|
Methanophenazine
Methanophenazine, a phenazine derivative, is a strongly hydrophobic redox-active cofactor with a role in electron transport in some methanogens. This chromophore can be purified from membranes of methanogenic archaea such as ''Methanosarcina mazei ''Methanosarcina'' is a genus of euryarchaeote archaea that produce methane. These single-celled organisms are known as anaerobic methanogens that produce methane using all three metabolic pathways for methanogenesis. They live in diverse en ...''. The enzyme methanosarcina-phenazine hydrogenase (EC 1.12.98.3) has the name methanophenazine hydrogenase as a synonym. References Phenazines Cofactors {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenazines
Phenazine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2N2. It is a dibenzo annulated pyrazine, and the parent substance of many dyestuffs, such as the toluylene red, indulines, and safranines (and the closely related eurhodines). Phenazine crystallizes in yellow needles, which are only sparingly soluble in alcohol. Sulfuric acid dissolves it, forming a deep-red solution. Synthesis Classically phenazine are prepared by the reaction of nitrobenzene and aniline in the Wohl-Aue reaction. Other methods include: * pyrolysis of the barium salt of azobenzoate * oxidation of aniline with lead oxide * oxidation of dihydrophenazine, which is prepared by heating pyrocatechin with o-phenylenediamine. * oxidation of ortho-aminodiphenylamine with lead peroxide. Derivatives * The more complex phenazines, such as the naphthophenazines, naphthazines, and naphthotolazines, may be prepared by condensing ortho-diamines with ortho-quinones or by the oxidation of an ortho-diamine in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
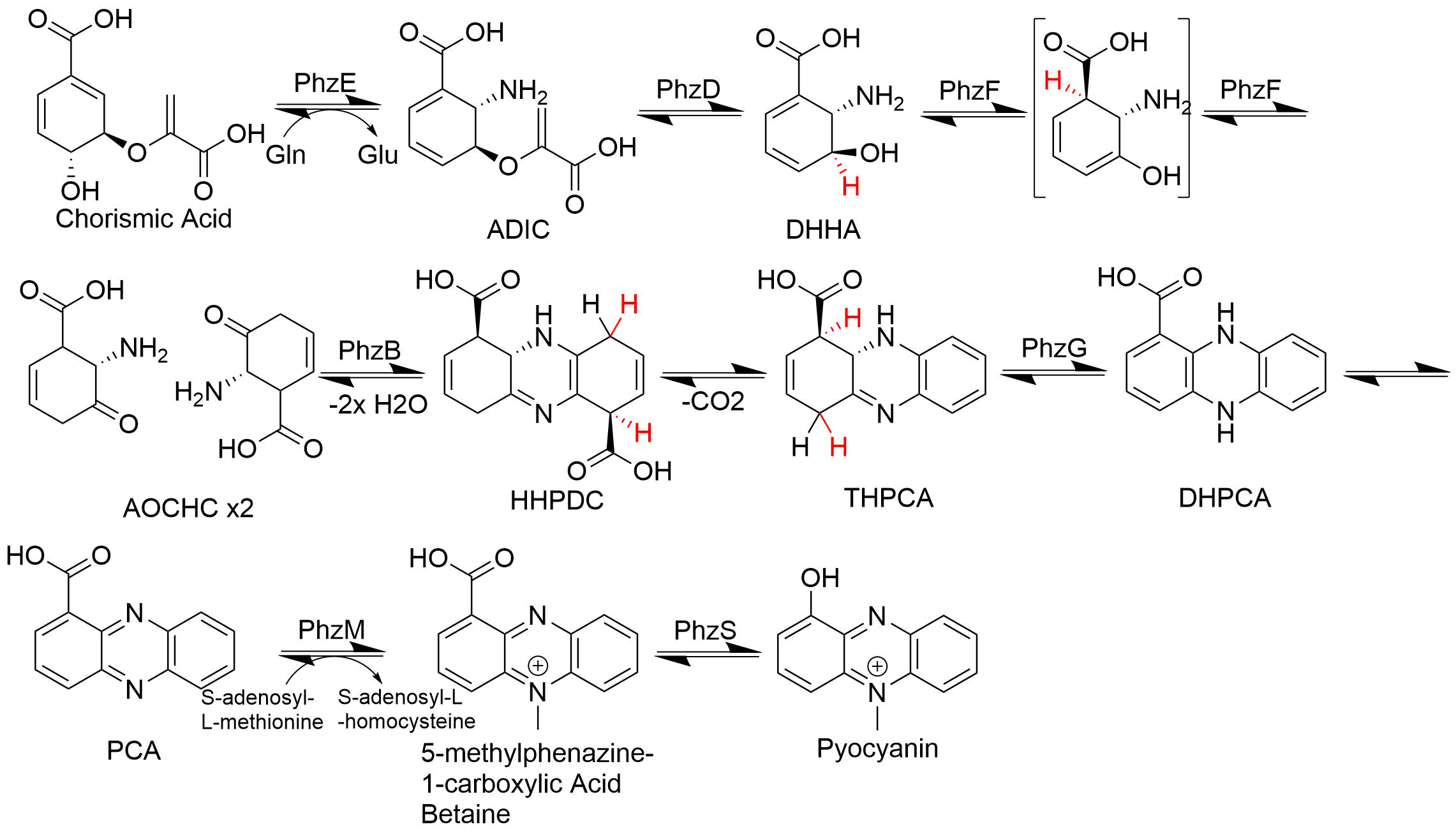
Phenazine
Phenazine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2N2. It is a dibenzo annulation, annulated pyrazine, and the parent substance of many dyestuffs, such as the toluylene red, indulines, and safranines (and the closely related eurhodines). Phenazine crystallizes in yellow needles, which are only sparingly soluble in ethanol, alcohol. Sulfuric acid dissolves it, forming a deep-red solution. Synthesis Classically phenazine are prepared by the reaction of nitrobenzene and aniline in the Wohl-Aue reaction. Other methods include: * pyrolysis of the barium salt (chemistry), salt of azobenzoate * oxidation of aniline with lead oxide * oxidation of dihydrophenazine, which is prepared by heating pyrocatechin with o-phenylenediamine. * oxidation of ortho-aminodiphenylamine with lead peroxide. Derivatives * The more complex phenazines, such as the naphthophenazines, naphthazines, and naphthotolazines, may be prepared by condensing Toluidine, ortho-diamines with quinone, ortho-quinones or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanosarcina-phenazine Hydrogenase
In enzymology, a Methanosarcina-phenazine hydrogenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ... the chemical reaction :H2 + 2-(2,3-dihydropentaprenyloxy)phenazine \rightleftharpoons 2-dihydropentaprenyloxyphenazine Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are H2 and 2-(2,3-dihydropentaprenyloxy)phenazine, whereas its product is 2-dihydropentaprenyloxyphenazine. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on hydrogen as donor with other, known, acceptors. The systematic name of this enzyme class is hydrogen:2-(2,3-dihydropentaprenyloxy)phenazine oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include methanophenazine hydrogenase, and methylviologen-reducing hydrogenase. References * * * EC 1.12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be divided into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Note that some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently) and permanently bound to a protein. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Transport
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. The electrons that transferred from NADH and FADH2 to the ETC involves 4 multi-subunit large enzymes complexes and 2 mobile electron carriers. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are membrane-bound. The flow of electrons through the electron transport chain is an exergonic process. The energy from the redox reactions creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In aerobic respiration, the flow of electrons terminates with molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor. In anaerobic respiration, other electron acceptors are used, such as sulfate. In an electron transport chain, the redox r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are common in wetlands, where they are responsible for marsh gas, and in the digestive tracts of animals such as ruminants and many humans, where they are responsible for the methane content of belching in ruminants and flatulence in humans. In marine sediments, the biological production of methane, also termed methanogenesis, is generally confined to where sulfates are depleted, below the top layers. Moreover, methanogenic archaea populations play an indispensable role in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Others are extremophiles, found in environments such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of Earth's crust, kilometers below the surface. Physical description Methanogens are coccoid (spherical shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color that is seen by our eyes is the one not absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavelength spectrum of visible light. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two separate molecular orbitals falls within the range of the visible spectrum. Visible light that hits the chromophore can thus be absorbed by exciting an electron from its ground state into an excited state. In biological molecules that serve to capture or detect light energy, the chromophore is the moiety that causes a conformational change in the molecule when hit by light. Conjugated pi-bond system chromophores Just like how two adjacent p-orbitals in a molecule will form a pi-bond, three or more adjacent p-orbitals in a molecule can form a conjugated pi-system. In a conjugated pi-system, electrons are able to capture certain photons as the electrons resonate along a certain distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Biological membranes include cell membranes (outer coverings of cells or organelles that allow passage of certain constituents); nuclear membranes, which cover a cell nucleus; and tissue membranes, such as mucosae and serosae. Synthetic membranes are made by humans for use in laboratories and industry (such as chemical plants). This concept of a membrane has been known since the eighteenth century but was used little outside of the laboratory until the end of World War II. Drinking water supplies in Europe had been compromised by the war and membrane filters were used to test for water safety. However, due to the lack of reliability, slow operation, reduced selectivity and elevated costs, membranes were not widely exploited. The first us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanosarcina Mazei
''Methanosarcina'' is a genus of euryarchaeote archaea that produce methane. These single-celled organisms are known as anaerobic methanogens that produce methane using all three metabolic pathways for methanogenesis. They live in diverse environments where they can remain safe from the effects of oxygen, whether on the earth's surface, in groundwater, in deep sea vents, and in animal digestive tracts. ''Methanosarcina'' grow in colonies. The amino acid pyrrolysine was first discovered in a ''Methanosarcina'' species, '' M. barkeri''. Primitive versions of hemoglobin have been found in ''M. acetivorans'', suggesting the microbe or an ancestor of it may have played a crucial role in the evolution of life on Earth. Species of ''Methanosarcina'' are also noted for unusually large genomes. ''M. acetivorans'' has the largest known genome of any archaeon. According to a theory published in 2014, ''Methanosarcina'' may have been largely responsible for the largest extinction eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpeg/1200px-Fall_Leaves_(199582361).jpeg)

.jpg)
