|
Michael Fleischer (mineralogist)
Michael Fleischer ( 27 February 1908 – 5 September 1998) was an American chemist and mineralogist. He worked as a geochemist with the U.S. Geological Survey from 1939 to 1978. He published a huge number of chemical abstracts and reviews of proposed mineral names, and is known for his authoritative ''Glossary of Mineral Species'', first published in 1971. Early years (1908–39) Michael Fleischer was born on 27 February 1908 in Bridgeport, Connecticut, the son of Hungarian Jewish immigrants. He studied chemistry and mineralogy at Yale University from 1927 to 1933. He obtained a Bachelor of Science degree magna cum laude in 1930 and a doctorate in physics in 1933. He graduated during the Great Depression. His first job was a chemist in a toothpaste factory. He married Helen Isenberg and they had two sons, Walter and David. From 1933 to 1934 Fleischer was a research associate at Yale's Department of Chemistry. From 1934 to 1936 he was an assistant to Professor William Ebenezer For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridgeport, Connecticut
Bridgeport is the List of municipalities in Connecticut, most populous city and a major port in the U.S. state of Connecticut. With a population of 148,654 in 2020, it is also the List of cities by population in New England, fifth-most populous in New England. Located in eastern Fairfield County, Connecticut, Fairfield County at the mouth of the Pequonnock River on Long Island Sound, it is from Manhattan and from The Bronx. It is bordered by the towns of Trumbull, Connecticut, Trumbull to the north, Fairfield, Connecticut, Fairfield to the west, and Stratford, Connecticut, Stratford to the east. Bridgeport and other towns in Fairfield County make up the Greater Bridgeport, Bridgeport-Stamford-Norwalk-Danbury metropolitan statistical area, the second largest Metropolitan statistical area, metropolitan area in Connecticut. The Bridgeport-Stamford-Norwalk-Danbury metropolis forms part of the New York metropolitan area. Inhabited by the Golden Hill Paugussett Indian Nation, Paugus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
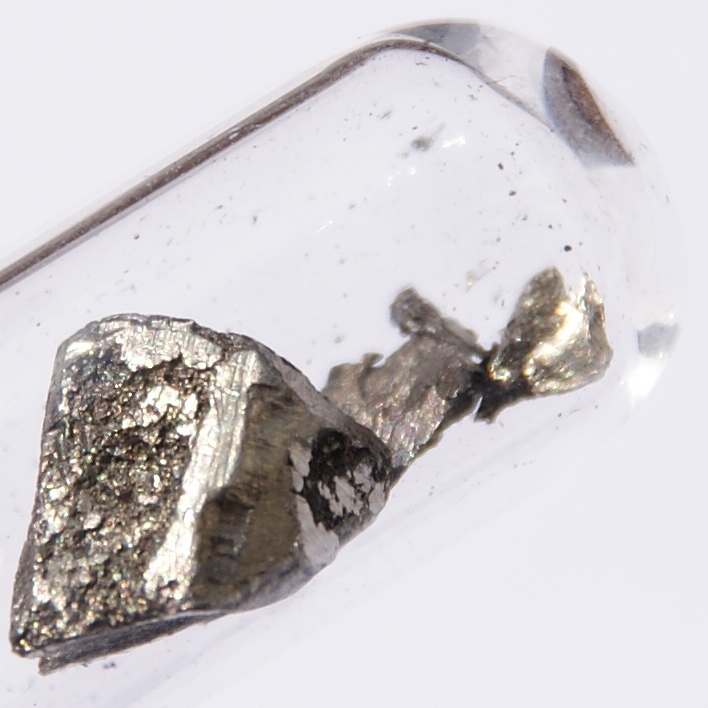
Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group (aluminium, indium, and thallium). Elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal in standard temperature and pressure. In its liquid state, it becomes silvery white. If too much force is applied, the gallium may fracture conchoidally. Since its discovery in 1875, gallium has widely been used to make alloys with low melting points. It is also used in semiconductors, as a dopant in semiconductor substrates. The melting point of gallium is used as a temperature reference point. Gallium alloys are used in thermometers as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to mercury, and can withstand higher temperatures than mercury. An even lower melting point of , well below the freezing point of water, is claimed for the alloy galinstan (62–� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bursaite
Bursaite is a sulfosalt of the lillianite family. It has the formula Pb5Bi4S11 and orthorhombic structure. Bursaite is named after Bursa Province, Turkey, where it was discovered.Rasit, T. (1954-55A study on the concentration tests and beneficiation of the Uludag tungsten ore. Bull. Mineral Research and Exploralion Inst. Turkey, Foreign Ed., No. 46-47, 106-127. It is generally located in regions rich in sulfur and commonly occurs alongside other sulfosalts. Its areas of formation are usually those that were once volcanogenic because it is generally aggregated with other minerals under intense heating.Borodaev, Y., Garavelli, A., Garbarino, C, Grillo, S, Mozgova, N, Uspenskaya, T. A Rare Sulfosalts from Volcano. (2001) The Canadian Mineralogist, 39 1383-1396. It was officially delisted as a mineral in 2006, being cited as an intergrowth of two other sulfosalts. History Bursaite was discovered in a contact zone between a set of marbles and granites amidst the Uludağ massif in Bursa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William F
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Mineralogist
''American Mineralogist: An International Journal of Earth and Planetary Materials'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the general fields of mineralogy, crystallography, geochemistry, and petrology. It is an official journal of the Mineralogical Society of America, publishing both subscription and open access articles. The journal is a hybrid open-access journal. The editors-in-chief are Hongwu Xu (Los Alamos National Laboratory), and Don Baker (McGill University). History The journal was established in 1916, with the first issue appearing in July of that year, under the auspices of the ''Philadelphia Mineralogical Society'', the ''New York Mineralogical Club'', and the ''Mineral Collectors' Association''. On December 30, 1919, the Mineralogical Society of America was formed and ''American Mineralogist'' became the society's journal. Abstracting and indexing The ''American Mineralogist'' is abstracted and indexed in Chemical Abstracts, the Science Citation Index, Geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankdicksonite
Frankdicksonite is a halide mineral with the chemical formula Ba F2 which corresponds to the chemical compound barium fluoride. It occurs in the Carlin gold deposit of Eureka County, Nevada as cubic crystals sized between 0.1 and 4 mm, and is of hydrothermal origin. Its only associated mineral is quartz and the frankdicksonite crystals are always completely encapsulated in it. Frankdicksonite has fluorite crystal structure with a cubic symmetry and the lattice constant ''a'' = 619.64 pm. Its Vickers hardness on the cleavage crystal faces varies between 88 and 94 kg/mm2 and is close to that of the synthetic barium fluoride (95 kg/mm2). Its refractive index (1.475) is almost identical to that of BaF2 (1.474). Under electron irradiation, it emits strong blue cathodoluminescence. The major impurity in frankdicksonite is strontium with concentrations up to 0.5% by weight. Also present are silicon (0.02%) and magnesium (0.0015%); other impurities have concentrations below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element. The most common minerals of barium are baryte ( barium sulfate, BaSO4) and witherite (barium carbonate, BaCO3). The name ''barium'' originates from the alchemical derivative "baryta", from Greek (), meaning 'heavy'. ''Baric'' is the adjectival form of barium. Barium was identified as a new element in 1774, but not reduced to a metal until 1808 with the advent of electrolysis. Barium has few industrial applications. Historically, it was used as a getter for vacuum tubes and in oxide form as the emissive coating on indirectly heated cathodes. It is a component of YBCO (high-temperature superconductors) and electroceramics, and is added to steel and cast iron to reduce the size of carbon grains within the microstructure. Barium compounds ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–71, from lanthanum through lutetium. These elements, along with the chemically similar elements scandium and yttrium, are often collectively known as the rare-earth elements or rare-earth metals. The informal chemical symbol Ln is used in general discussions of lanthanide chemistry to refer to any lanthanide. All but one of the lanthanides are f-block elements, corresponding to the filling of the 4f electron shell. There is some dispute on whether lanthanum or lutetium is a d-block element, but lutetium is usually considered so by those who study the matter; it is included due to its chemical similarities with the other 14. All lanthanide elements form trivalent cations, Ln3+, whose chemistry is largely determined by the ionic radius, which decreases steadily from lanthanum to lutetium. These elements are called lanthanides because the elements i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. It is part of the refractory metals group, which are widely used as components of strong high-melting-point alloys. It is a group 5 element, along with vanadium and niobium, and it always occurs in geologic sources together with the chemically similar niobium, mainly in the mineral groups tantalite, columbite and coltan. The chemical inertness and very high melting point of tantalum make it valuable for laboratory and industrial equipment such as reaction vessels and vacuum furnaces. It is used in tantalum capacitors for electronic equipment such as computers. Tantalum is considered a technology-critical element by the European Commission. History Tantalum was discovered in Sweden in 1802 by Anders Ekeberg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has similar ductility to iron. Niobium oxidizes in Earth's atmosphere very slowly, hence its application in jewelry as a hypoallergenic alternative to nickel. Niobium is often found in the minerals pyrochlore and columbite, hence the former name "columbium". Its name comes from Greek mythology: Niobe, daughter of Tantalus, the namesake of tantalum. The name reflects the great similarity between the two elements in their physical and chemical properties, which makes them difficult to distinguish. English chemist Charles Hatchett reported a new element similar to tantalum in 1801 and named it columbium. In 1809, English chemist William Hyde Wollaston wrongly concluded that tantalum and columbium were identical. German chemist Heinrich Rose determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts per million of the Earth's crust. Indium has a melting point higher than sodium and gallium, but lower than lithium and tin. Chemically, indium is similar to gallium and thallium, and it is largely intermediate between the two in terms of its properties. Indium was discovered in 1863 by Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymous Theodor Richter by spectroscopic methods. They named it for the indigo blue line in its spectrum. Indium was isolated the next year. Indium is a minor component in zinc sulfide ores and is produced as a byproduct of zinc refinement. It is most notably used in the semiconductor industry, in low-melting-point metal alloys such as solders, in soft-metal high-vacuum seals, and in the production of transparent conductive coati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |