|
Miacis Lushiensis
''Miacis'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous mammals that appeared in the late Paleocene and continued through the Eocene. The genus ''Miacis'' is not monophyletic but a diverse collection of species that belong to the stemgroup within the Carnivoramorpha.Wesley-Hunt, G.D.; Flynn J.J. (2005). Phylogeny of the Carnivora: Basal Relationships Among the Carnivoramorphans, and Assessment of the Position of 'Miacoidea' Relative to Carnivora. ''Journal of Systematic Palaeontology'', 3: 1-28. As such, most ''Miacis'' species belong to the group of early carnivores that represent the ancestors of the modern order, the crown-group Carnivora. However, the species ''Miacis cognitus'' (now ''Gustafsonia'') is placed not in the stem-group but among the Caniformia,Spaulding, M.; Flynn J.J.; Stucky, R.K. (2010) Anew basal Carnivoramorphan (Mammalia) from the ‘Bridger B’ (Black’s Fork Member, Bridger Formation, Bridgerian NALMA, Middel Eocene) of Wyoming, USA. ''Paleontology'' 53: 81 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Drinker Cope
Edward Drinker Cope (July 28, 1840 – April 12, 1897) was an American zoologist, paleontologist, comparative anatomist, herpetologist, and ichthyologist. Born to a wealthy Quaker family, Cope distinguished himself as a child prodigy interested in science; he published his first scientific paper at the age of 19. Though his father tried to raise Cope as a gentleman farmer, he eventually acquiesced to his son's scientific aspirations. Cope married his cousin and had one child; the family moved from Philadelphia to Haddonfield, New Jersey, although Cope would maintain a residence and museum in Philadelphia in his later years. Cope had little formal scientific training, and he eschewed a teaching position for field work. He made regular trips to the American West, prospecting in the 1870s and 1880s, often as a member of United States Geological Survey teams. A personal feud between Cope and paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh led to a period of intense fossil-finding competition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Diller Matthew
William Diller Matthew Royal Society, FRS (February 19, 1871 – September 24, 1930) was a vertebrate paleontologist who worked primarily on mammal fossils, although he also published a few early papers on mineralogy, petrological geology, one on botany, one on trilobites, and he described ''Tetraceratops insignis'', which was much later suggested to be the oldest known (Cisuralian, Early Permian) therapsid. Matthew was born in Saint John, New Brunswick, Saint John, New Brunswick, the son of George Frederic Matthew and Katherine (Diller) Matthew. His father was an amateur geologist and paleontologist who instilled his son with an abiding interest in the earth sciences. Matthew received an A.B. at the University of New Brunswick in 1889 and then earned his Ph.D. at Columbia University in 1894. Matthew was curator of the American Museum of Natural History from the mid-1890s to 1927, and director of the University of California Museum of Paleontology from 1927 to 1930. He was the fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Lawson Wortman
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Jacob first appears in the Book of Genesis, where he is described as the son of Isaac and Rebecca, and the grandson of Abraham, Sarah, and Bethuel. According to the biblical account, he was the second-born of Isaac's children, the elder being Jacob's fraternal twin brother, Esau. Jacob is said to have bought Esau's birthright and, with his mother's help, deceived his aging father to bless him instead of Esau. Later in the narrative, following a severe drought in his homeland of Canaan, Jacob and his descendants, with the help of his son Joseph (who had become a confidant of the pharaoh), moved to Egypt where Jacob died at the age of 147. He is supposed to have been buried in the Cave of Machpelah. Jacob had twelve sons through four women, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodaphaenus
''Prodaphaenus'' is an extinct genus of Miacidae Miacids are extinct primitive carnivoramorphans within the family Miacidae that lived during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs, about 62–34 million years ago. Miacids existed for approximately . Miacids are thought to have evolved into the .... The genus has at least one known species: ''Prodaphaenus scotti''. References *zipcodezoo.com Miacids Eocene carnivorans [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphicyon
''Amphicyon'' ("ambiguous dog") is an extinct genus of large carnivorous bone-crushing mammals, popularly known as bear dogs, of the family Amphicyonidae, subfamily Amphicyoninae, from the Burdigalian Epoch until the late Pliocene, with the creature having bear-like and dog-like features. They ranged over North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa from 16.9 to 2.6 Ma ago, existing for approximately . Morphology ''Amphicyon'' was the typical bear-dog amphicyonid with morphology similar to both bears and dogs. With its robust build and maximum length of 2.5 m (8 ft), the largest species looked more like a bear than a dog. It had a large heavy tail, thick neck, robust limbs and teeth like a wolf. It was probably an omnivore with a lifestyle comparable to that of the brown bear. The ''Amphicyon'' was very large for predators of its time but this advantage eventually became a disadvantage because its large body mass was too large to take faster prey. ''A. major'' has been est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
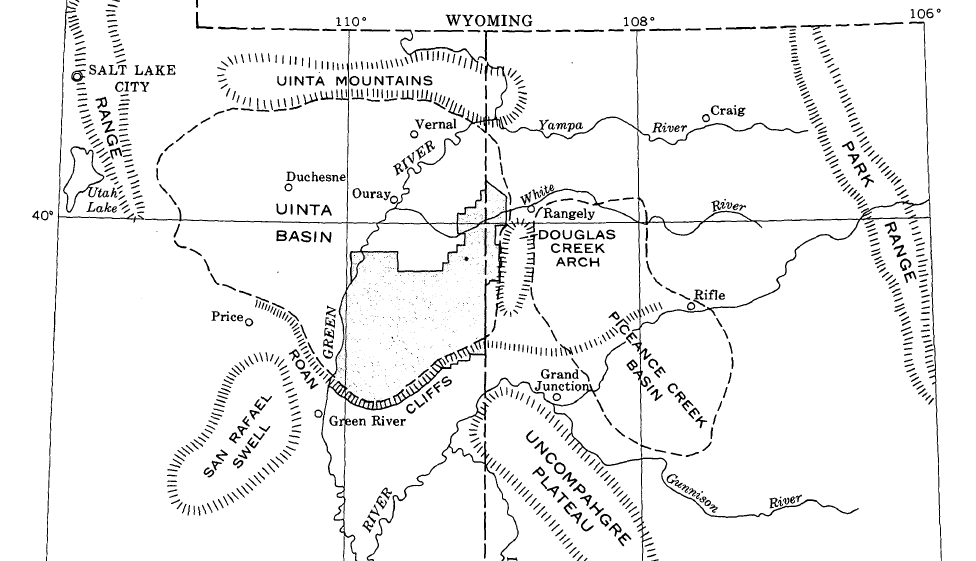
Uinta Basin
The Uinta Basin (also known as the Uintah Basin) is a physiographic section of the larger Colorado Plateaus province, which in turn is part of the larger Intermontane Plateaus physiographic division. It is also a geologic structural basin in eastern Utah, east of the Wasatch Mountains and south of the Uinta Mountains. The Uinta Basin is fed by creeks and rivers flowing south from the Uinta Mountains. Many of the principal rivers (Strawberry River, Currant Creek, Rock Creek, Lake Fork River, and Uintah River) flow into the Duchesne River which feeds the Green River—a tributary of the Colorado River. The Uinta Mountains forms the northern border of the Uinta Basin. They contain the highest point in Utah, Kings Peak, with a summit 13,528 feet (4123 metres) above sea level. The climate of the Uinta Basin is semi-arid, with occasionally severe winter cold. History Father Escalante's expedition visited the Uinta Basin in September 1776. 1822–1840 French Canadian tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Berryman Scott
William Berryman Scott (February 12, 1858 – March 29, 1947) was an American vertebrate paleontologist, authority on mammals, and principal author of the White River Oligocene monographs. He was a professor of geology and paleontology at Princeton University. Family and education Scott was born in Cincinnati, Ohio, on February 12, 1858, the son of Mary Elizabeth Hodge Scott and William McKendree Scott, a Presbyterian minister. He was the youngest of three sons; his brother Hugh Lenox Scott went on to become superintendent of West Point and Army Chief of Staff. Shortly after the family moved to Princeton, New Jersey in 1861, his father died and the family lived with his maternal grandfather who was also a Presbyterian minister and an instructor at the Princeton Theological Seminary.American National Biography 1999Sterling 1997 His early education focused on theology, philosophy and the classics in preparation for an expected career as a minister. However, when he entered P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Othniel Charles Marsh
Othniel Charles Marsh (October 29, 1831 – March 18, 1899) was an American professor of Paleontology in Yale College and President of the National Academy of Sciences. He was one of the preeminent scientists in the field of paleontology. Among his legacies are the discovery or description of dozens of new species and theories on the origins of birds. Born into a modest family, Marsh was able to afford higher education thanks to the generosity of his wealthy uncle George Peabody. After graduating from Yale College in 1860 he travelled the world, studying anatomy, mineralogy and geology. He obtained a teaching position at Yale upon his return. From the 1870s to 1890s, he competed with rival paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope in a period of frenzied Western American expeditions known as the Bone Wars. Marsh's greatest legacy is the collection of Mesozoic reptiles, Cretaceous birds, and Mesozoic and Tertiary mammals that now constitute the backbone of the collections of Yale's Peabo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viverravus
''Viverravus'' ("ancestor of ''Viverra''") is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Viverravinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America, Europe and Asia from the middle Paleocene to middle Eocene. Classification and phylogeny Taxonomy Phylogeny The phylogenetic relationships of genus ''Viverravus'' are shown in the following cladogram:P. D. Gingerich and D. A. Winkler (1985."Systematics of Paleocene Viverravidae (Mammalia, Carnivora) in the Bighorn Basin and Clark's Fork Basin, Wyoming."Contributions from the Museum of Paleontology, University of Michigan 27(4):87-128P. D. Polly (1997."Ancestry and Species Definition in Paleontology: A Stratocladistic Analysis of Paleocene-Eocene Viverravidae (Mammalia, Carnivora) from Wyoming."Contributions from the Museum of Paleontology, University of Michigan 30(1):1-53S. Faurby, L. Werdelin, A. Antonelli (2019."Dispersal ability predicts evolutionary success among mammalian carnivores"Departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridger Formation
The Bridger Formation is a geologic formation in southwestern Wyoming. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ypresian Epoch of the Paleogene Period. The formation was named by American geologist Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden for Fort Bridger, which had itself been named for mountain man Jim Bridger. The Bridger Wilderness covers much of the Bridger Formation's area. History Before colonization, the lands making up the Bridger Formation had been inhabited by the Apsáalooke, Bannock, Eastern Shoshone, Hinono'eino, Očhéthi Šakówiŋ, Só'taeo'o, Tsétsêhéstâhese, and Ute nations. European settlers began to settle the area around the Bridger Formation in the 19th century, beginning with the establishment of the Oregon Trail in 1830. Fort Bridger – for which the formation would later be named – was established in 1843 by Jim Bridger and Louis Vasquez. In 1868, the remaining Indigenous communities in the area were displaced by the Treaty of Fort Bridger, removing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)
