|
Metal Production In Ukraine
Metal production, in particular iron and steel industry, is the dominant heavy industry in Ukraine. Ukraine is the world's eighth largest producer and third largest exporter of iron and steel (2007).Oxford Business Group 2007, p. 100. Ukrainian iron and steel industry accounts for around 2% of worldwide crude steel output,Global Crude Steel Production in 2009 down 8% on the same 2008 period''. Iron and Steel Statistics Bureau (London). 5% to 6% of the national gross domestic product and 34% of Ukrainian export revenue (2007 data).Levine et al., p. 44.1 In 2007 it employed 420,000 people – 10% of industrial labor and 2% of the total workforce. It has the highest, by a wide margin, revealed comparative advantage of all branches of the Ukrainian economy. The industry peaked at 42.8 million tonnes in 2007Levine et al., p. 44.2 but has been gravely affected by the financial crisis of 2007–2010 and declined to 29.8 million tonnes in 2009. Ukraine possesses substantial natural reserves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Ukraine Political Metalurgiia
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese was first isolated in 1774. It is familiar in the laboratory in the form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for "crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city of Saint Petersburg, located on Kotlin Island, west of Saint Petersburg, near the head of the Gulf of Finland. It is linked to the former Russian capital by a combination levee-causeway-seagate, the St Petersburg Dam, part of the city's flood defences, which also acts as road access to Kotlin island from the mainland. Founded in the early 18th century by Peter the Great, it became an important international centre of commerce whose trade role was later eclipsed by its strategic significance as the primary maritime defence outpost of the former Russian capital. Kaplan, 1995 The main base of the Russian Baltic Fleet was located in Kronstadt, guarding the approaches to Saint Petersburg. In March 1921, the island city was the site of the Krons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catacomb Culture
The Catacomb culture (russian: Катакомбная культура, Katakombnaya kul'tura, uk, Катакомбна культура, Katakombna kul'tura) was a Bronze Age culture which flourished on the Pontic steppe in 2500–1950 BC.Parpola, Asko, (2012)"Formation of the Indo-European and Uralic (Finno-Ugric) language families in the light of archaeology: Revised and integrated ‘total’ correlations" in Mémoires de la Société Finno-Ougrienne, Helsinki, p. 138. Originating on the southern steppe as an outgrowth of the Yamnaya culture, the Catacomb culture came to cover a large area. It was probably Indo-European-speaking. Influences of the Catacomb culture have been detected as far as Mycenaean Greece. It spawned the Multi-cordoned ware culture and was eventually succeeded by the Srubnaya culture. Origins The Catacomb culture emerged on the southern part of the Pontic steppe in 2500 BC, as a western descendant of the Yamnaya culture. Influences from the west appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sredny Stog Culture
The Sredny Stog culture (, romanized: ''Serednʹostohivsʹka kulʹtura'') is a pre-Kurgan archaeological culture from the 5th millennium BC. It is named after the Russian term for the Dnieper river islet of today's Seredny Stih, Ukraine, where it was first located. Distribution The Sredny Stog culture was situated across the Dnieper river on both its shores, with sporadic settlements to the west and east. It seems to have had contact with the agricultural Cucuteni-Trypillian culture in the west, centered on modern-day Moldova, and was a contemporary of the Khvalynsk culture in the north-east, located in the middle Volga region. Sites One of the sites most associated with this culture is Deriivka (Ukrainian: Деріївка, Russian: Дериевка), located on the right bank of the Omelnik, a tributary of the Dnieper, and is the largest site within the Sredny Stog culture complex, being about in area. Characteristics The Sredny Stog people lived rather mobile lives. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikentiy Khvoyka
Vikentiy Viacheslavovych Khvoyka ( ua, Вікентій В'ячеславович Хвойка; russian: Викентий Вячеславович Хвойка; cz, Vincenc Častoslav Chvojka; born Čeněk Chvojka; 1850–1914) was a Czech-born Ukrainian archaeologist, who discovered the Neolithic Trypillia culture of Ukraine. He also researched the Scythian, Zarubintsy, Chernyakhov and early Slavic archaeological cultures. Biography Khvoyka was born on 21 February 1850 in the village of Semín in the Kingdom of Bohemia (then part of the Austrian Empire). After graduating from the Academy of Commerce in Chrudim, he lived in Prague for a time before emigrating to the Russian Empire. From 1876 he lived in Kyiv and worked as a teacher. He turned his attention to archaeology in the 1890s and excavated around Kyiv and the Dnieper region. He was one of the founders of Kyiv's Museum of Antiquities and Art, now the National Historical Museum, and the first curator of its archaeologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
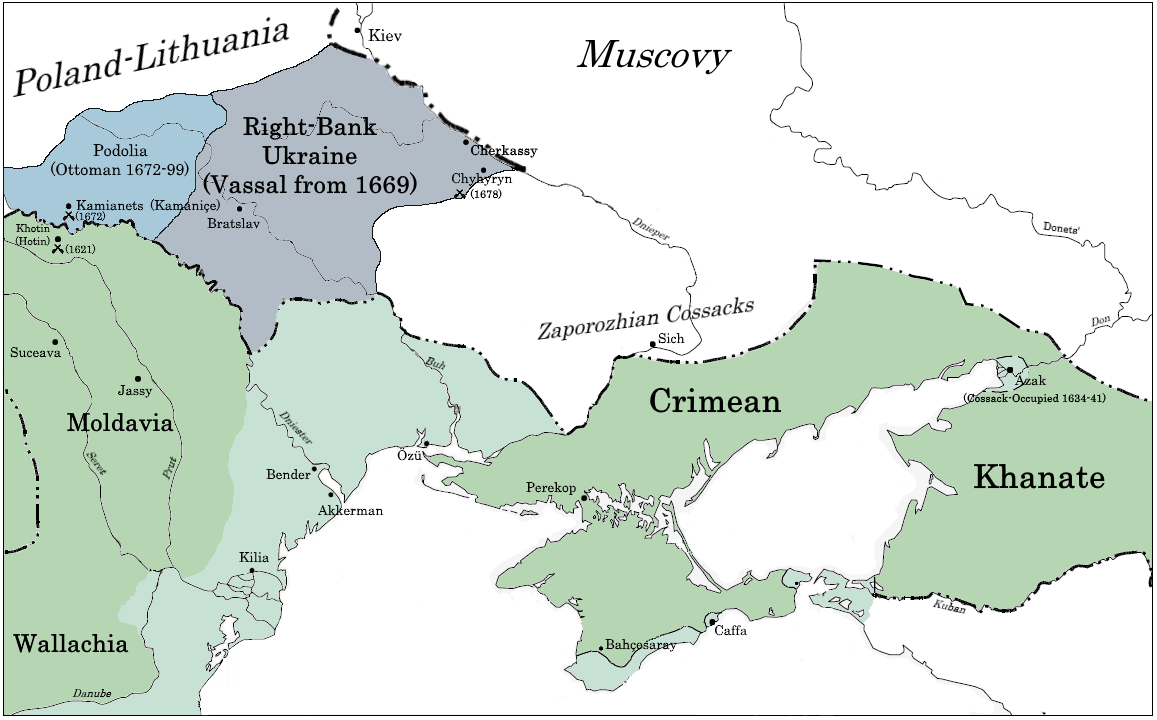
Right-bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine ( uk , Правобережна Україна, ''Pravoberezhna Ukrayina''; russian: Правобережная Украина, ''Pravoberezhnaya Ukraina''; pl, Prawobrzeżna Ukraina, sk, Pravobrežná Ukrajina, hu, Jobb parti Ukrajna) is a historical and territorial name for a part of modern Ukraine on the right (west) bank of the Dnieper River, corresponding to the modern-day oblasts of Vinnytsia, Zhytomyr, Kirovohrad, as well as the western parts of Kyiv and Cherkasy. It was separated from the left bank during the Ruin. Right-bank Ukraine is bordered by the historical regions of Volhynia and Podolia to the west, Moldavia to the southwest, Yedisan and Zaporizhzhia to the south, left-bank Ukraine to the east, and Polesia to the north. Main cities of the region include Cherkasy, Kropyvnytskyi, Bila Tserkva, Zhytomyr and Oleksandriia. History The history of right- and left-bank Ukraine is closely associated with the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648–57. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Age
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular human manipulation of copper, but prior to the discovery of bronze alloys. Modern researchers consider the period as a subset of the broader Neolithic, but earlier scholars defined it as a transitional period between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from (7000 BP). The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age covered about the same period, beginning in the late and lasting for about a millennium before it gave rise to the Early Bronze Age. Terminology The multiple names result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with the advent of metalworking. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of gold and copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3,000 BC, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys (bronze: originally copper and arsenic, later copper and tin) into tools, supplanting stone in many uses. Stone Age artifacts that have been discovered include tools used by modern humans, by their predecessor species in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnipropetrovsk Oblast
Dnipropetrovsk Oblast ( uk, Дніпропетро́вська о́бласть, translit=Dnipropetrovska oblast), also referred to as Dnipropetrovshchyna ( uk, Дніпропетро́вщина), is an administrative divisions of Ukraine, oblast (province) of central-eastern Ukraine, the most important industrial region of the country. It was created on February 27, 1932. Dnipropetrovsk Oblast has a population of about approximately 80% of whom live centering on administrative centers: Dnipro, Kryvyi Rih, Kamianske, Nikopol, Ukraine, Nikopol and Pavlohrad. The Dnieper River runs through the oblast. In 2019, the Constitutional Court of Ukraine approved the change of the oblast's name to Sicheslav Oblast ( uk, Січесла́вська о́бласть, translit=Sicheslavska oblast). Geography The Dnipropetrovsk Oblast is located in southeastern Ukraine. The area of the oblast (31,974 km2) comprises about 5.3% of the total area of the country. Its longitude from north to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly radioactive because all isotopes of uranium are unstable; the half-lives of its naturally occurring isotopes range between 159,200 years and 4.5 billion years. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead, and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals such as uraninite. In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)