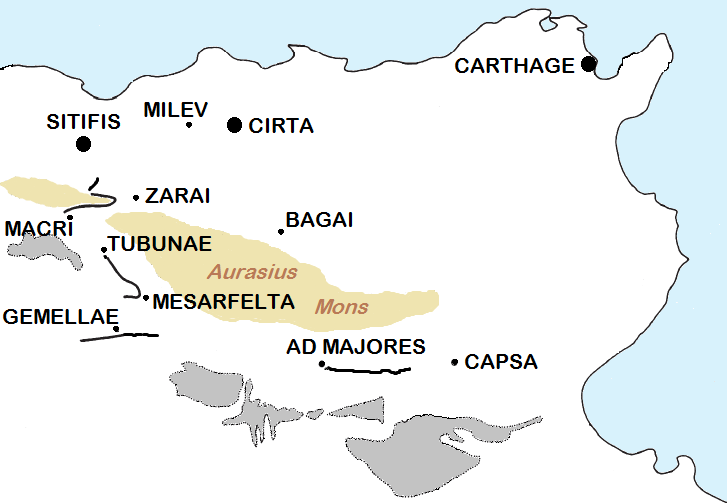
Cirta
Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria. Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city was Russicada. Although Numidia was a key ally of the ancient Roman Republic during the Punic Wars (264–146BC), Cirta was subject to Roman invasions during the 2nd and 1st centuriesBC. Eventually it fell under Roman dominion during the time of Julius Caesar. Cirta was then repopulated with Roman colonists by Caesar and Augustus and was surrounded by the autonomous territory of a " Confederation of four free Roman cities" (with Chullu, Russicada, and Milevum), ruled initially by Publius Sittius. The city was destroyed in the beginning of the 4thcentury and was rebuilt by the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, who gave his name to the newly constructed city, Constantine. The Vandals damaged Cirta, but emperor reconquered and improved th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiempsal I
Hiempsal I (died c. 117 BC), son of Micipsa and grandson of Masinissa, was a king of Numidia in the late 2nd century BC. Micipsa, on his deathbed, left his two sons, Adherbal and Hiempsal, together with his cousin, Jugurtha, joint heirs of his kingdom. Sallust claims the arrangement fell apart almost immediately due to the unprincipled ambition of Jugurtha and the longtime jealousy of his two half-brothers. At the very first meeting of the three princes their animosity displayed broke into the open. Hiempsal, the younger and most impetuous of the two brothers, gave mortal offence to Jugurtha. After this interview, it being agreed to divide the kingdom of Numidia, as well as the treasures of the late king, between the three princes, they took up their quarters in different towns in the neighborhood of Cirta. But as Hiempsal had imprudently established himself at Thirmida, in a house belonging to a dependant of Jugurtha, the latter took advantage of this circumstance to introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherchel Micipsa Inscr 118bce Louvre
Cherchell (Arabic: شرشال) is a town on Algeria's Mediterranean coast, west of Algiers. It is the seat of Cherchell District in Tipaza Province. Under the names Iol and Caesarea, it was formerly a Roman colony and the capital of the kingdoms of Numidia and Mauretania. Names The town was originally known by the Phoenician and Punic name , meaning "island of sand". The Punic name was hellenized as ''Iṑl'' ( grc-gre, Ἰὼλ) and Latinized as Iol. Cherchel and Cherchell are French transcriptions of the Arabic name Shershel ( ar, شرشال), derived from the town's old Latin name Caesarea ( grc-gre, ἡ Καισάρεια, ''hē Kaisáreia''), which was given to it in 25BC by to honor his benefactor Augustus,. who had legally borne the name "Gaius Julius Caesar" after his posthumous adoption by Julius Caesar in 44BC. It was later distinguished from the many other Roman towns named Caesarea by calling it , ("Mauretania's Caesarea"), (, ''Iṑl Kaisáreia''), o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherchell
Cherchell (Arabic: شرشال) is a town on Algeria's Mediterranean coast, west of Algiers. It is the seat of Cherchell District in Tipaza Province. Under the names Iol and Caesarea, it was formerly a Roman colony and the capital of the kingdoms of Numidia and Mauretania. Names The town was originally known by the Phoenician and Punic name , meaning "island of sand". The Punic name was hellenized as ''Iṑl'' ( grc-gre, Ἰὼλ) and Latinized as Iol. Cherchel and Cherchell are French transcriptions of the Arabic name Shershel ( ar, شرشال), derived from the town's old Latin name Caesarea ( grc-gre, ἡ Καισάρεια, ''hē Kaisáreia''), which was given to it in 25BC by to honor his benefactor Augustus,. who had legally borne the name "Gaius Julius Caesar" after his posthumous adoption by Julius Caesar in 44BC. It was later distinguished from the many other Roman towns named Caesarea by calling it , ("Mauretania's Caesarea"), (, ''Iṑl Kaisáreia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidian Language
Numidian was a language spoken in ancient Numidia, a territory covering much of northern Africa. The script in which it was written, the Libyco-Berber alphabet (from which Tifinagh descended), has been almost fully deciphered and most characters (apart from a few exceptions restricted to specific areas) have known values. Despite this, the language has barely been deciphered and only a few words are known. Libyco-Berber inscriptions are attested from the 3rd century BC to the 3rd century AD. The language is scarcely attested and can be confidently identified only as belonging to the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic family, although it was most likely part of the Berber languages, spoken at the start of the breakup of the Proto-Berber language. Dialects and relation to other ancient languages Dialects and foreign influences It is known that there was an orthographical difference between the western and eastern Numidian language. Starting at Kabylia, which was a kind of mixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elephant-mounted troops. Description War elephants played a critical role in several key battles in antiquity, especially in Ancient India. While seeing limited and periodic use in Ancient China, they became a permanent fixture in armies of historical kingdoms in Southeast Asia. During classical antiquity they were also used in ancient Persia and in the Mediterranean world within armies of Macedon, Hellenistic Greek states, the Roman Republic and later Empire, and Carthage in North Africa. In some regions they maintained a firm presence on the battlefield throughout the Middle Ages. However, their use declined with the spread of firearms and other gunpowder weaponry in early modern warfare. After this, war elephants became restricted to non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |