|
Metabolic Adaptation
Starvation response in animals (including humans) is a set of adaptive biochemical and physiological changes, triggered by lack of food or extreme weight loss, in which the body seeks to conserve energy by reducing the amount of calories it burns.Adapted from Wang et al. 2006, p 223. Equivalent or closely related terms include famine response, starvation mode, famine mode, starvation resistance, starvation tolerance, adapted starvation, adaptive thermogenesis, fat adaptation, and metabolic adaptation. Bacteria become highly tolerant to antibiotics when nutrients are limited. Starvation contributes to antibiotic tolerance during infection, as nutrients become limited when they are sequestered by host defenses and consumed by proliferating bacteria. One of the most important causes of starvation induced tolerance in vivo is biofilm growth, which occurs in many chronic infections. Starvation in biofilms is due to nutrient consumption by cells located on the periphery of biofilm clu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemical
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research.Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells, Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs, as well as organism structure and function. Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, which is the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrates
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may not be different from ''n''), which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O (for example with , H has a covalent bond with C but not with O). However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition (e.g., uronic acids, deoxy-sugars such as fucose), nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid). The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecular weight) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon dissolving, the substance separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly throughout the solvent. Solid-state electrolytes also exist. In medicine and sometimes in chemistry, the term electrolyte refers to the substance that is dissolved. Electrically, such a solution is neutral. If an electric potential is applied to such a solution, the cations of the solution are drawn to the electrode that has an abundance of electrons, while the anions are drawn to the electrode that has a deficit of electrons. The movement of anions and cations in opposite directions within the solution amounts to a current. Some gases, such as hydrogen chloride (HCl), under conditions of high temperature or low pressure can also function as elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possibly defibrillation are needed until further treatment can be provided. Cardiac arrest results in a rapid unconsciousness, loss of consciousness, and breathing may be respiratory arrest, abnormal or absent. While cardiac arrest may be caused by myocardial infarction, heart attack or heart failure, these are not the same, and in 15 to 25% of cases, there is a non-cardiac cause. Some individuals may experience chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, an elevated heart rate, and a light-headed feeling immediately before entering cardiac arrest. The most common cause of cardiac arrest is an underlying heart problem like coronary artery disease that decreases the amount of oxygenated blood supplying the heart muscle. This, in turn, damages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the Cardiac cycle, heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be presyncope, lightheadedness, Syncope (medicine), passing out, shortness of breath or chest pain. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in cardiac arrest, sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: premature heart beat, extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
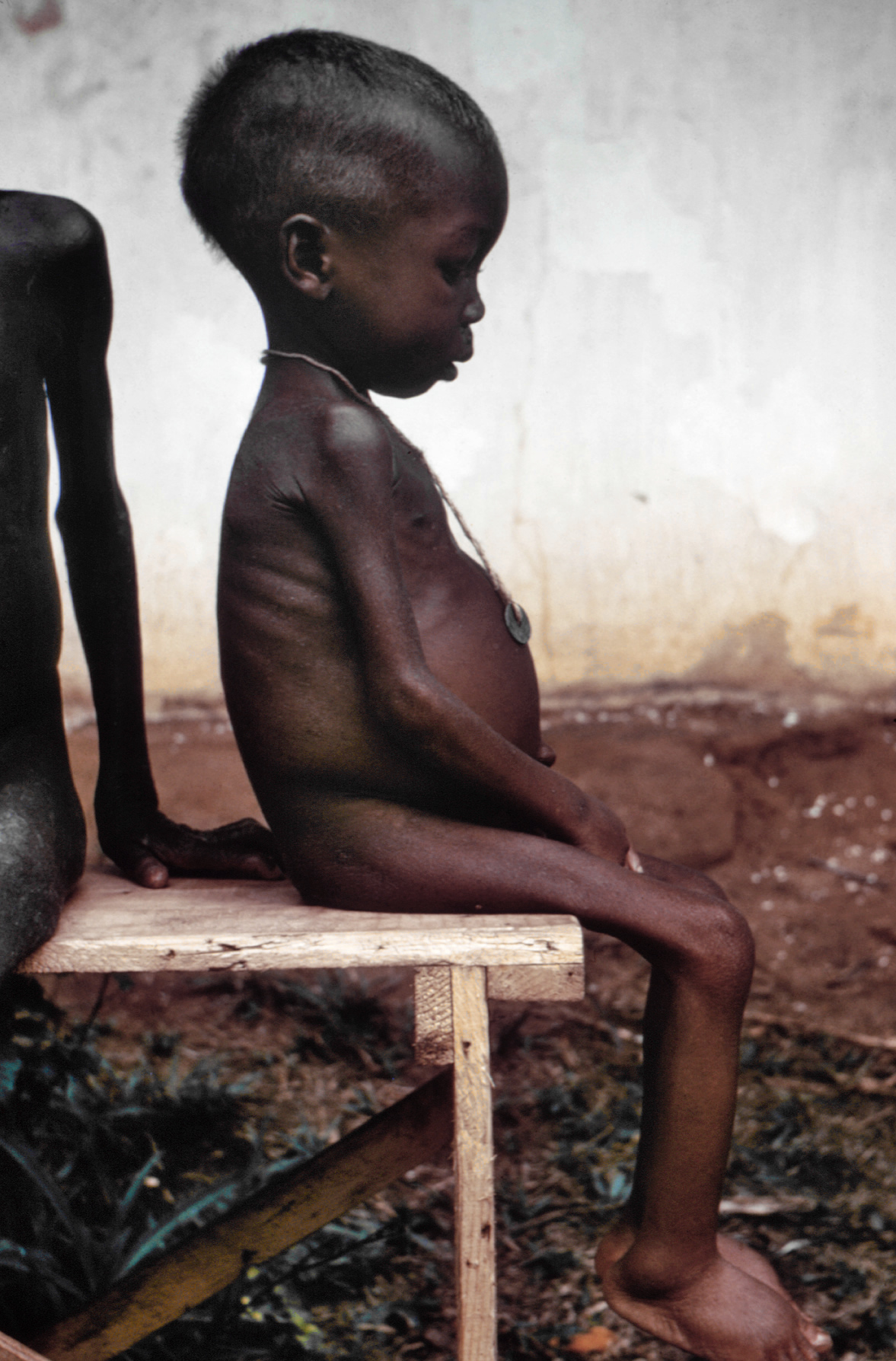
Starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, death. The term ''inanition'' refers to the symptoms and effects of starvation. Starvation may also be used as a means of torture or execution. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hunger is the single gravest threat to the world's public health.Malnutrition The Starvelings The WHO also states that is by far the biggest contributor to [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid ''residues'' form the second-largest component ( water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for energy production. Coenzyme A (CoASH or CoA) consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid (B5) through an amide linkage and 3'-phosphorylated ADP. The acetyl group (indicated in blue in the structural diagram on the right) of acetyl-CoA is linked to the sulfhydryl substituent of the β-mercaptoethylamine group. This thioester linkage is a "high energy" bond, which is particularly reactive. Hydrolysis of the thioester bond is exergonic (−31.5 kJ/mol). CoA is acetylated to acetyl-CoA by the breakdown of carbohydrates through glycolysis and by the breakdown of fatty acids through β-oxidation. Acetyl-CoA then enters the citric acid cycle, where the acetyl group is oxidized to carbon dioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
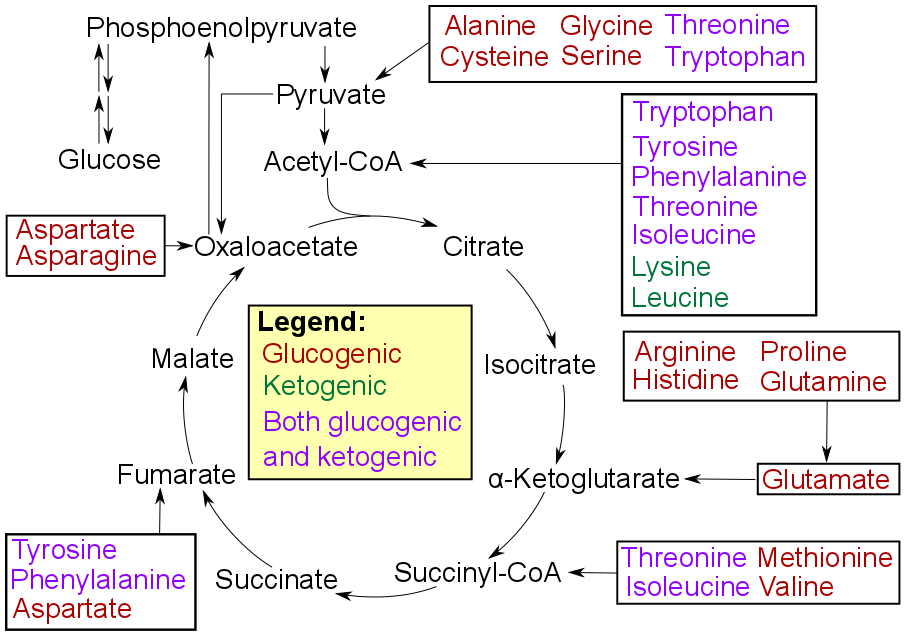
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non- carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. It is one of two primary mechanisms – the other being degradation of glycogen (glycogenolysis) – used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood sugar levels, avoiding low levels ( hypoglycemia). In ruminants, because dietary carbohydrates tend to be metabolized by rumen organisms, gluconeogenesis occurs regardless of fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, exercise, etc. In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise. In humans, substrates for gluconeogenesis may come from any non-carbohydrate sources that can be converted to pyruvate or intermed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acids
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone Bodies
Ketone bodies are water-soluble molecules that contain the ketone groups produced from fatty acids by the liver ( ketogenesis). Ketone bodies are readily transported into tissues outside the liver, where they are converted into acetyl-CoA (acetyl-Coenzyme A)—which then enters the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and is oxidized for energy. These liver-derived ketone groups include acetoacetic acid (acetoacetate), beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone, a spontaneous breakdown product of acetoacetate (see graphic). Ketone bodies are produced by the liver during periods of caloric restriction of various scenarios: low food intake ( fasting), carbohydrate restrictive diets, starvation, prolonged intense exercise, alcoholism, or during untreated (or inadequately treated) type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ketone bodies are produced in liver cells by the breakdown of fatty acids. They are released into the blood ''after'' glycogen stores in the liver have been depleted. (Glycogen stores ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)