|
Metabolized
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic'' – the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may not be different from ''n''), which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O (for example with , H has a covalent bond with C but not with O). However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition (e.g., uronic acids, deoxy-sugars such as fucose), nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid). The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell releases chemical energy to fuel cellular activity. The overall reaction occurs in a series of biochemical steps, some of which are redox reactions. Although cellular respiration is technically a combustion reaction, it is an unusual one because of the slow, controlled release of energy from the series of reactions. Nutrients that are commonly used by animal and pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as '' catabolic'' – the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
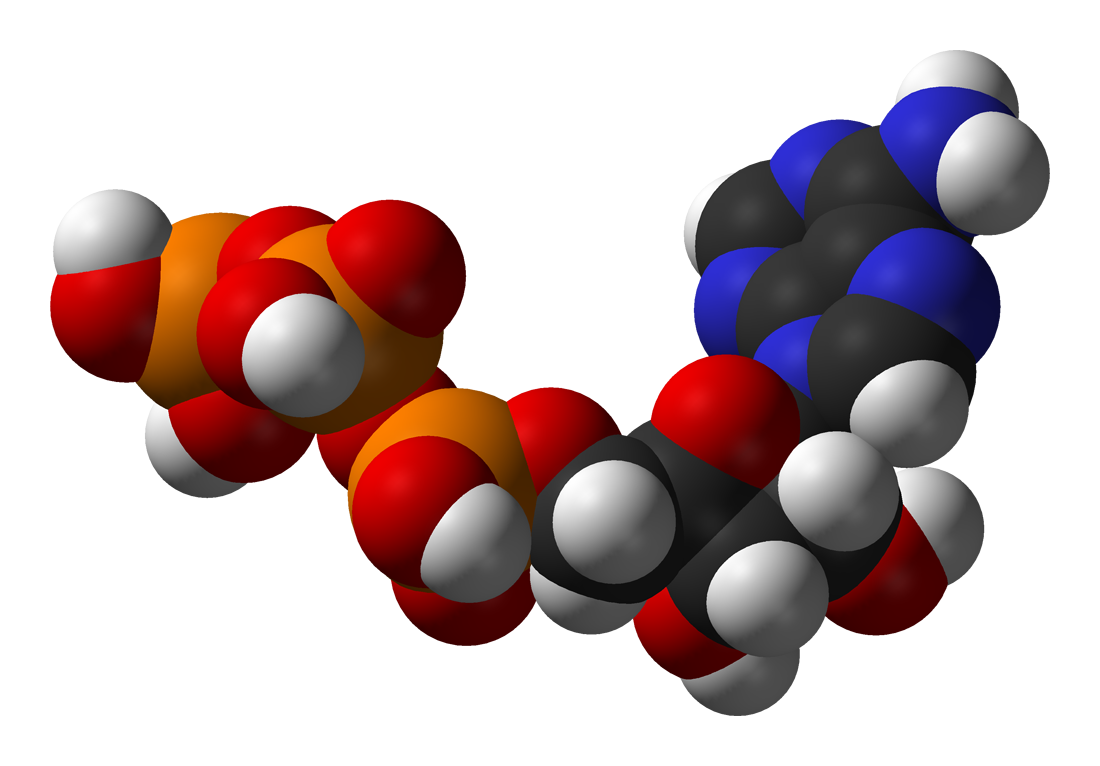
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire (as opposed to organisms that ferment) to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism and may have originated abiogenically. Even though it is branded as a 'cycle', it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized. The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from the citric acid (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Metabolic Rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. It is reported in energy units per unit time ranging from watt (joule/second) to ml O2/min or joule per hour per kg body mass J/(h·kg). Proper measurement requires a strict set of criteria to be met. These criteria include being in a physically and psychologically undisturbed state and being in a thermally neutral environment while in the post-absorptive state (i.e., not actively digesting food). In bradymetabolic animals, such as fish and reptiles, the equivalent term standard metabolic rate (SMR) applies. It follows the same criteria as BMR, but requires the documentation of the temperature at which the metabolic rate was measured. This makes BMR a variant of standard metabolic rate measurement that excludes the temperature data, a practice that has led to problems in defining "standard" rates of metabolism for many mammals. Metabolism comprises the processes that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The underground mine gas term for foul-smelling hydrogen sulfide-rich gas mixtures is ''stinkdamp''. Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of purified hydrogen sulfide in 1777. The British English spelling of this compound is hydrogen sulphide, a spelling no longer recommended by the Royal Society of Chemistry or the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic to humans and most other animals by inhibiting cellular respiration in a manner similar to hydrogen cyanide. When it is inhaled or it or its salts are ingested in high amounts, damage to organs occurs rapidly with symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to convulsions and death. Despite this, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain sufficient nutrients causes malnutrition. Nutritional science is the study of nutrition, though it typically emphasizes human nutrition. The type of organism determines what nutrients it needs and how it obtains them. Organisms obtain nutrients by consuming organic matter, consuming inorganic matter, absorbing light, or some combination of these. Some can produce nutrients internally by consuming basic elements, while some must consume other organisms to obtain preexisting nutrients. All forms of life require carbon, energy, and water as well as various other molecules. Animals require complex nutrients such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, obtaining them by consuming other organisms. Humans have developed agriculture and cooking to rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coupling (physics)
In physics, two objects are said to be coupled when they are interacting with each other. In classical mechanics, coupling is a connection between two oscillating systems, such as pendulums connected by a spring. The connection affects the oscillatory pattern of both objects. In particle physics, two particles are coupled if they are connected by one of the four fundamental forces. Wave mechanics Coupled harmonic oscillator If two waves are able to transmit energy to each other, then these waves are said to be "coupled." This normally occurs when the waves share a common component. An example of this is two pendulums connected by a spring. If the pendulums are identical, then their equations of motion are given by m\ddot = -mg\frac - k(x-y) m\ddot = -mg \frac + k(x-y) These equations represent the simple harmonic motion of the pendulum with an added coupling factor of the spring. This behavior is also seen in certain molecules (such as CO2 and H2O), wherein two of the atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connections". Pearson Education. San Francisco: 2003. In the two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. But in the three-domain system, based upon molecular analysis, prokaryotes are divided into two domains: ''Bacteria'' (formerly Eubacteria) and '' Archaea'' (formerly Archaebacteria). Organisms with nuclei are placed in a third domain, Eukaryota. In the study of the origins of life, prokaryotes are thought to have arisen before eukaryotes. Besides the absence of a nucleus, prokaryotes also lack mitochondria, or most of the other membrane-bound organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. It was once thought that prokaryotic cellular components within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broad sense. Whether something is considered a poison may change depending on the amount, the circumstances, and what living things are present. Poisoning could be accidental or deliberate, and if the cause can be identified there may be ways to neutralise the effects or minimise the symptoms. In biology, a poison is a chemical substance causing death, injury or harm to organisms or their parts. In medicine, poisons are a kind of toxin that are delivered passively, not actively. In industry the term may be negative, something to be removed to make a thing safe, or positive, an agent to limit unwanted pests. In ecological terms, poisons introduced into the environment can later cause unwanted effects elsewhere, or in other parts of the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
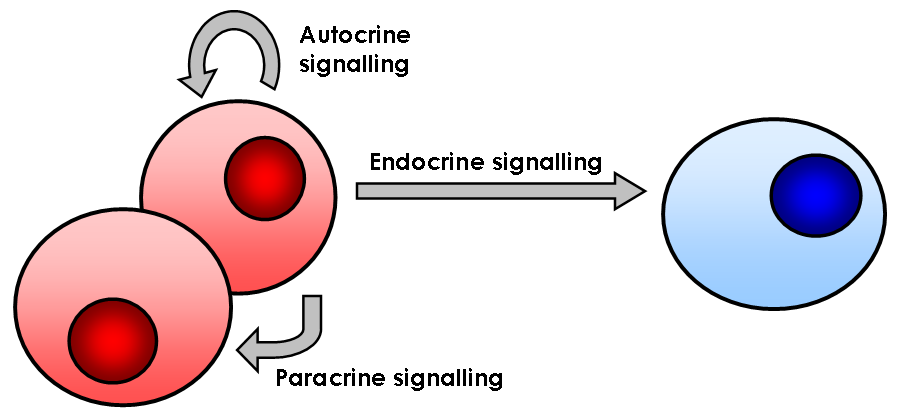
Cell Signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |