|
Metasystem Transition
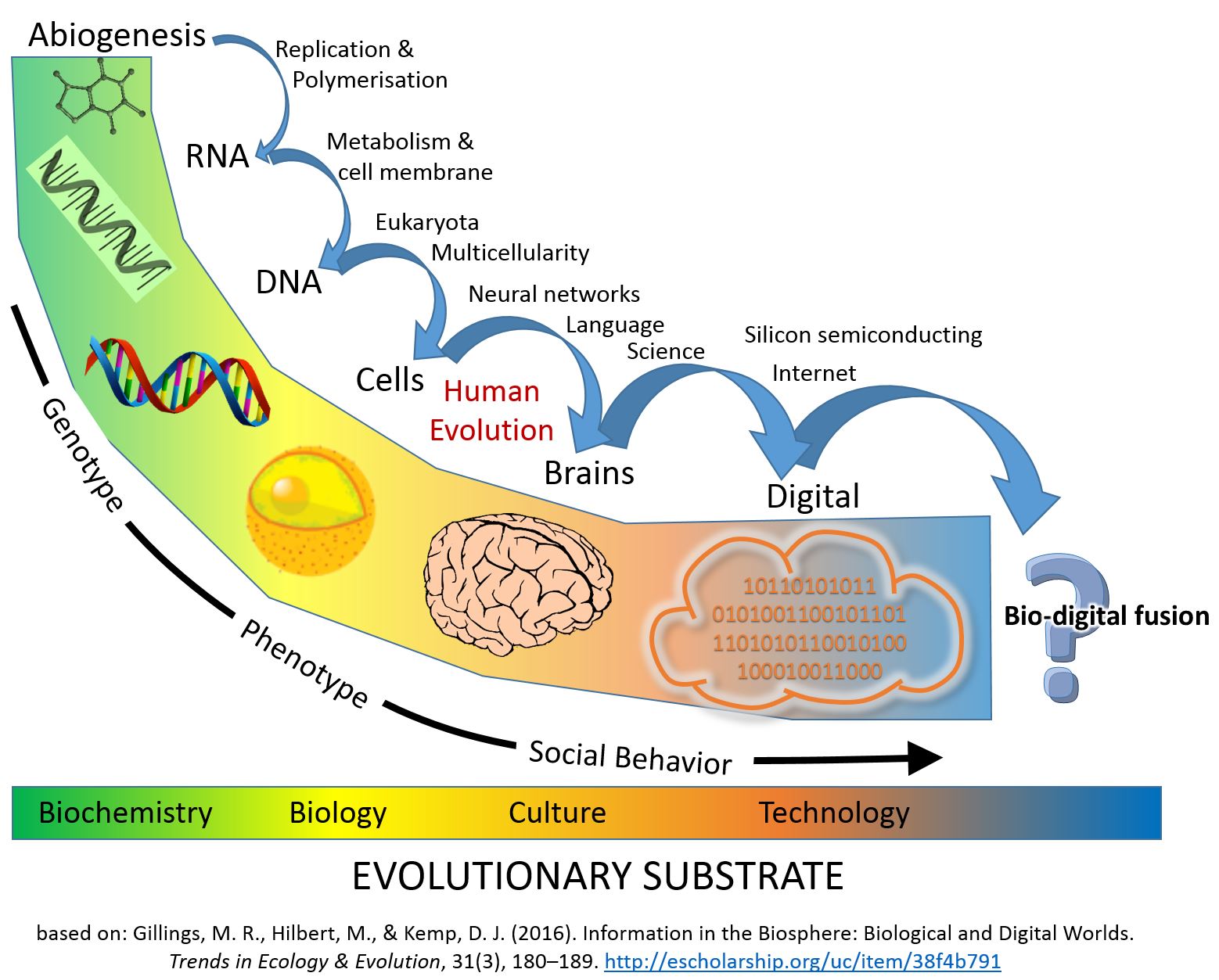
A metasystem transition is the emergence, through evolution, of a higher :wikt:level, level of organization or Control theory, control. A metasystem is formed by the integration of a number of initially independent components, such as molecules (as theorized for instance by Hypercycle_(chemistry), hypercycles), cell (biology), cells, or individuals, and the emergence of a system steering or controlling their interactions. As such, the collective of components becomes a new, goal-directed individual, capable of acting in a coordinated way. This metasystem is more Complex systems, complex, more intelligent, and more flexible in its actions than the initial component systems. Prime examples are the origin of life, the transition from unicellular to multicellular organisms, the emergence of eusociality or symbolic thought. The concept of metasystem transition was introduced by the cybernetician Valentin Turchin in his 1970 book ''The Phenomenon of Science'', and developed among others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergence
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when an entity is observed to have properties its parts do not have on their own, properties or behaviors that emerge only when the parts interact in a wider whole. Emergence plays a central role in theories of integrative levels and of complex systems. For instance, the phenomenon of life as studied in biology is an emergent property of chemistry. In philosophy, theories that emphasize emergent properties have been called emergentism. In philosophy Philosophers often understand emergence as a claim about the etiology of a system's properties. An emergent property of a system, in this context, is one that is not a property of any component of that system, but is still a feature of the system as a whole. Nicolai Hartmann (1882–1950), one of the first modern philosophers to write on emergence, termed this a ''categorial novum'' (new category). Definitions This concept of emergence dates from at lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentin Turchin
Valentin Fyodorovich Turchin (russian: Валенти́н Фёдорович Турчи́н, 14 February 1931 in Podolsk – 7 April 2010 in Oakland, New Jersey) was a Soviet and American physicist, cybernetician, and computer scientist. He developed the Refal programming language, the theory of metasystem transitions and the notion of supercompilation. He was as a pioneer in artificial intelligence and a proponent of the global brain hypothesis. Biography Turchin was born in 1931 in Podolsk, Soviet Union. In 1952, he graduated from Moscow University in Theoretical Physics, and got his Ph.D. in 1957. After working on neutron and solid-state physics at the Institute for Physics of Energy in Obninsk, in 1964 he accepted a position at the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics in Moscow. There he worked in statistical regularization methods and authored REFAL, one of the first AI languages and the AI language of choice in the Soviet Union. In the 1960s, Turchin became politi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association (psychology)
Association in psychology refers to a mental connection between concepts, events, or mental states that usually stems from specific experiences.Klein, Stephen (2012). ''Learning: Principles and Applications'' (6 ed.). SAGE Publications. . Associations are seen throughout several schools of thought in psychology including behaviorism, associationism, psychoanalysis, social psychology, and structuralism. The idea stems from Plato and Aristotle, especially with regard to the succession of memories, and it was carried on by philosophers such as John Locke, David Hume, David Hartley, and James Mill.Boring, E. G. (1950) It finds its place in modern psychology in such areas as memory, learning, and the study of neural pathways. Learned associations Associative learning is when a subject creates a relationship between stimuli (e.g. auditory or visual) or behavior and the original stimulus. The higher the concreteness of stimulus items, the more likely are they to evoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus. Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs via neural pathways in the nervous system called reflex arcs. A stimulus initiates a neural signal, which is carried to a synapse. The signal is then transferred across the synapse to a motor neuron which evokes a target response. These neural signals do not always travel to the brain, so many reflexes are an automatic response to a stimulus that does not receive or need conscious thought. Many reflexes are fine-tuned to increase organism survival and self-defense. This is observed in reflexes such as the startle reflex, which provides an automatic response to an unexpected stimuli, and the feline righting reflex, which reorients a cat's body when falling to ensure safe landing. The simplest type of reflex, a short-latency reflex, has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentience
Sentience is the capacity to experience feelings and sensations. The word was first coined by philosophers in the 1630s for the concept of an ability to feel, derived from Latin '' sentientem'' (a feeling), to distinguish it from the ability to think (''reason''). In modern Western philosophy, sentience is the ability to experience sensations. In different Asian religions, the word 'sentience' has been used to translate a variety of concepts. In science fiction, the word "sentience" is sometimes used interchangeably with " sapience", " self-awareness", or "consciousness". Some writers differentiate between the mere ability to perceive sensations, such as light or pain, and the ability to perceive emotions, such as fear or grief. The subjective awareness of experiences by a conscious individual are known as qualia in Western philosophy. Philosophy and sentience In philosophy, different authors draw different distinctions between ''consciousness'' and sentience. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy. Definitions Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms that do not possess a means of self-locomotion and are normally immobile. Motility differs from mobility, the ability of an object to be moved. The term vagility encompasses both motility and mobility; sessile organisms including plants and fungi often have vagile parts such as fruits, seeds, or spores which may be dispersed by other agents such as wind, water, or other organisms. Motility is genetically determined, but may be affected by environmental factors such as toxins. The nervous system and musculoskeletal system provide the majority of mammalian motility. In addition to animal locomotion, most animals are motile, though some are vagile, described as having passive locomotion. Many bacteria and other microorganisms, and multice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapience
Wisdom, sapience, or sagacity is the ability to contemplate and act using knowledge, experience, understanding, common sense and insight. Wisdom is associated with attributes such as unbiased judgment, compassion, experiential self-knowledge, self-transcendence and non-attachment, and virtues such as ethics and benevolence. Wisdom has been defined in many different ways, including several distinct approaches to assess the characteristics attributed to wisdom. Definitions The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' defines wisdom as "Capacity of judging rightly in matters relating to life and conduct; soundness of judgment in the choice of means and ends; sometimes, less strictly, sound sense, esp. in practical affairs: opp. to folly;" also "Knowledge (esp. of a high or abstruse kind); enlightenment, learning, erudition." Charles Haddon Spurgeon defined wisdom as "the right use of knowledge". Robert I. Sutton and Andrew Hargadon defined the "attitude of wisdom" as "acting with k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacompilation
Metacompilation is a computation which involves metasystem transitions (MST) from a computing machine ''M'' to a metamachine ''M' '' which controls, analyzes and imitates the work of ''M''. Semantics-based program transformation, such as partial evaluation and supercompilation (SCP), is metacomputation. Metasystem transitions may be repeated, as when a program transformer gets transformed itself. In this manner MST hierarchies of any height can be formed. The Fox paper reviews one strain of research which was started in Russia by Valentin Turchin's REFAL Refal ("Recursive functions algorithmic language"; russian: РЕФАЛ) "is a functional programming language oriented toward symbolic computations", including "string processing, language translation, ndartificial intelligence". It is one of th ... system in the late 1960s-early 1970s and became known for the development of supercompilation as a distinct method of program transformation. After a brief description of the hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Operator Theory
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eörs Szathmáry
Eörs Szathmáry (born 1959) is a Hungarian theoretical evolutionary biologist at the now-defunct Collegium Budapest Institute for Advanced Study and at the Department of Plant Taxonomy and Ecology of Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest. He is the co-author with John Maynard Smith of '' The Major Transitions in Evolution'', a seminal work which continues to contribute to ongoing issues in evolutionary biology. Also He is a member of the Batthyány Society of Professors. Main interest His main interest is theoretical evolutionary biology and focuses on the common principles of the major steps in evolution, such as the origin of life, the emergence of cells, the origin of animal societies, and the appearance of human language. Together with his mentor, John Maynard Smith, he has published two important books which serve as the main references in the field (''The Major Transitions in Evolution, Freeman, 1995, and The Origins of Life, Oxford University Press, 1999''). Both book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Maynard Smith
John Maynard Smith (6 January 1920 – 19 April 2004) was a British theoretical and mathematical evolutionary biologist and geneticist. Originally an aeronautical engineer during the Second World War, he took a second degree in genetics under the well-known biologist J. B. S. Haldane. Maynard Smith was instrumental in the application of game theory to evolution with George R. Price, and theorised on other problems such as the evolution of sex and signalling theory. Biography Early years John Maynard Smith was born in London, the son of the surgeon Sidney Maynard Smith, but following his father's death in 1928, the family moved to Exmoor, where he became interested in natural history. Quite unhappy with the lack of formal science education at Eton College, Maynard Smith took it upon himself to develop an interest in Darwinian evolutionary theory and mathematics, after having read the work of old Etonian J. B. S. Haldane, whose books were in the school's library d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)