|
Mere Ownership Effect
The mere ownership effect is the observation that people who own a good tend to evaluate it more positively than people who do not. It is typically demonstrated in a paradigm in which some participants in an experiment are randomly assigned to own a good ("owners") by receiving it for free. Other participants are randomly assigned to simply evaluate the same good without receiving it. Participants who own the good typically rate it as more attractive or as liking it more than do participants who do not own it. It is not necessary to actually own a good to exhibit the mere ownership effect. Simply touching or imagining that one owns a good is enough to instantiate the mere ownership effect. The mere ownership effect is often used as a case in which people show the endowment effect that cannot be parsimoniously explained by loss aversion. Origins Two routes have been proposed to explain the mere ownership effect. Both rely on the association of a good with the self. ;Attachment t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endowment Effect
In psychology and behavioral economics, the endowment effect (also known as divestiture aversion and related to the mere ownership effect in social psychology) is the finding that people are more likely to retain an object they own than acquire that same object when they do not own it. The endowment theory can be defined as "an application of prospect theory positing that loss aversion associated with ownership explains observed exchange asymmetries." This is typically illustrated in two ways. In a valuation paradigm, people's maximum willingness to pay (WTP) to acquire an object is typically lower than the least amount they are willing to accept (WTA) to give up that same object when they own it—even when there is no cause for attachment, or even if the item was only obtained minutes ago. In an exchange paradigm, people given a good are reluctant to trade it for another good of similar value. For example, participants first given a Swiss chocolate bar were generally willing to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
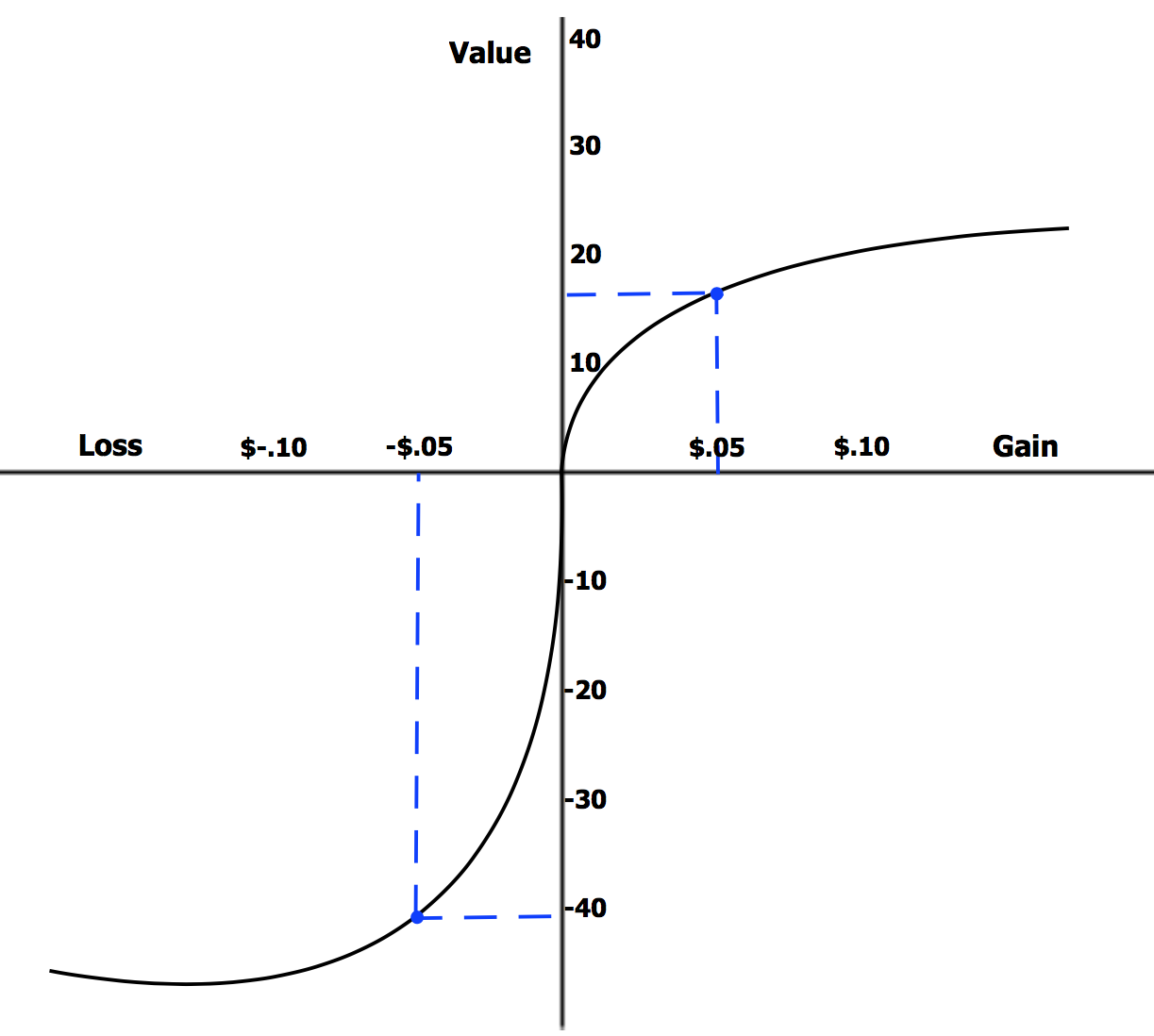
Loss Aversion
Loss aversion is the tendency to prefer avoiding losses to acquiring equivalent gains. The principle is prominent in the domain of economics. What distinguishes loss aversion from risk aversion is that the utility of a monetary payoff depends on what was previously experienced or was expected to happen. Some studies have suggested that losses are twice as powerful, psychologically, as gains. Loss aversion was first identified by Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman. Loss aversion implies that one who loses $100 will lose more satisfaction than the same person will gain satisfaction from a $100 windfall. In marketing, the use of trial periods and rebates tries to take advantage of the buyer's tendency to value the good more after the buyer incorporates it in the status quo. In past behavioral economics studies, users participate up until the threat of loss equals any incurred gains. Recent methods established by Botond Kőszegi and Matthew Rabin in experimental economics illustrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encoding (memory)
Memory has the ability to encode, store and recall information. Memories give an organism the capability to learn and adapt from previous experiences as well as build relationships. Encoding allows a perceived item of use or interest to be converted into a construct that can be stored within the brain and recalled later from long-term memory. Working memory stores information for immediate use or manipulation which is aided through hooking onto previously archived items already present in the long-term memory of an individual. History Encoding is still relatively new and unexplored but origins of encoding date back to age old philosophers such as Aristotle and Plato. A major figure in the history of encoding is Hermann Ebbinghaus (1850–1909). Ebbinghaus was a pioneer in the field of memory research. Using himself as a subject he studied how we learn and forget information by repeating a list of nonsense syllables to the rhythm of a metronome until they were committed to his m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recall (memory)
Recall in memory refers to the mental process of retrieval of information from the past. Along with encoding and storage, it is one of the three core processes of memory. There are three main types of recall: free recall, cued recall and serial recall. Psychologists test these forms of recall as a way to study the memory processes of humansrecall. (2010). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved March 04, 2010, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/493353/recal/ref> and animals. Two main theories of the process of recall are the two-stage theory and the theory of Encoding specificity principle, encoding specificity. Theories Two-stage theory The ''two-stage theory'' states that the process of recall begins with a search and retrieval process, and then a decision or recognition process where the correct information is chosen from what has been retrieved. In this theory, recognition only involves the latter of these two stages, or processes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spreading Activation
Spreading activation is a method for searching associative networks, biological and artificial neural networks, or semantic networks. The search process is initiated by labeling a set of source nodes (e.g. concepts in a semantic network) with weights or "activation" and then iteratively propagating or "spreading" that activation out to other nodes linked to the source nodes. Most often these "weights" are real values that decay as activation propagates through the network. When the weights are discrete this process is often referred to as marker passing. Activation may originate from alternate paths, identified by distinct markers, and terminate when two alternate paths reach the same node. However brain studies show that several different brain areas play an important role in semantic processing.Karalyn Patterson, Peter J. Nestor & Timothy T. Rogers: "Where do you know what you know? The representation of semantic knowledge in the human brain/ref> Spreading activation in semanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |