|
Michael Brüggemann
Michael Brüggeman(n) (; ; 1583, Stolp – 1654) was a German Lutheran pastor, preacher and translator living in the town of Schmolsin (Smołdzino), Duchy of Pomerania. He was born in Stolp (now Słupsk). Acting on the request of the last Griffin duchess, Anna von Croy, Brüggemann translated several liturgical texts, hymnals, prayer books and funeral speeches into Slovincian, a dialect of Kashubian Kashubian can refer to: * Pertaining to Kashubia, a region of north-central Poland * Kashubians, an ethnic group of north-central Poland * Kashubian language See also *Kashubian alphabet The Kashubian or Cassubian alphabet (''kaszëbsczi alf .... He also preached regularly in that language. 1583 births 1654 deaths People from Słupsk 17th-century German Lutheran clergy People from the Duchy of Pomerania German male non-fiction writers 17th-century German translators {{Germany-translator-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Słupsk
Słupsk (; , ; formerly german: Stolp, ; also known by several alternative names) is a city with powiat rights located on the Słupia River in the Pomeranian Voivodeship in northern Poland, in the historical region of Pomerania or more specifically in its part known in contemporary Poland as Central Pomerania (''Pomorze Środkowe'') within the wider West Pomerania (''Pomorze Zachodnie''), while in Germany the corresponding area is known as East Pomerania (''Ostpommern'') within the wider Farther Pomerania (''Hinterpommern''). According to Statistics Poland, it has a population of 88,835 inhabitants while occupying , thus being one of the most densely populated cities in the country as of December 2021 . In addition, the city is the administrative seat of Słupsk County and the rural Gmina Słupsk, despite belonging to neither, while until 1999 it was the capital of Słupsk Voivodeship. Słupsk had its origins as a Pomeranian settlement in the early Middle Ages. In 1265 it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation, Protestant Reformation. The reaction of the government and church authorities to the international spread of his writings, beginning with the ''Ninety-five Theses'', divided Western Christianity. During the Reformation, Lutheranism became the state religion of numerous states of northern Europe, especially in northern Germany, Scandinavia and the then-Livonian Order. Lutheran clergy became civil servants and the Lutheran churches became part of the state. The split between the Lutherans and the Roman Catholics was made public and clear with the 1521 Edict of Worms: the edicts of the Diet (assembly), Diet condemned Luther and officially banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from defending or propagatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smołdzino, Kartuzy County
Smołdzino is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Przodkowo, within Kartuzy County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately south of Przodkowo, east of Kartuzy, and west of the regional capital Gdańsk. For details of the history of the region, see History of Pomerania The history of Pomerania starts shortly before 1000 AD with ongoing conquests by newly arrived Polans rulers. Before that, the area was recorded nearly 2000 years ago as Germania, and in modern-day times Pomerania is split between Germany and Pol .... References Villages in Kartuzy County {{Kartuzy-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country had existed in the Middle Ages, in years 1121–1160, 1264–1295, 1478–1531 and 1625–1637. The duchy originated from the realm of Wartislaw I, a Slavic Pomeranian duke, and was extended by the Lands of Schlawe and Stolp in 1317, the Principality of Rügen in 1325, and the Lauenburg and Bütow Land in 1455. During the High Middle Ages, it also comprised the northern Neumark and Uckermark areas as well as Circipania and Mecklenburg-Strelitz. The Duchy of Pomerania was established as a vassal state of Poland in 1121, which it remained until the fragmentation of Poland after the death of Polish ruler Bolesław III Wrymouth in 1138. Afterwards the Dukes of Pomerania were independent, and later were vassals of the Duchy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Pomerania
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty (german: Greifen; pl, Gryfici, da, Grif) was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century and had been taken from the ducal coat of arms. Duke Wartislaw I (died 1135) was the first historical ruler of the Duchy of Pomerania and the founder of the Griffin dynasty. The most prominent Griffin was Eric of Pomerania, who became king of the Kalmar Union in 1397, thus ruling Denmark, Sweden and Norway. The last Griffin duke of Pomerania was Bogislaw XIV, who died during the Thirty Years' War, which led to the division of Pomerania between Brandenburg-Prussia and Sweden. Duchess Anna von Croy, daughter of Duke Bogislaw XIII and the last Griffin, died in 1660. Name of the Dynasty The dynasty is known by two names, ''Pomerania'', after their primary fief, and ''Griffin'', after their coat of arms, which had featured a griffin since the late 12th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Von Croy
Anna of Pomerania (also known as ''Anne de Croy et Aerschot'', ''Anna von Croy und Aerschot, Anna von Pommern'') (3 October 1590, Barth - 7 July 1660, Stolp) was Duchess-Consort of Croy and Havré, and allodial heiress of the extinct ducal house of Pomerania. She was youngest daughter of Bogislaw XIII, Duke of Pomerania and Princess Klara of Brunswick-Lüneburg. She was the last surviving member of the Griffins (Greifen). In 1619 she married Ernst von Croÿ (1588–1620), prince and duke of Croÿ (1583–1620), an imperial general, he would however die the following year. Ernst was the son of Charles Philippe de Croÿ (1549–1613), who was the only son of Philippe II of Croÿ by his second wife, Anna of Lorraine. Their son, Ernst Bogislaw von Croy (1620–1684), became the last Lutheran bishop of Kammin (now Kamień Pomorski). See also *House of Croÿ The House of Croÿ () is a family of European mediatized nobility, which held a seat in the Imperial Diet from 1486, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovincian Language
Slovincian is the extinct language formerly spoken by the Slovincians living between lakes Gardno and Łebsko near Słupsk in Pomerania. Slovincian is classified either as a language (first by Friedrich Lorentz, 1902/3Dicky Gilbers, John A. Nerbonne, J. Schaeken, ''Languages in Contact'', Rodopi, 2000, p.329, ), or as a Kashubian dialectChristina Yurkiw Bethin, ''Slavic Prosody: Language Change and Phonological Theory'', pp.160ff, Cambridge University Press, 1998, Edward Stankiewicz, ''The Accentual Patterns of the Slavic Languages'', Stanford University Press, 1993, p.291, (first by Lorentz, after 1903) or variant,Roland Sussex, Paul Cubberley, ''The Slavic Languages'', Cambridge University Press, 2006, p.97, with Kashubian itself being classified either as a language or as a Polish dialect.Harry Hulst, Georg Bossong, ''Eurotyp'', Walter de Gruyter, 1999, p.837, Slovincian and Kashubian are both classified as Pomeranian. Slovincian became extinct in the early twentieth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashubian Language
Kashubian or Cassubian (Kashubian: ', pl, język kaszubski) is a West Slavic language belonging to the Lechitic subgroup along with Polish and Silesian.Stephen Barbour, Cathie Carmichael, ''Language and Nationalism in Europe'', Oxford University Press, 2000, p.199, Although often classified as a language in its own right, it is sometimes viewed as a dialect of Pomeranian or as a dialect of Polish. In Poland, it has been an officially recognized ethnic-minority language since 2005. Approximately 108,000 people use mainly Kashubian at home. It is the only remnant of the Pomeranian language. It is close to standard Polish with influence from Low German and the extinct Polabian (West Slavic) and Old Prussian (West Baltic) languages. The Kashubian language exists in two different forms: vernacular dialects used in rural areas, and literary variants used in education. Origin Kashubian is assumed to have evolved from the language spoken by some tribes of Pomeranians called K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1583 Births
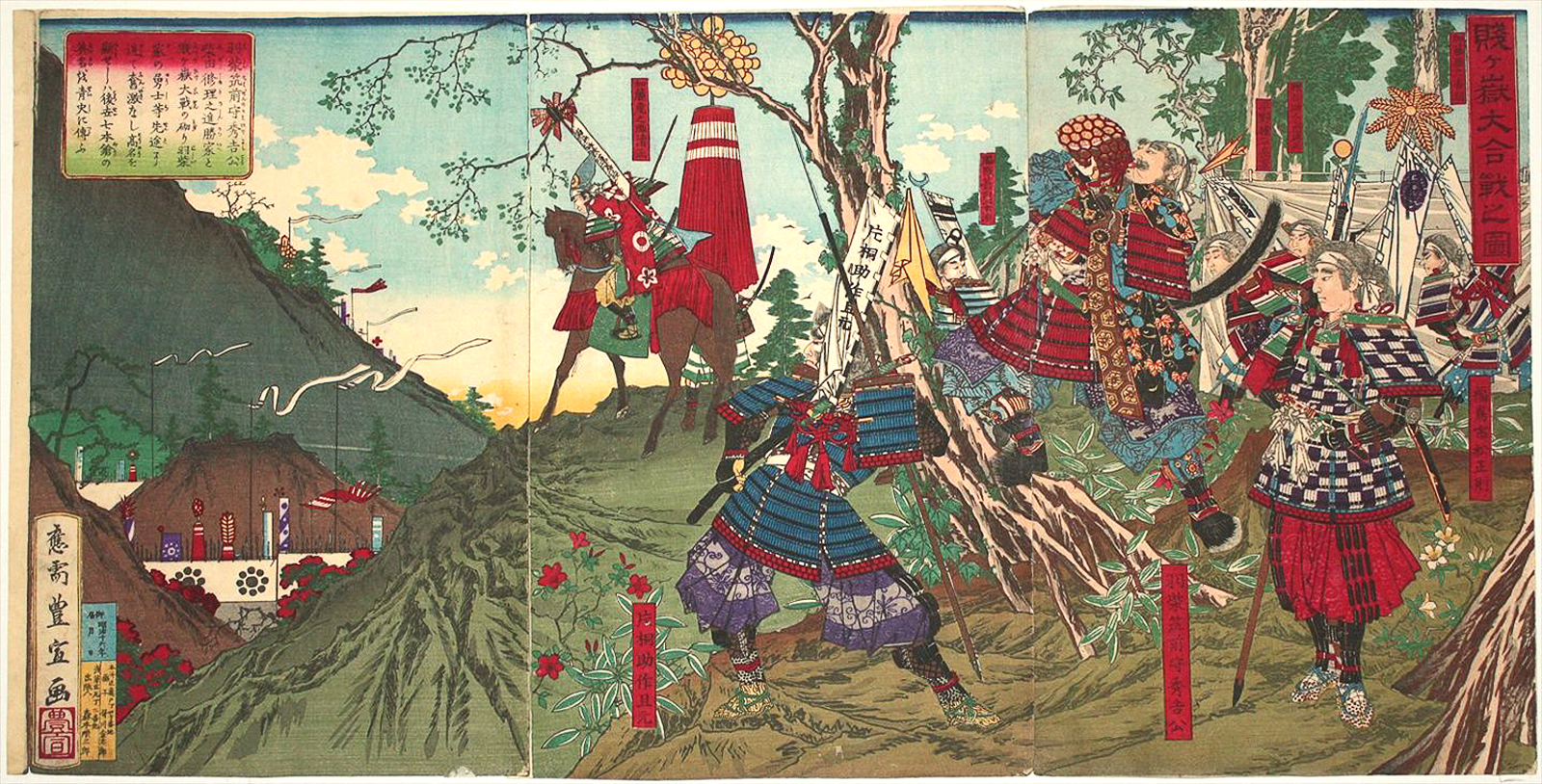
__NOTOC__ Events January–June * January 18 – François, Duke of Anjou, attacks Antwerp. * February 4 – Gebhard Truchsess von Waldburg, newly converted to Calvinism, formally marries Agnes von Mansfeld-Eisleben, a former canoness of Gerresheim, while retaining his position as Archbishop-Elector of Cologne. * March 10 – The ''Queen Elizabeth's Men'' troupe of actors is ordered to be founded in England. * May – Battle of Shizugatake in Japan: Shibata Katsuie is defeated by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, who goes on to commence construction of Osaka Castle. * May 22 – Ernest of Bavaria is elected as Roman Catholic Archbishop of Cologne, in opposition to Gebhard Truchsess von Waldburg. The opposition rapidly turns into armed struggle, the Cologne War within the Electorate of Cologne, beginning with the Destruction of the Oberstift. July–December * July 25 – Cuncolim Revolt: The first documented battle of India's in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1654 Deaths
Events January–March * January 6– In India, Jaswant Singh of Marwar (in what is now the state of Rajasthan) is elevated to the title of Maharaja by Emperor Shah Jahan. * January 11– In the Battle of Río Bueno in southern Chile during the Arauco War, the indigenous Huilliche warriors rout Spanish troops from Fort Nacimiento who are attempting to cross the Bueno River. * January 26– Portugal recaptures the South American city of Recife from the Netherlands after a siege of more than two years during the Dutch-Portuguese War, bringing an end to Dutch rule of what is now Brazil. The Dutch West India Company had held the city (which they called Mauritsstad) for more than 23 years. * February 9– Spanish troops led by Don Gabriel de Rojas y Figueroa successfully attack the Fort de Rocher, a pirate-controlled base on the Caribbean island of Tortuga. * February 10– The Battle of Tullich takes place in Aberdeenshire in Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Słupsk
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century German Lutheran Clergy
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French '' Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



_1938.jpg)
